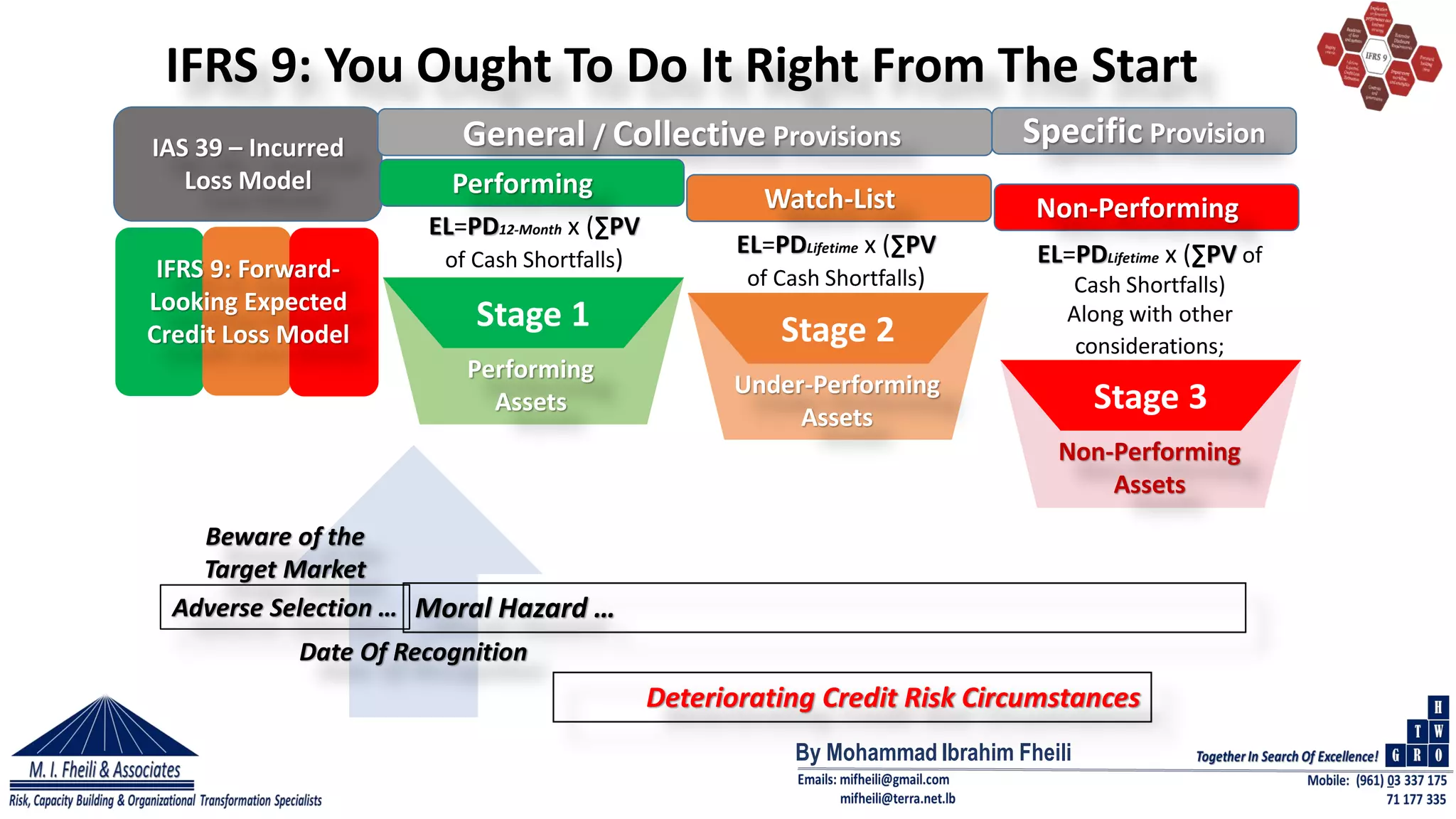
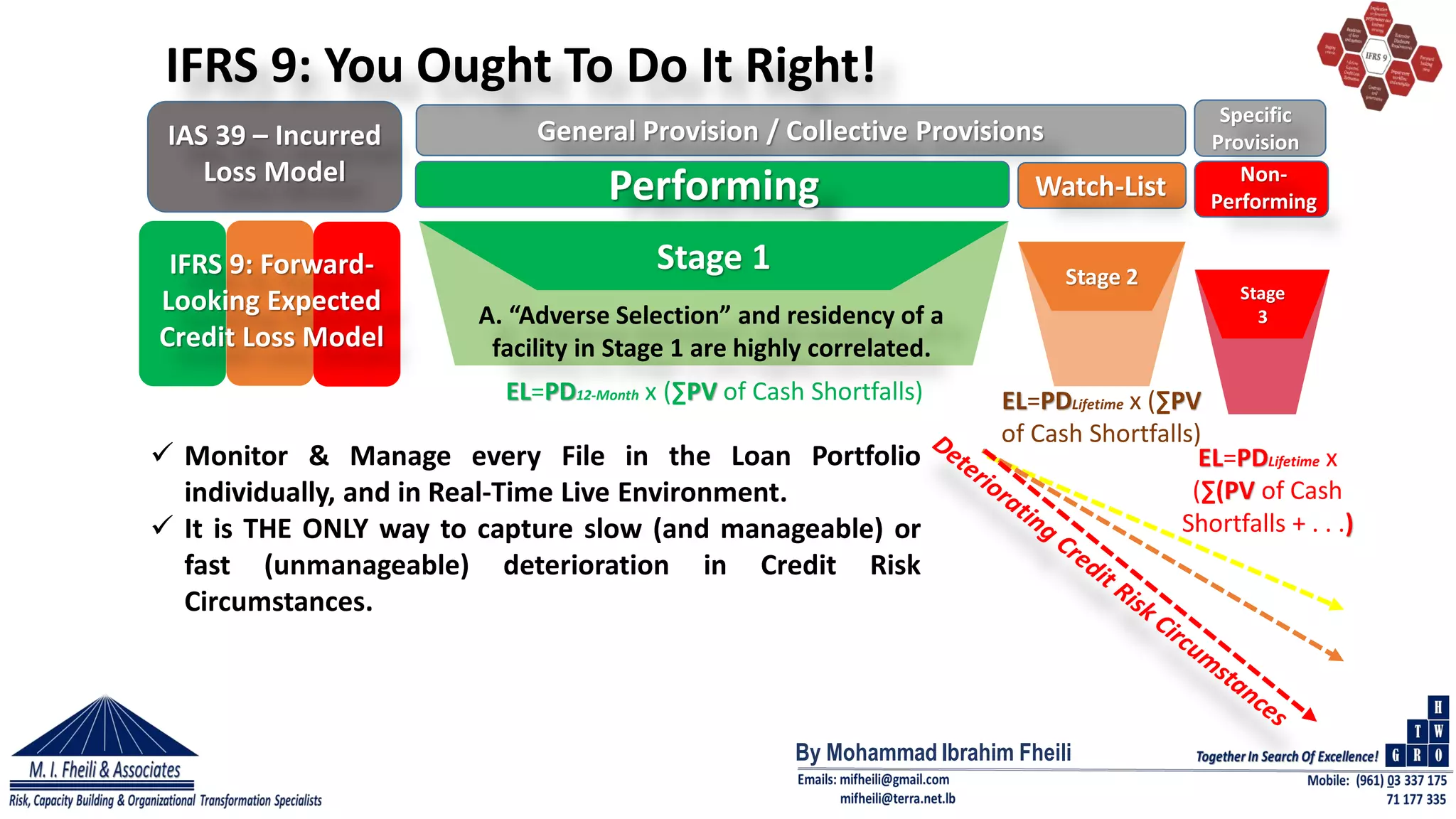
This document discusses the Basel II framework, focusing on its three pillars for risk and capital management in banks, with an emphasis on Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) and how it addresses risks not fully captured by Pillar 1. It highlights the changes introduced by IFRS 9, which replaced IAS 39, emphasizing the forward-looking expected credit loss model and the importance of effective risk management and compliance. The author asserts that banks need to demonstrate compliance and adjust their internal capital management strategies to adequately address emerging risks and improve asset quality.

































![By Mohammad Ibrahim Fheili
Consequences:
Losses
Risk
Event:
Loan
Default
a) Dried up Cash Flow Sources: Client’s business
received a bad hit causing dramatic changes in his
business environment.
b) Collaboration between the RM and the Client in the
provision of inflated figures (Sales, Revenues, Cash
Flows, …) leading to a false-favorable credit decision.
c) Over-worked, and Under-Staffed Business Unit
leading to overlooking some critical changes in
Operational Environment of the Client.
d) Incompetent Bank Employee(s) Gave False analysis
and Recommendation which led to a False-favorable
Credit Decision.
e) Poor/Inadequate Follow-up and Reviews rendering
the process weak in capturing “Early Warning
Signals”
f) Etc….. there could be Violations to AML and/or
other Rules
Numbers Are Not Enough! These are Noted [Actual] Causes of Asset Failures.
Possible
Causes
Causes of Default.
a) Credit Risk
b) Ethics & Moral Value
c) Workforce Planning
d) Training & Development
e) Performance Management
f) AML Concerns](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ifrs9assessmentandstrategicimplications-190705200024/75/Ifrs9-assessment-and-strategic-implications-36-2048.jpg)









