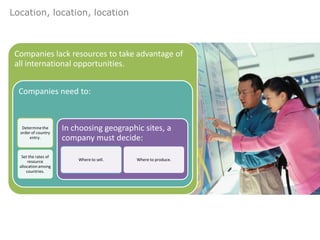
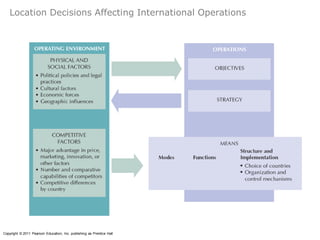
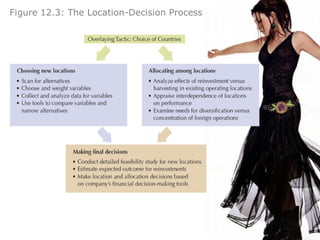
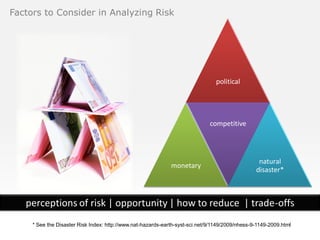
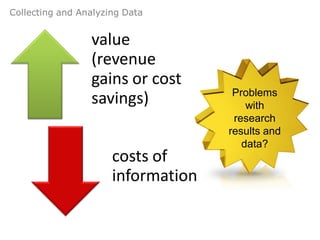
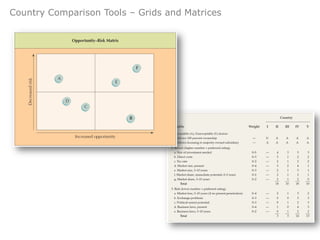
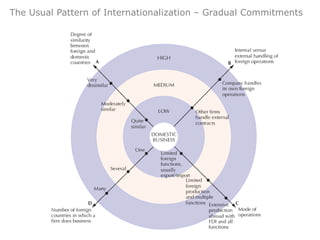
The document provides an agenda for a class on country evaluation and selection for international business expansion. It outlines factors to consider when evaluating countries such as economic, demographic, cost, and risk variables. It also discusses methods for collecting and analyzing country data, common problems with research results, and strategies for allocating resources among locations.