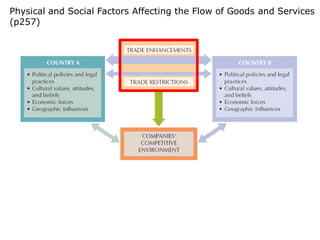
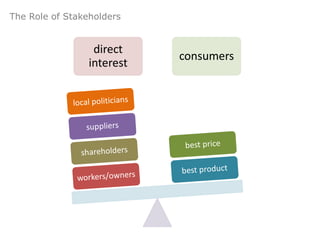
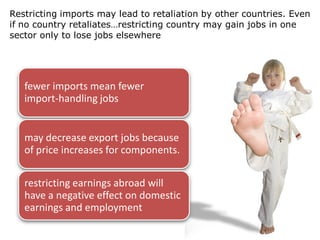
This document provides an overview of a chapter on governmental influence on trade. It discusses the rationales governments have for influencing trade, including economic reasons like fighting unemployment, protecting infant industries, developing an industrial base, and improving economic relations with other countries. It also discusses non-economic rationales like maintaining essential industries, dealing with unfriendly countries, and maintaining spheres of influence. The objectives of the chapter are explained and examples are given of different government trade policies and their potential effects.