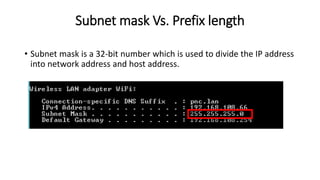
This document provides an overview of IPv4 subnetting. It defines IP and IP addresses, and distinguishes between public and private IP addresses. It explains subnet masks versus prefix lengths and how to assign IP addresses. The key parts of an IP address are identified as the network ID and host ID. Specific IP address classes and private IP address ranges are listed. The roles of network IP, host IP, and broadcast IP are defined. Methods for converting IPv4 addresses and subnet masks to binary are introduced, as are CIDR and VLSM concepts.