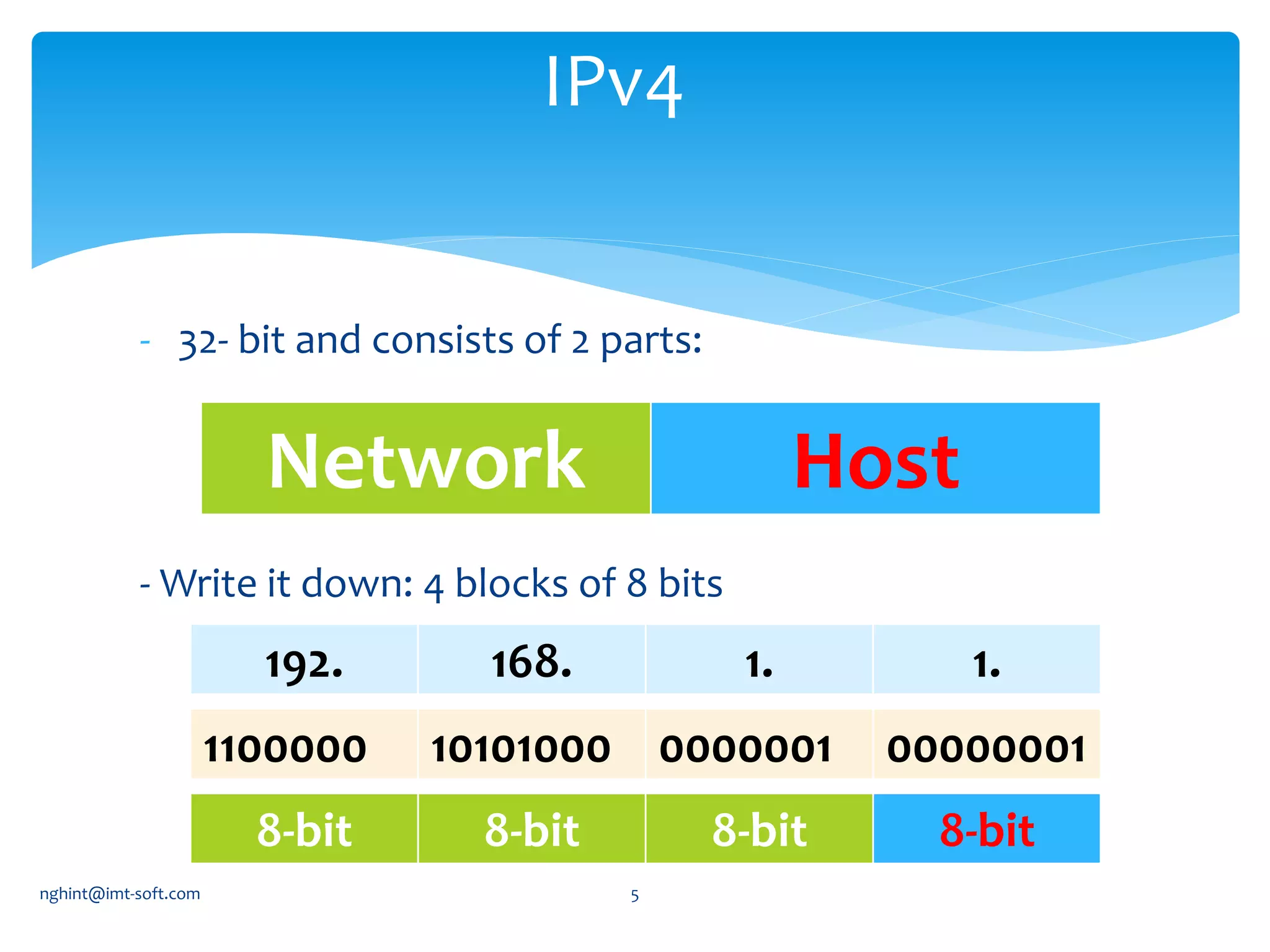
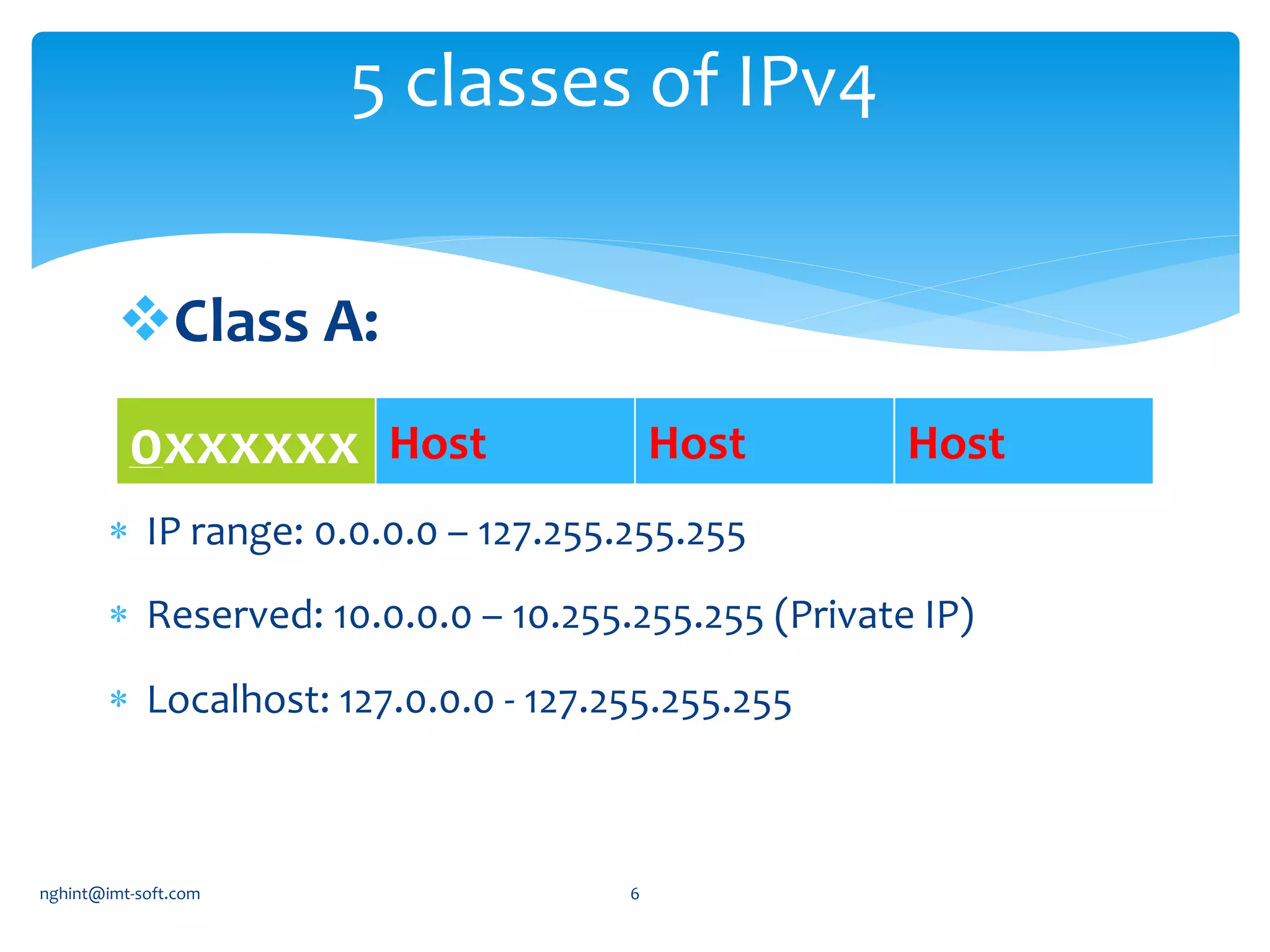
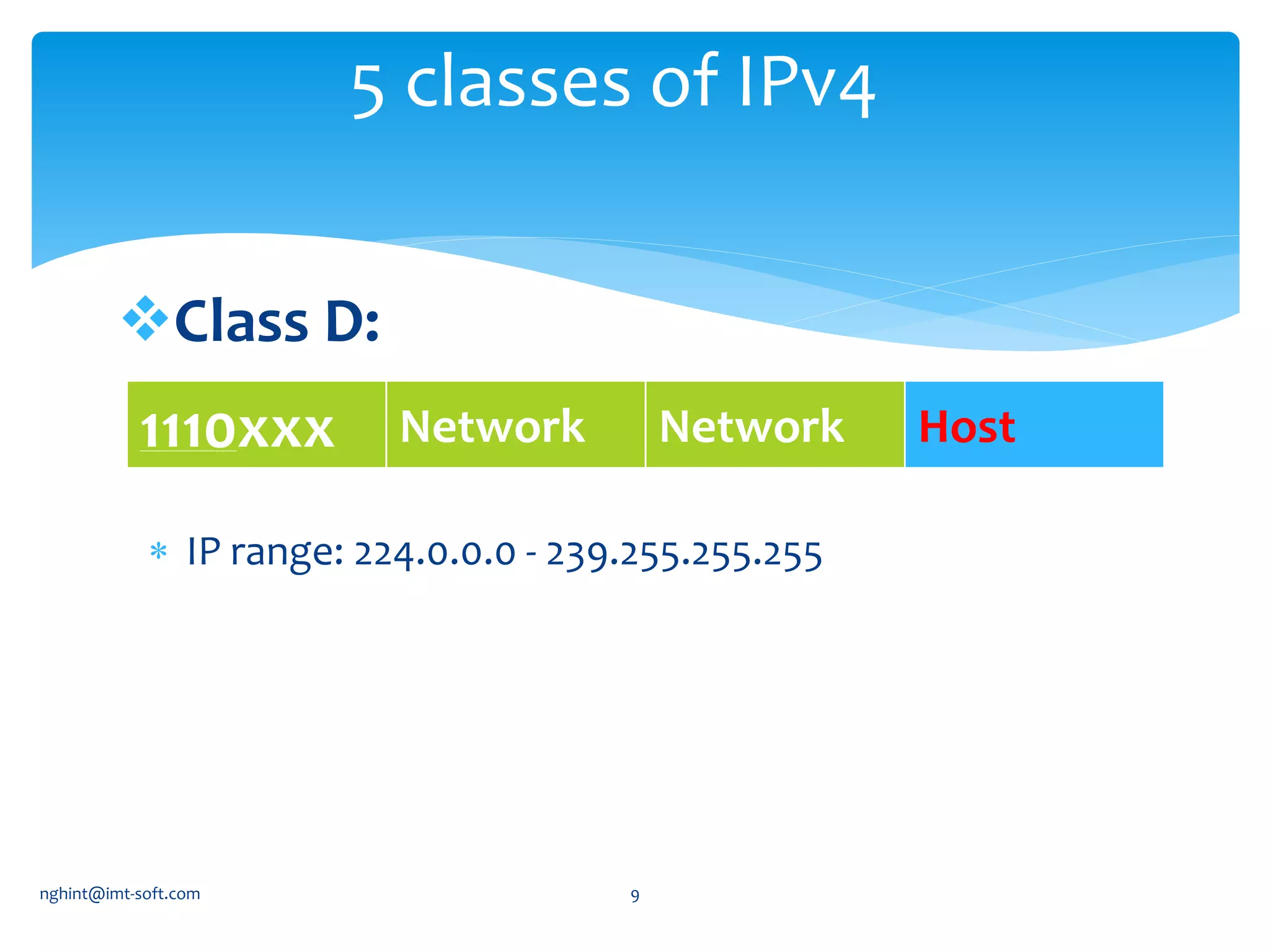
This document discusses IP addressing and subnetting. It begins by explaining IPv4 addressing in terms of its 32-bit structure and common address classes. It then covers subnetting, giving an example of how to plan an IP scheme for a network with 3 subnets and varying host requirements using variable length subnet masking. It also provides the network address, start address, end address and broadcast address for each subnet in the example IP plan.