Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times


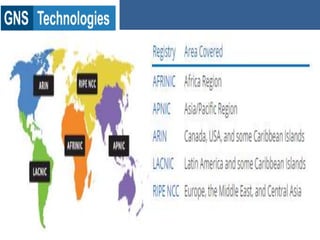


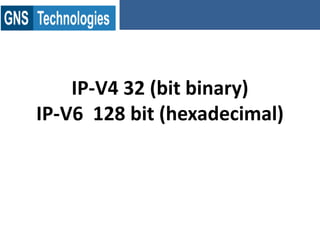
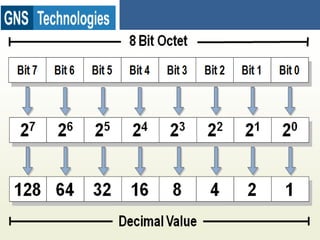
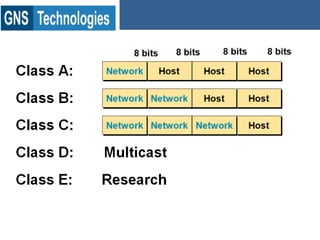
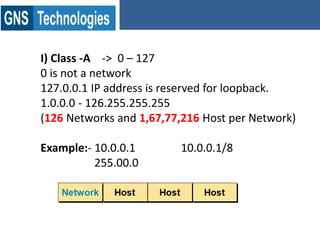
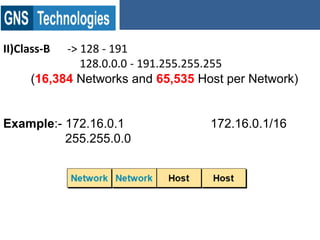
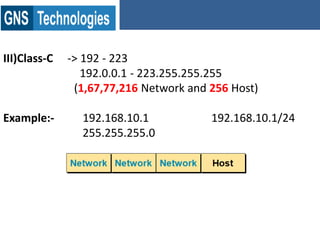




TCP/IP is the protocol that governs internet addressing and routing. The IANA and IETF define IP address types and classes, including Class A addresses from 0-127, Class B from 128-191, and Class C from 192-223. Routing protocols like RIP, IGRP, EIGRP, OSPF, and BGP search for the shortest path between routed protocols like IP, IPX, and Appletalk that carry data packets. IP version 4 uses 32-bit addresses while IP version 6 uses 128-bit hexadecimal addresses.














