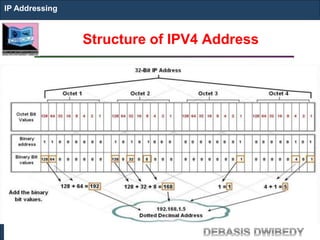
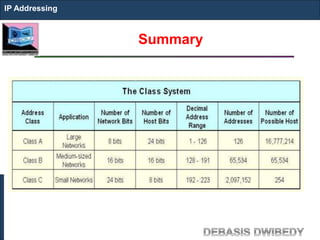
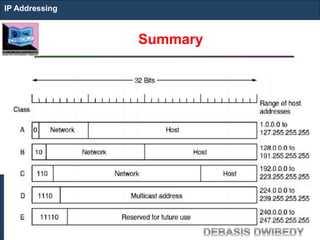
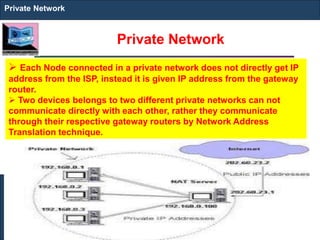
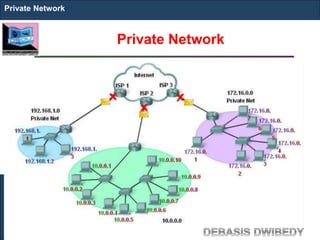
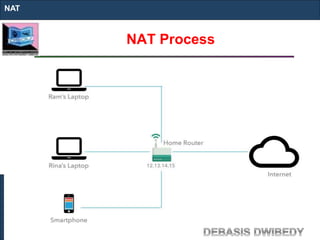
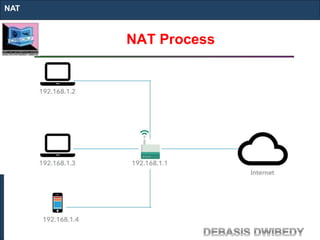
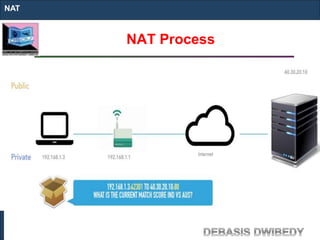
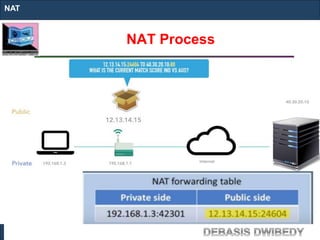
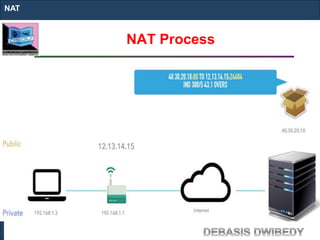
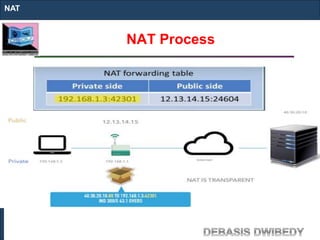
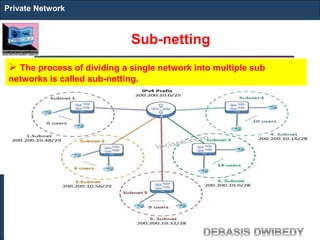
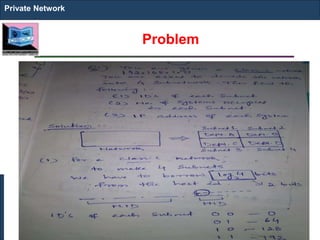
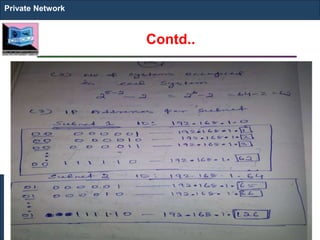
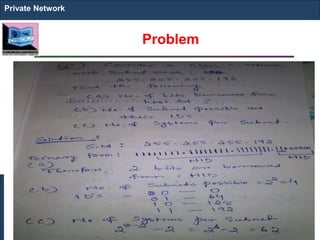
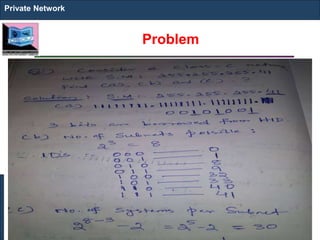
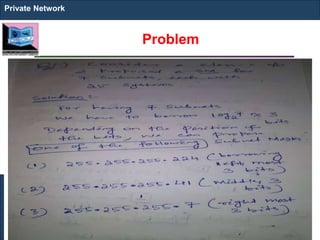
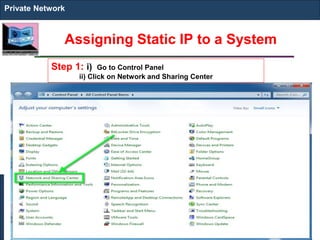
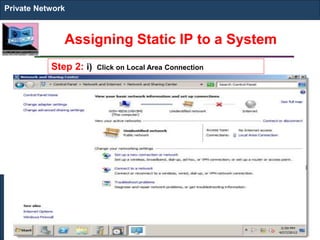
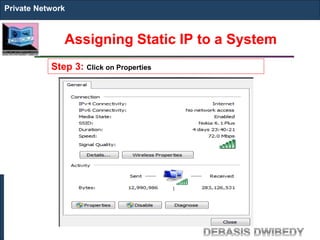
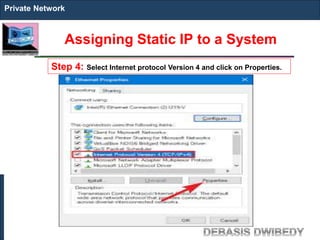
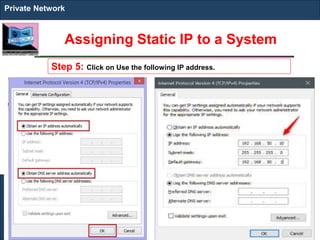
The document outlines key concepts of IP addressing, including the structure, classes, and distinctions between public and private networks. It explains how IPv4 addresses are formatted, the importance of Network Address Translation (NAT) for private networks, and the process of subnetting to create multiple sub-networks. Additionally, it details the advantages and disadvantages of private networks and the implications of IP address classes on network communication.