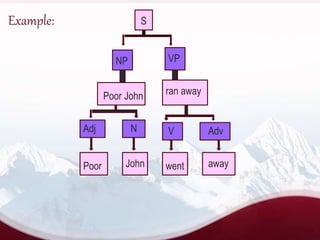
This document provides information about Immediate Constituent (IC) analysis, including:
- IC analysis breaks down sentences into constituent groups of words.
- Constituents are joined by horizontal lines to show their relationship.
- The analysis continues breaking down constituents until reaching individual morphemes.
- Examples demonstrate analyzing sentences with vertical lines and brackets.
- Limitations include not indicating grammatical functions, which labeling systems address.



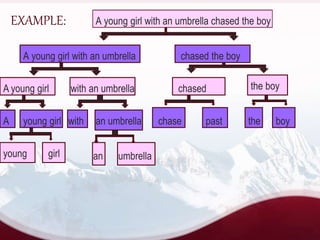
![ To other ways of showing the constituents are with vertical lines & with brackets.
For example:
a)Vertical lines:A || young ||| girl || with ||| an ||| umbrella | chased |||
the ||| boy
b) [ [ [ (A) ] ] ] [ (YOUNG) (GIRL) ] ] [ [WITH] [ (AN)
( UMBRELLA) ] ] ] [ [ (CHASED) [ (THE) (BOY) ] ] ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shranti2-151107143022-lva1-app6892/85/I-C-ANALYSIS-5-320.jpg)