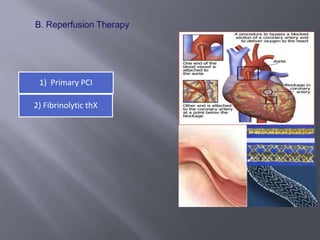
1) Management of acute myocardial infarction involves aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitors like prasugrel or ticagrelor, and revascularization with either primary PCI or fibrinolytic therapy.
2) Antiplatelet therapy with dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) for 1 year is indicated for all patients after drug-eluting or bare-metal stents.
3) Early use of beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins provides long-term benefits in reducing mortality for patients with acute MI.