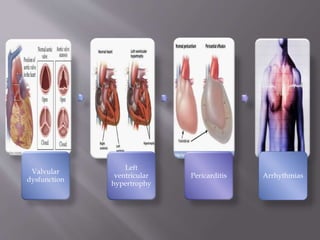
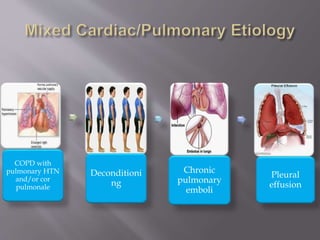
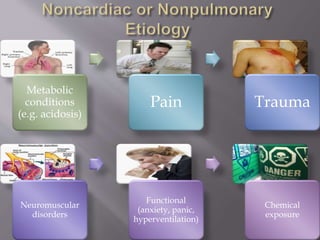
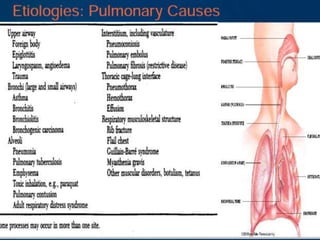
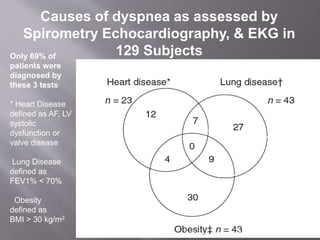
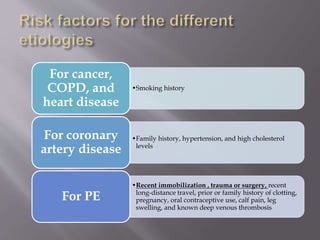
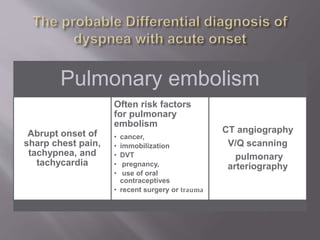
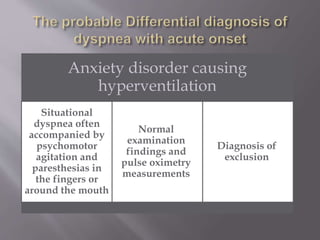
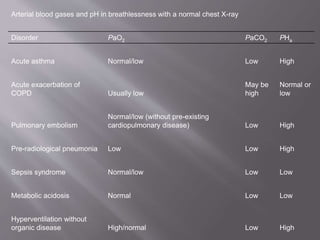
This document discusses dyspnea, or shortness of breath, from both clinical and physiological perspectives. Clinically, dyspnea is a subjective experience that varies in intensity, while physiologically it involves the stimulation of pulmonary and extra pulmonary receptors. The document outlines various lung volumes and capacities and explores the potential mechanisms of dyspnea. It also examines the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of different causes of dyspnea. A thorough history, physical exam, and testing are needed to diagnose the underlying condition and guide management.































![In this step, you should look for symptoms of
possible causes.
For
example:
chest pain
or pressure
suggests
pulmonary
embolism
[PE],
myocardial
ischemia,
or
pneumonia
dependent
edema,
orthopnea,
and
paroxysmal
nocturnal
dyspnea
suggests
heart
failure
fever,
chills,
cough, and
sputum
production
suggests
pneumonia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyspeniaddx-150807041403-lva1-app6892/85/dyspenia-ddx-mainpptx-45-320.jpg)




















![ CURRENT Medical Diagnosis and Treatment
2015
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19E
2-VOLUME SET (2015) [PDF] [UnitedVRG]
Rosen Emergency Medicine -2014 .
Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical
Physiology
Merck Manual of Diagnosis & Therapy
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dyspnea#Treatment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dyspeniaddx-150807041403-lva1-app6892/85/dyspenia-ddx-mainpptx-74-320.jpg)
