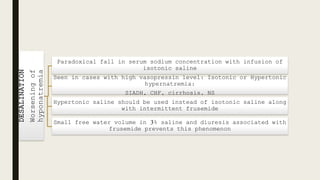
This document discusses the diagnosis and treatment of hyponatremia. It defines acute and chronic hyponatremia and outlines their differing risks. For severe symptoms, it recommends rapidly increasing serum sodium with 3% saline to prevent brain herniation. For moderate symptoms, the priority is preventing further sodium decreases rather than increases. Asymptomatic hyponatremia should be treated by optimizing volume status and restricting fluid intake. The risks of unpredictable rapid sodium correction are also covered.