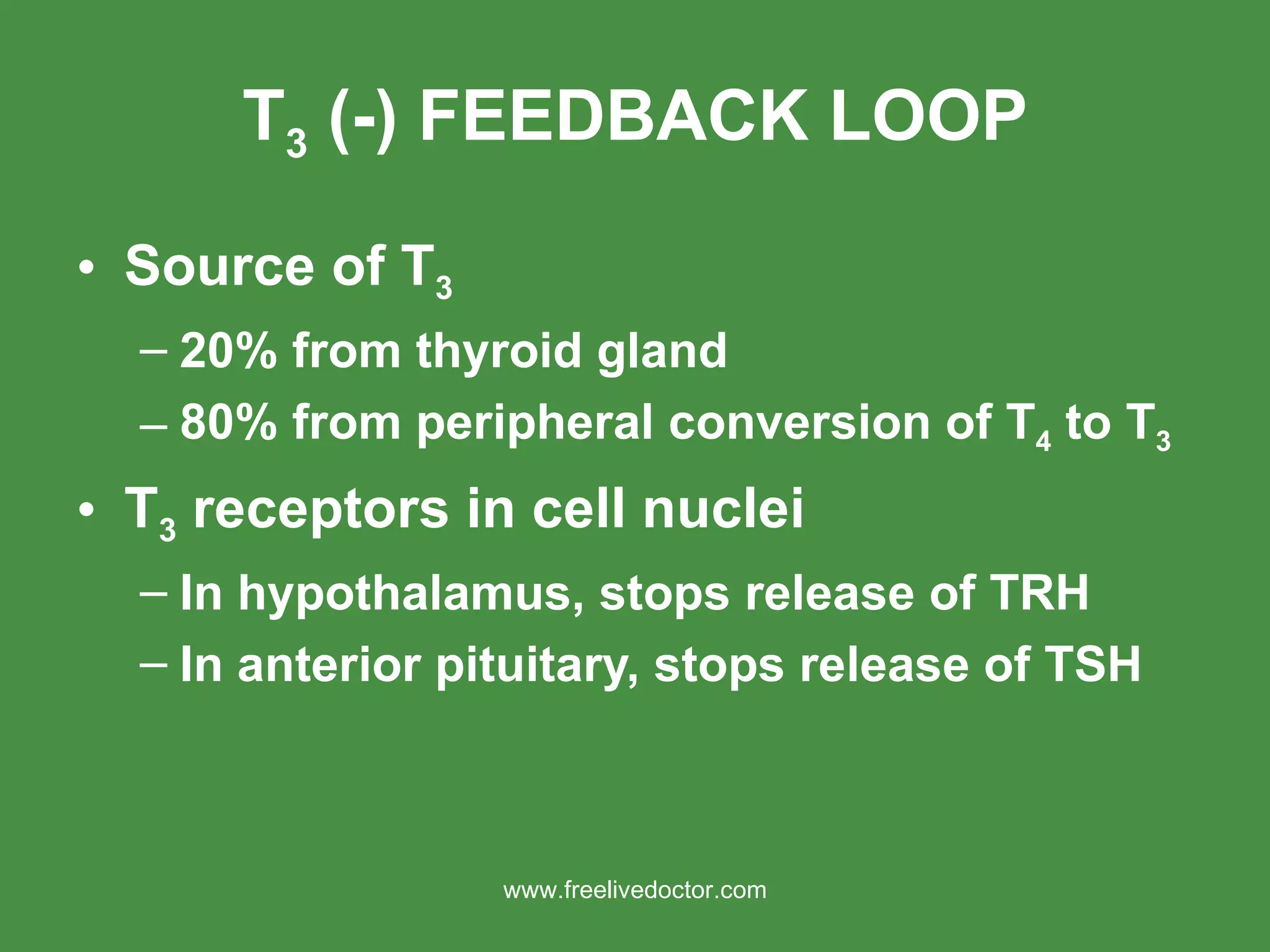
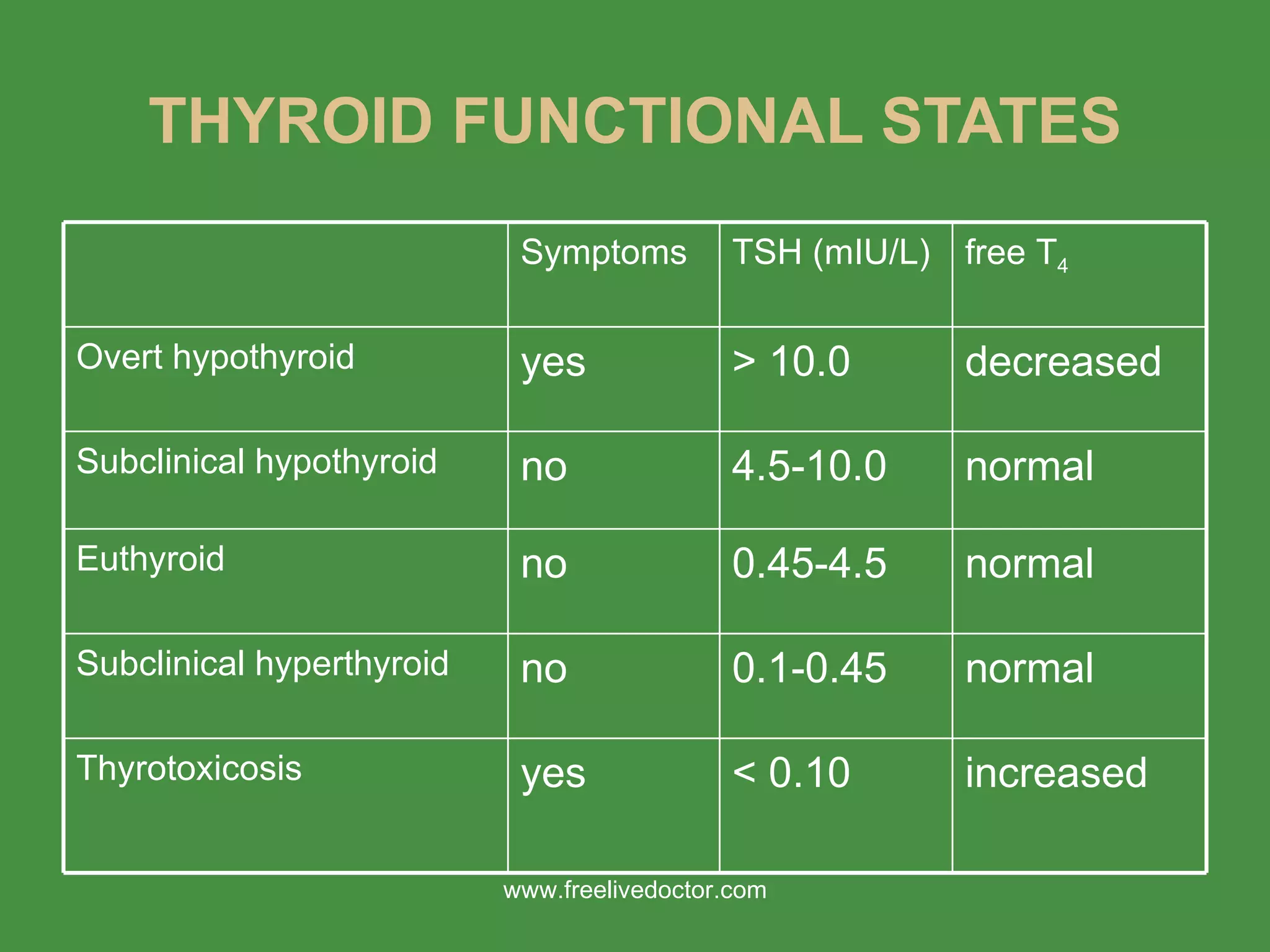
1) The document discusses hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, including thyroid physiology, clinical effects of thyroid hormones, and anesthetic considerations for patients with thyroid disorders.
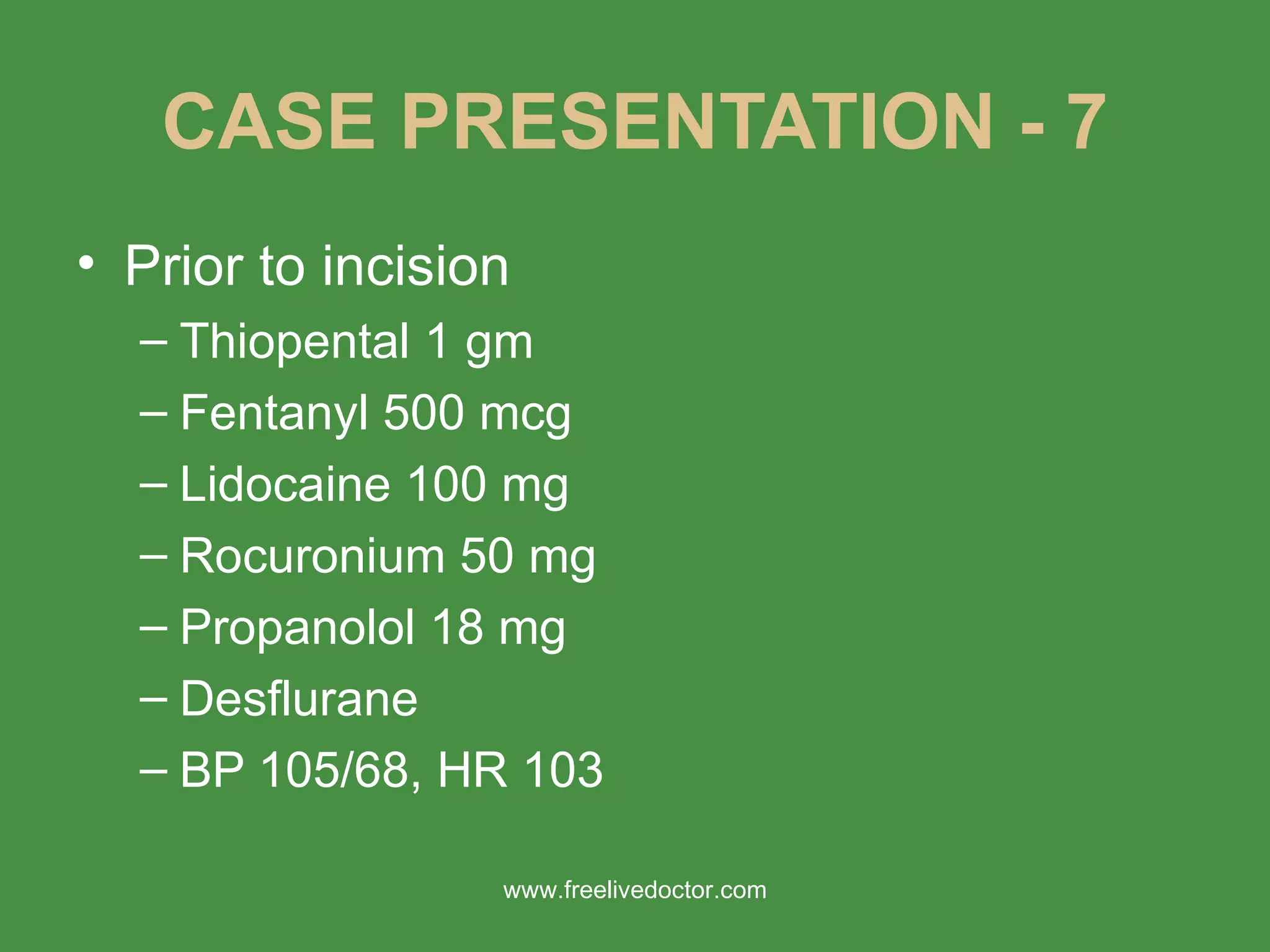
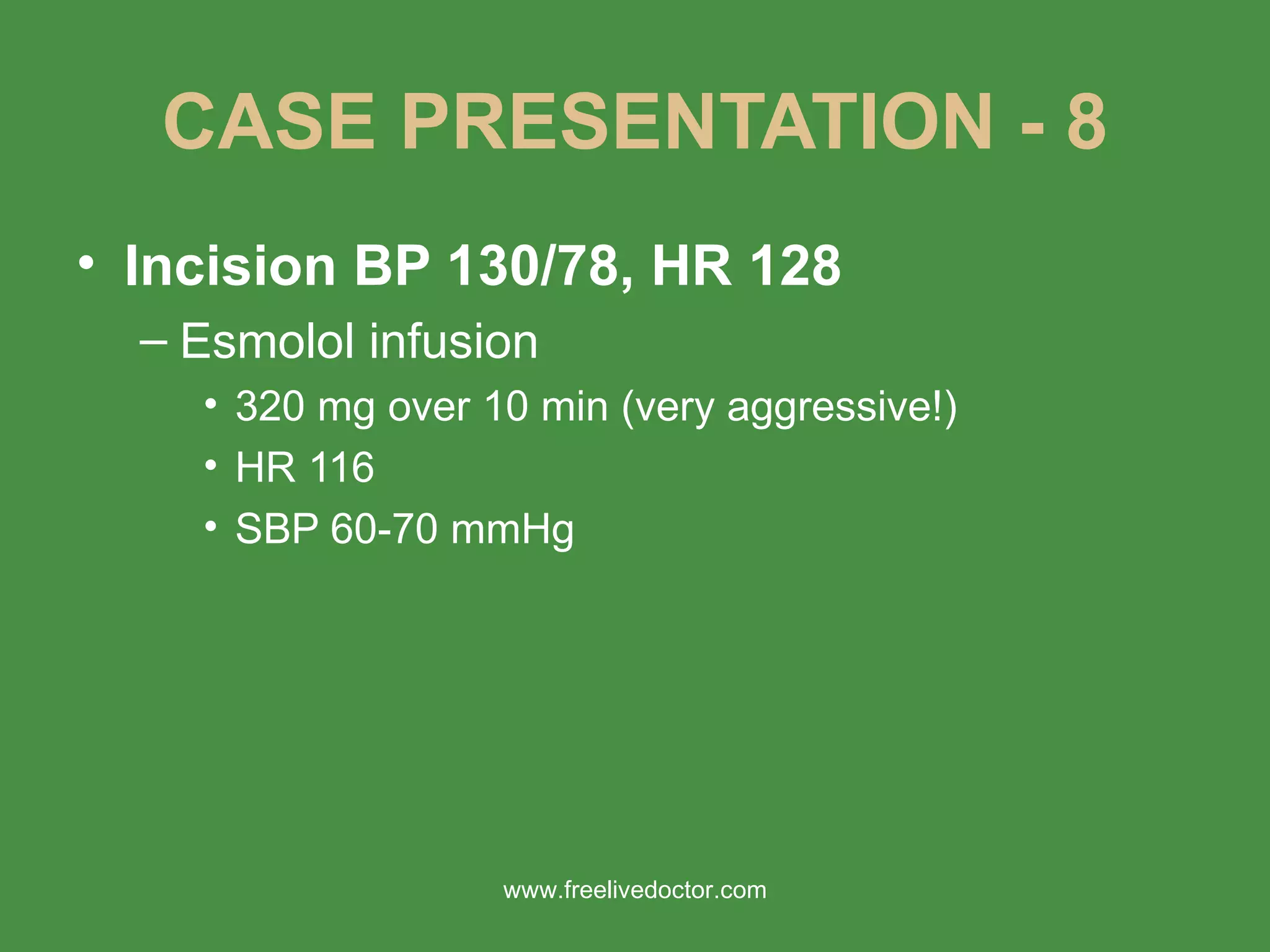
2) It presents a case of a 33-year-old woman with hyperthyroidism who developed thyroid storm in the PACU after undergoing thyroid surgery. Her signs and symptoms were not adequately controlled with beta-blockers and anti-thyroid medications prior to surgery.
3) The key lessons are the importance of adequately controlling hyperthyroidism before surgery to prevent thyroid storm, considering additional anti-thyroid medications for high-risk patients in the perioperative period, and being vigilant for signs of developing thyroid storm postoperatively