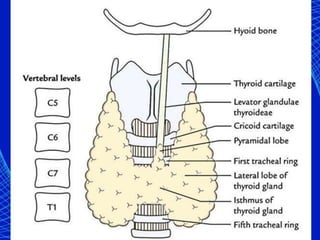
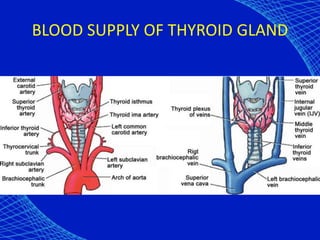
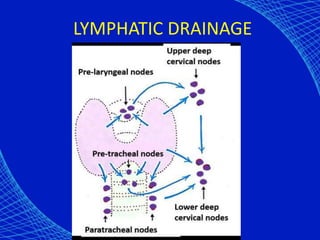
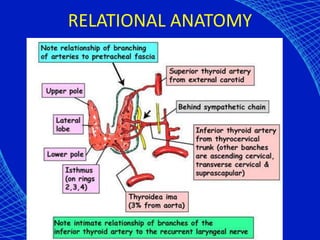
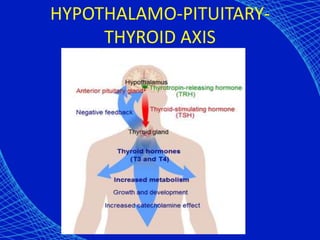
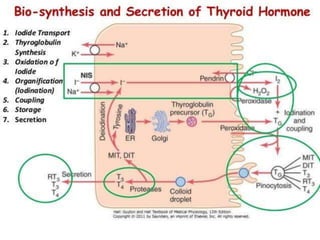
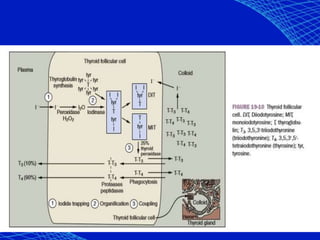
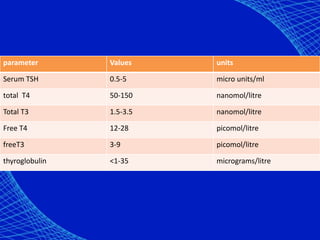
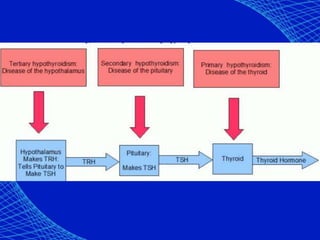
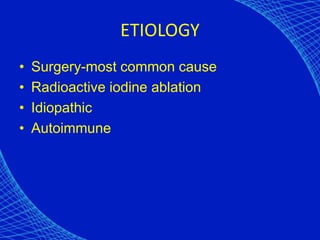
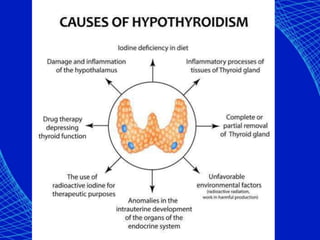
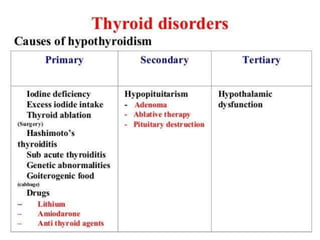
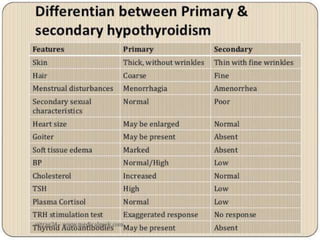
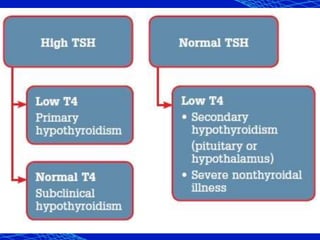
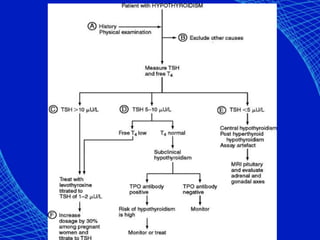
This document discusses the anesthetic considerations for patients with hypothyroidism. Key points include:
- Hypothyroidism can cause difficult airway management, cardiovascular instability, and hypothermia risks intraoperatively.
- Patients require cautious sedation, induction, and hemodynamic monitoring due to effects on circulation and metabolism.
- In pregnancy, hypothyroidism increases risks of complications for both mother and baby, so euthyroid state through levothyroxine is important.
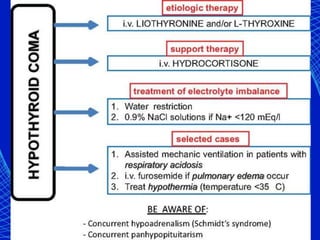
- Myxedema coma is a rare severe form treated with intravenous thyroid replacement and intensive care support.