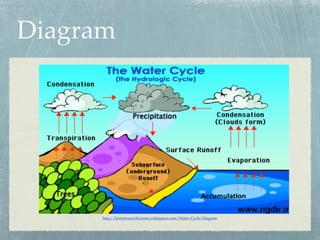
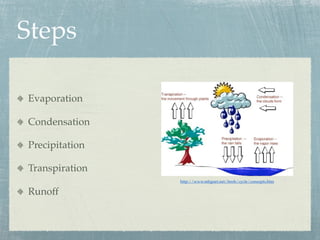
The hydrologic cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It involves the processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, and runoff. Water evaporates from bodies of water and transpires from plants into the atmosphere. It condenses to form clouds and precipitates as rain or snow. Precipitation that does not evaporate or transpire runs off into rivers and lakes and eventually flows back into the oceans, completing the cycle. The hydrologic cycle is essential for life and influences many geological and biological processes.