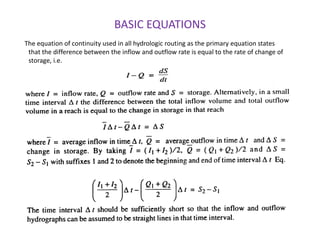
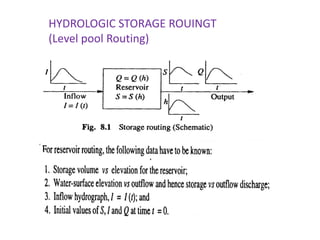
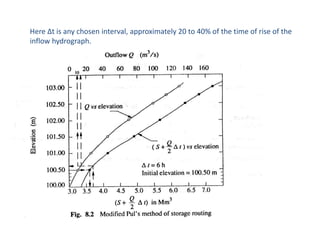
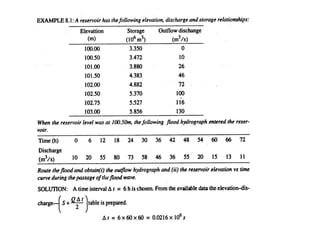
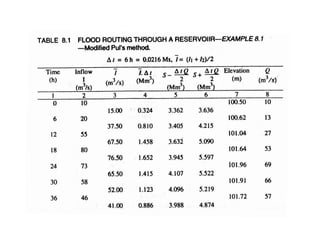
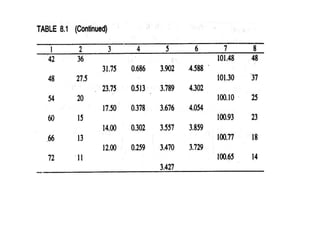
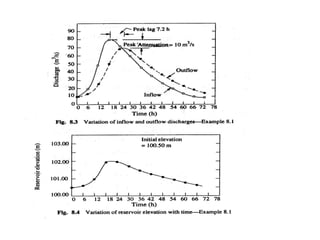
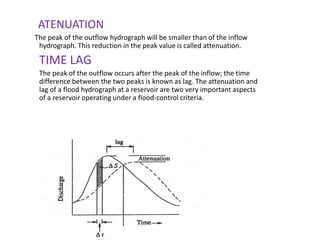
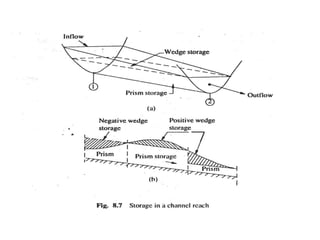
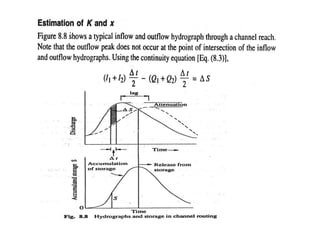
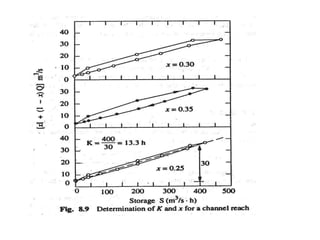
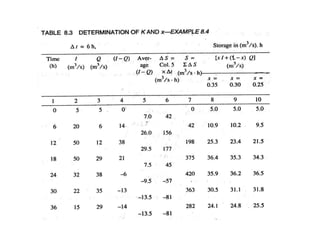
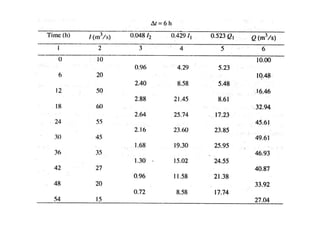
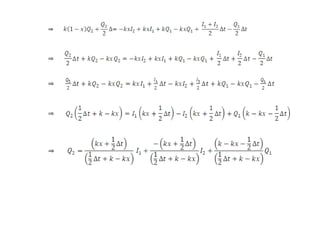This document discusses flood routing techniques used to determine flood levels at different points along a river. There are two main categories of routing: reservoir routing which analyzes flood levels upstream of reservoirs, and channel routing which analyzes flood levels along river channels. Hydrologic routing methods use continuity equations while hydraulic methods also use equations of motion. Storage routing in reservoirs assumes a horizontal water surface and routes floods through calculating changes in storage over time intervals. Channel routing considers storage as a function of both inflow and outflow, accounting for storage in the channel prism and as a wedge.