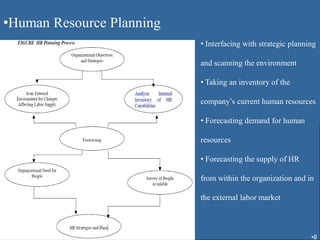
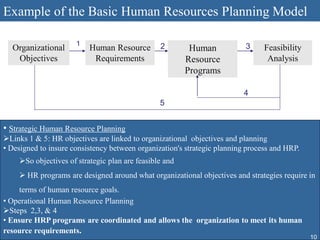
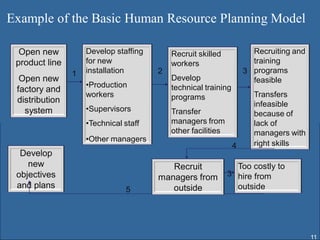
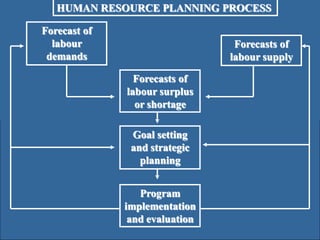
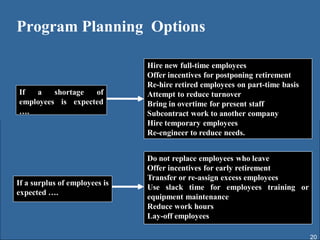
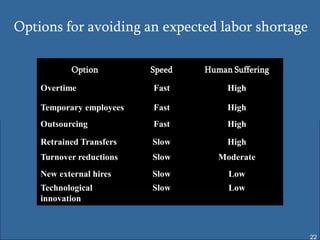
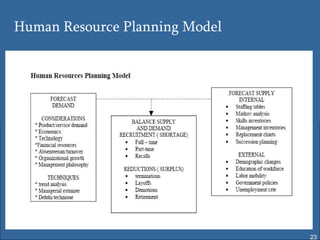
Human resource planning involves forecasting an organization's future human resource needs, determining how to meet those needs through various programs, and evaluating whether the programs are feasible given organizational objectives, environmental constraints, and costs versus benefits. The process includes assessing current and future labor demand and supply, identifying potential surpluses or shortages, and developing action plans to address imbalances through options like hiring, training, outsourcing, or layoffs. Effective HRP is important for strategic workforce management and controlling personnel costs.