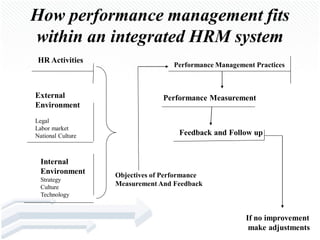
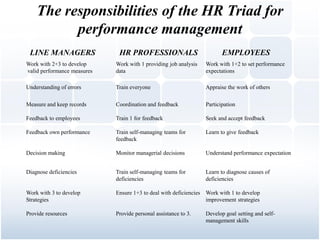
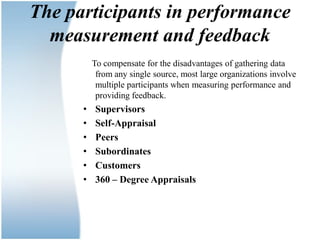
Performance management is a formal process used to measure, evaluate, and influence employee performance. It serves to enhance motivation, support strategic goals, and enable strategic planning. An effective performance management system incorporates measurement, feedback, goal setting between managers and employees. Several factors must be considered when implementing such a system, including the timing of reviews, participants, rating formats, and providing constructive feedback. Current issues involve greater use of automation and monitoring technologies.