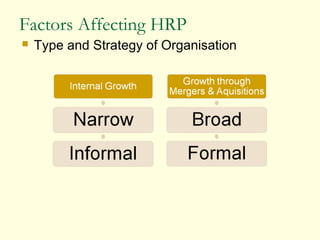
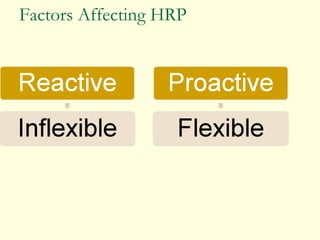
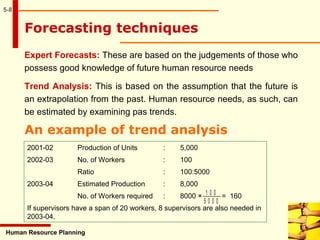
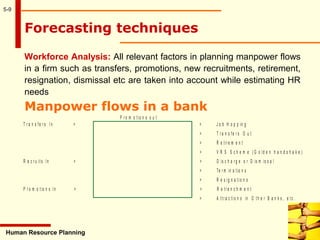
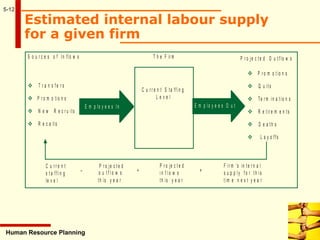
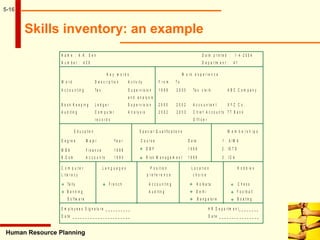
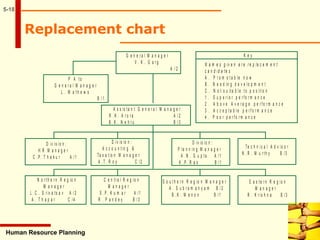
This document discusses human resource planning. It begins by defining HRP and its objectives, which include forecasting personnel requirements, coping with changes, using existing manpower productively, and promoting employees systematically. The document then covers factors affecting HRP, the HRP process, demand forecasting techniques, supply forecasting including internal and external labor sources, formulating HR plans, responsibilities for HRP, limitations of HRP, and keys to effective HRP. In summary, the document provides an overview of human resource planning, including its objectives, key components, and challenges.