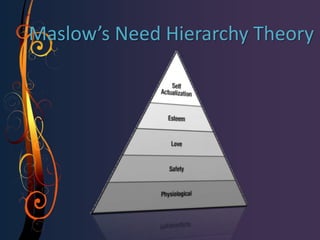
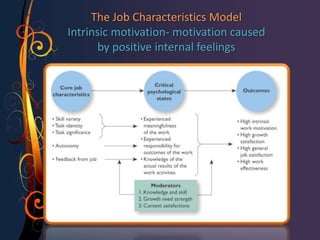
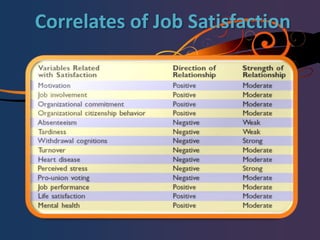
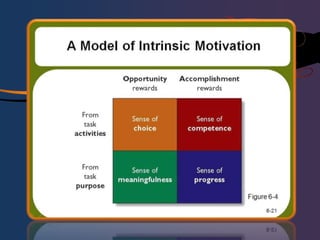
The document discusses various theories of motivation including Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, and the job characteristics model. It also covers intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, job satisfaction, and factors that influence counterproductive work behaviors. Key topics include what motivates individual performance, the relationship between job satisfaction and organizational outcomes, and balancing work and family responsibilities.