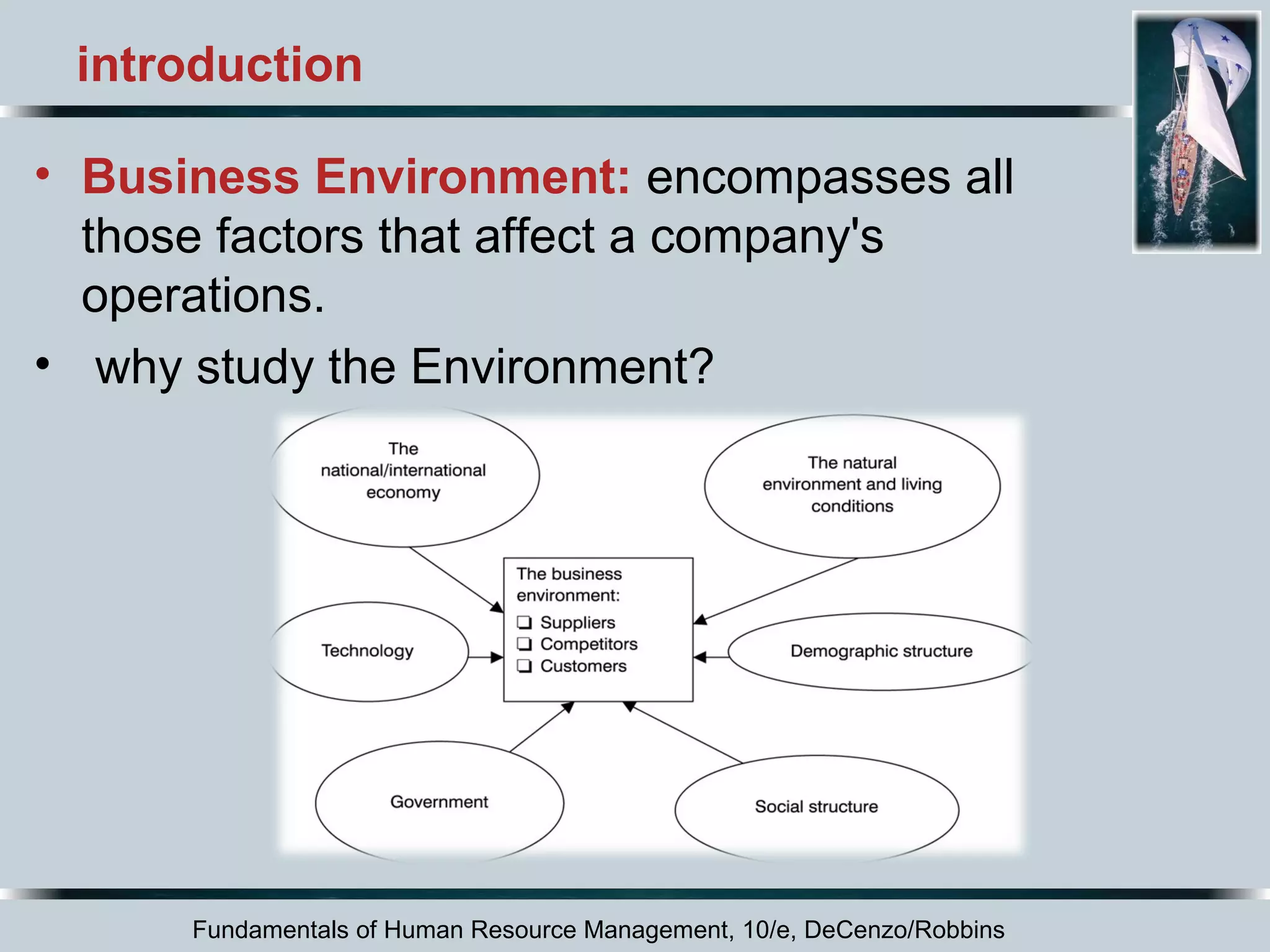
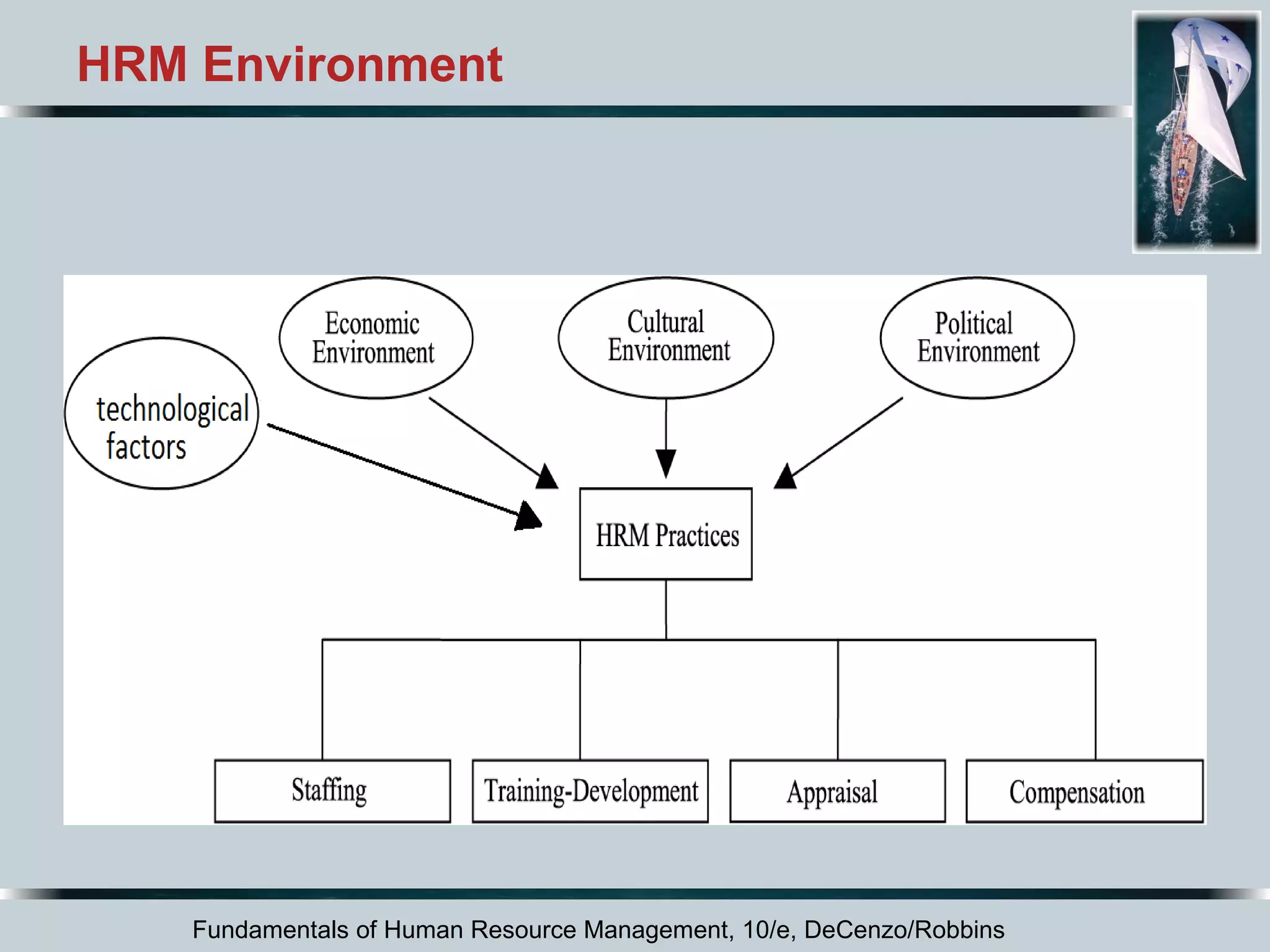
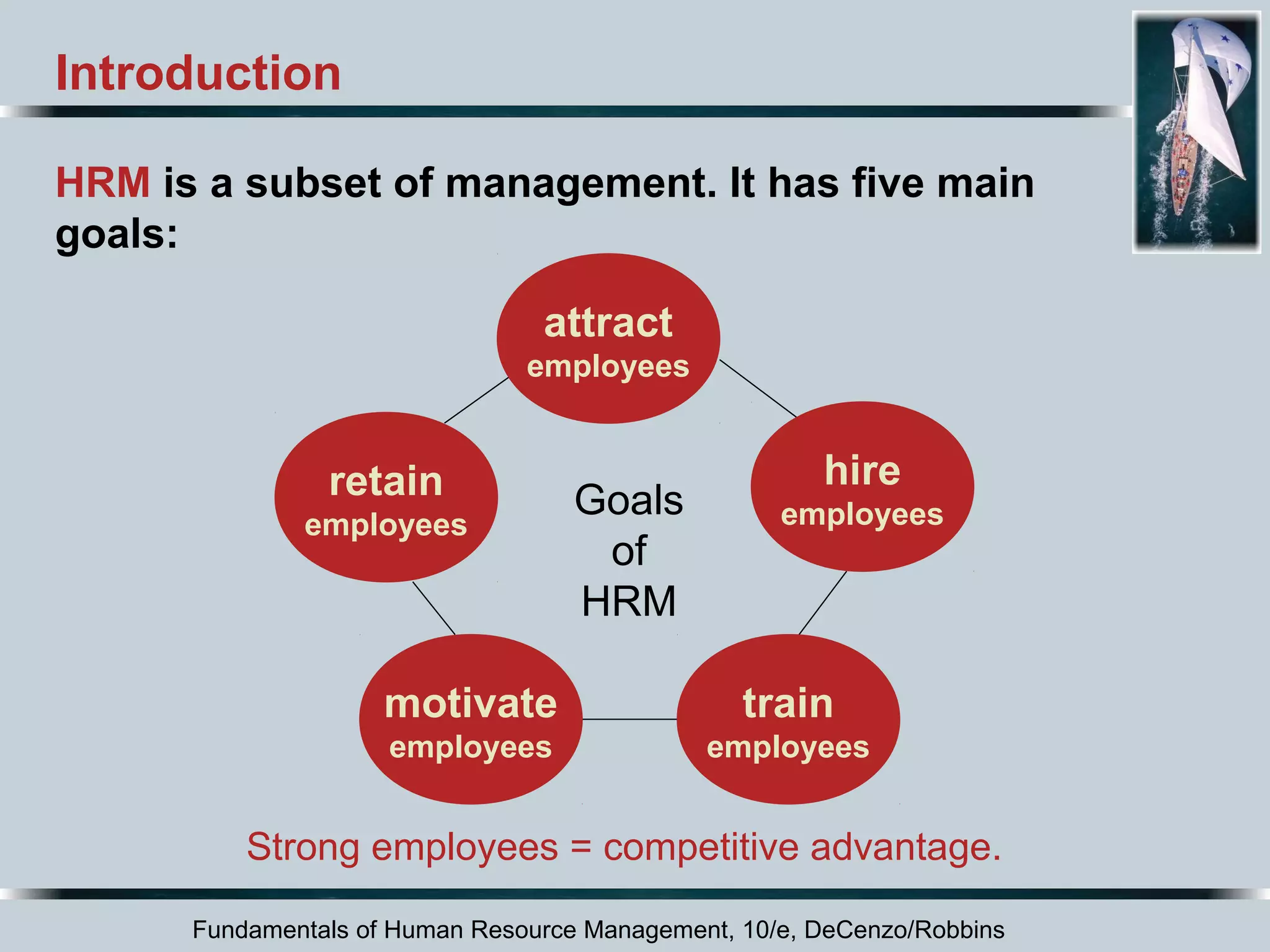
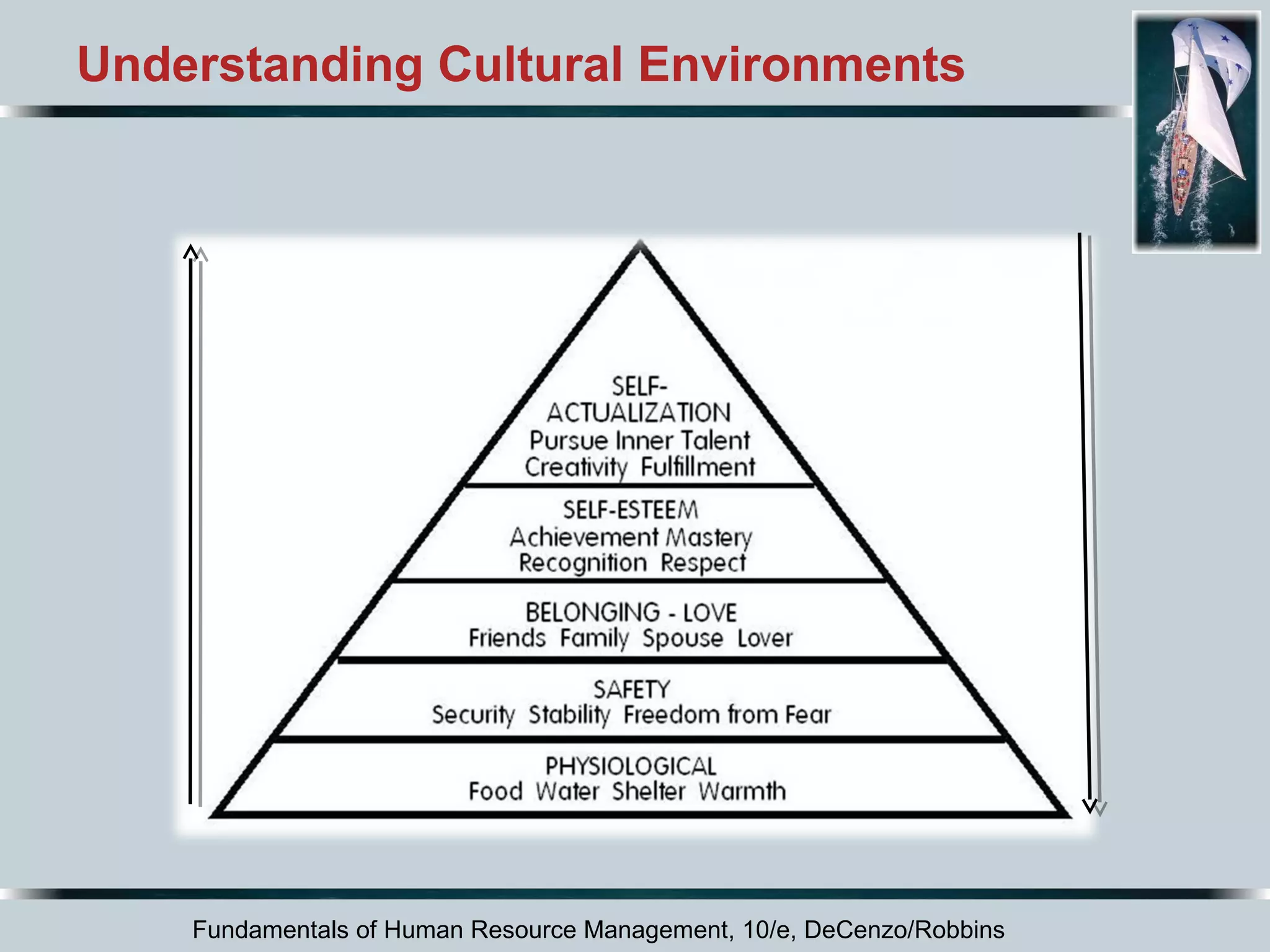
This document discusses the dynamic environment of human resource management. It covers how cultural, technological, and workforce diversity factors affect HRM practices. It also addresses challenges like responding to labor shortages, implementing continuous improvement programs, gaining employee involvement, dealing with recessions, offshoring jobs, and managing mergers and acquisitions. The overall document serves to outline the key external factors that influence HRM and how organizations must adapt their HRM strategies in response.