This document discusses various topics related to reproductive health, including definitions of reproductive health, population explosion and its causes in India, different contraception methods, sexually transmitted diseases, infertility, and assisted reproductive technologies. It provides an overview of India's family planning programs from the 1950s and current reproductive and child health care programs that aim to improve awareness and access to services.







![THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONTRACEPTIVES ARE:
1. Natural / Traditional method
2. Barrier method
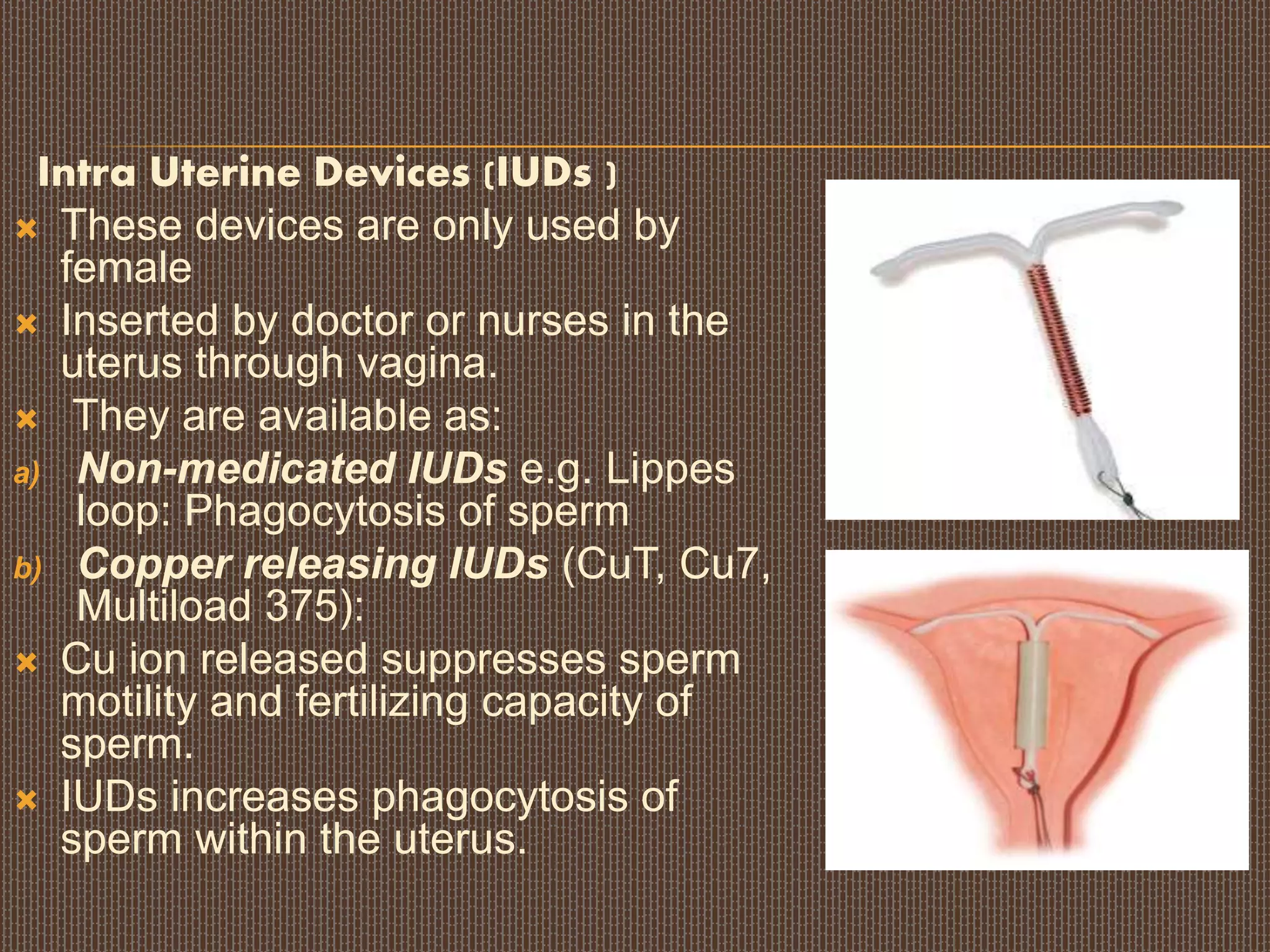
3. Intra uterine device [IUD’s]
4. Oral contraceptives
5. Injection and implants
6. Surgical method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irusnpdusjuugdoduozf-signature-e0143b94c39a94496b07ccc46c47f37a16313942f9bc2602263a4f9c6de5a76d-poli-141011131648-conversion-gate02/75/Reproductive-health-class-12-cbse-9-2048.jpg)