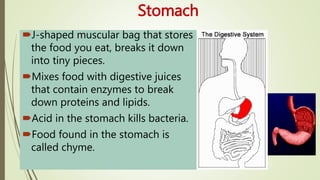
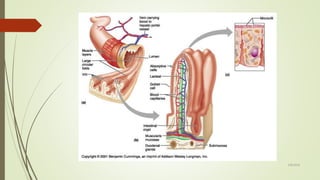
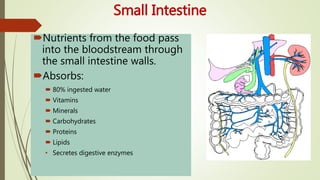
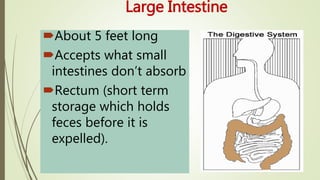
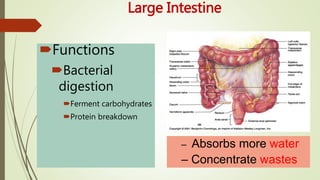
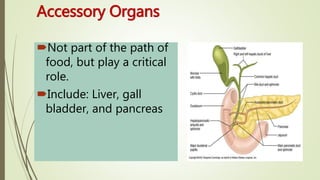
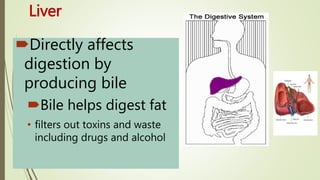
The digestive system involves several phases including ingestion, movement, digestion, absorption, and elimination, facilitated by various structures such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum. The small intestine plays a critical role in nutrient absorption while accessory organs like the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas assist in fat digestion and enzyme production. Overall, the system efficiently breaks down food and absorbs essential nutrients while managing waste.