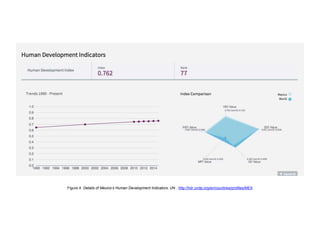
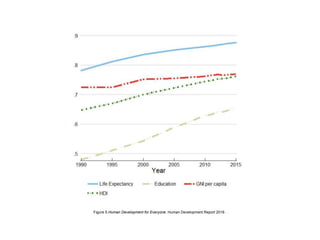
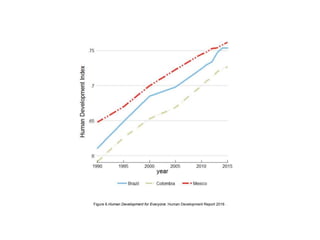
The document discusses various indices for measuring human development, including the Human Development Index (HDI), Gini Index, and Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI). It then analyzes Mexico's performance based on these indices, finding that Mexico has a relatively high HDI of 0.762, placing it in the "high development" category. However, there is still room for improvement in areas like access to education, inequality, poverty, and security to raise Mexico's score and quality of life overall.