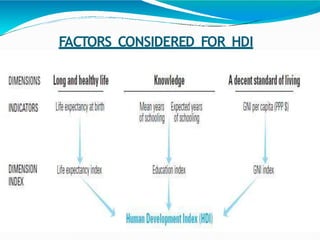
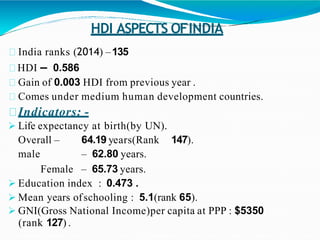
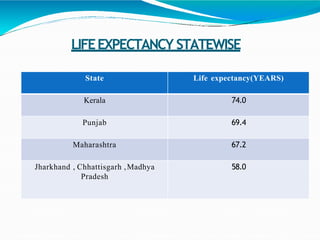
The document discusses the concepts of growth and development, noting that development requires positive growth. It introduces human development, which focuses on enlarging people's choices and improving lives through access to resources, health, and education. The four pillars of human development are equity, sustainability, productivity, and empowerment. The document then explains the Human Development Index (HDI), which ranks countries based on life expectancy, education, and income indicators. It provides details on India's HDI ranking and performance on key indicators, as well as India's human development programs and state-level differences in life expectancy.