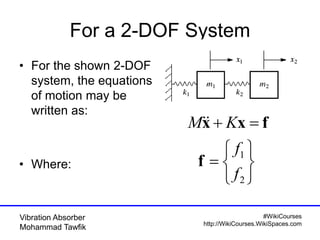
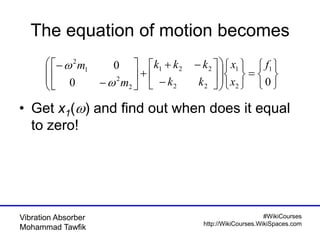
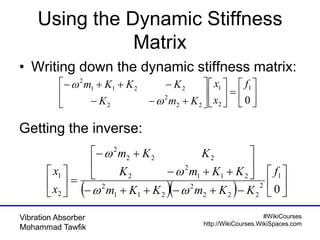
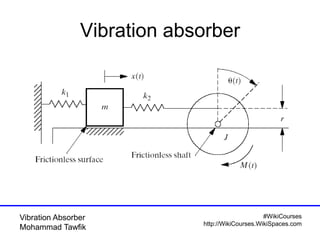
This document discusses vibration absorbers for damping vibrations in structures. It presents the equations of motion for a 2-degree of freedom system with an absorber and goes through the process of obtaining the solution. It is shown that for the primary system to be stationary, the excitation frequency must match the natural frequency of the absorber mass-spring system. Homework problems are assigned to further analyze systems with different excitation frequencies using the presented approach and modal decomposition.