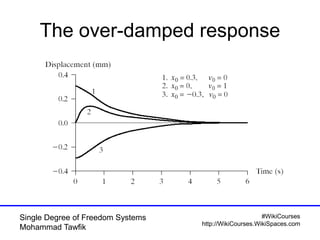
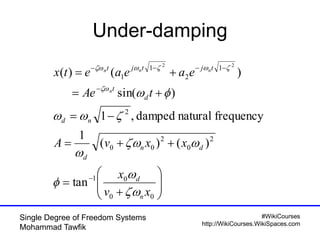
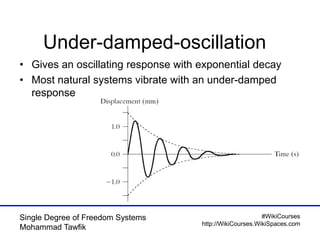
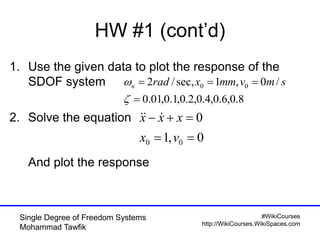
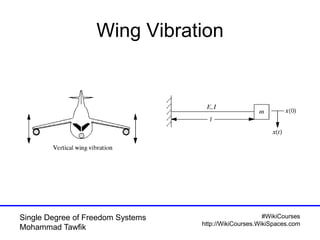
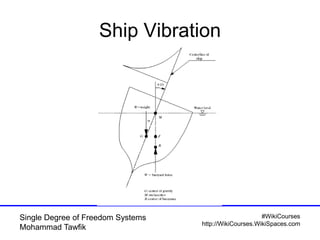
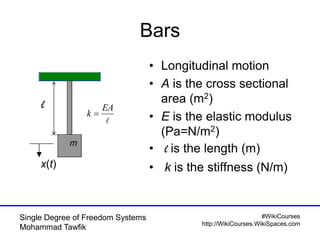
The document provides an overview of single degree of freedom (SDOF) systems, including their definition, equations of motion, and solutions for both undamped and damped systems. It discusses the impact of damping on motion, as well as the application of numerical tools for analyzing time response. Additionally, it covers related concepts such as natural frequency, amplitude, and various examples of vibrating systems.















![#WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
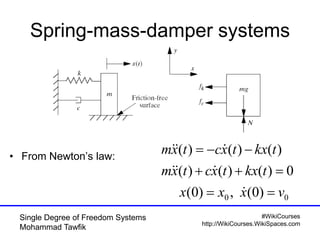
Single Degree of Freedom Systems
Mohammad Tawfik
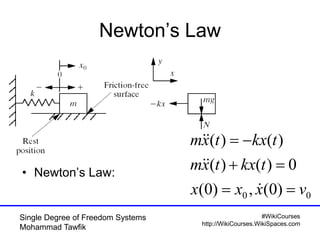
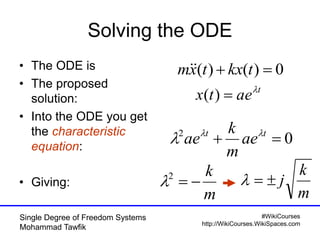
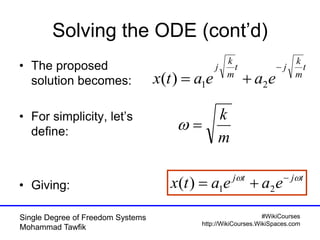
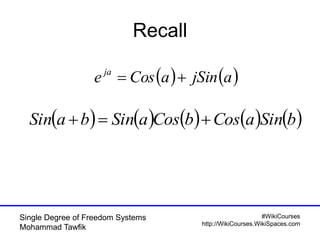
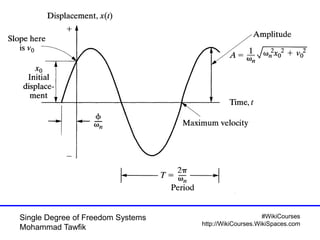
Critical damping cont’d
• No oscillation occurs
t
n
n
etxvxtx
])([)( 000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01singledof-100926051329-phpapp01/85/Single-Degree-of-Freedom-Systems-44-320.jpg)