HTML5 introduces new features that can be exploited if not implemented securely. Storage mechanisms like local storage, session storage, and IndexedDB can be used to steal sensitive user data if not set with the proper security flags. Cross-origin resource sharing and cross-document messaging allow communication between domains but need controls to prevent CSRF and information disclosure. New HTML5 features provide opportunities for old attacks like XSS through new vectors like autofocus. Developers must implement security best practices to prevent exploitation of HTML5 capabilities.




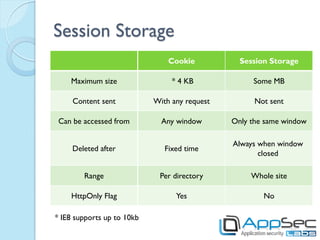
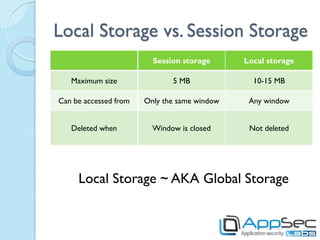









![SQL Storage attacks – Dump data
Get objects (connected to the DB)
var db = "";
for(i in window)
if(window[i] == “[object Database]”)
db += i + “ “;
Get tables:
SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table‘](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/html5-hacking-110817114523-phpapp01/85/Html5-hacking-17-320.jpg)