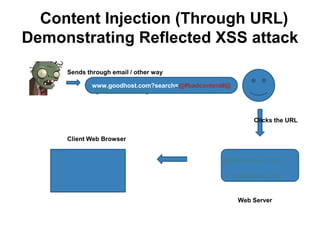
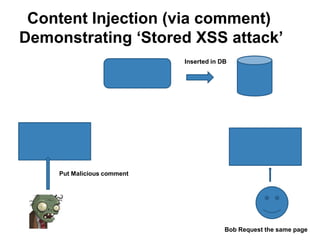
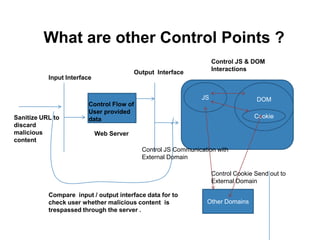
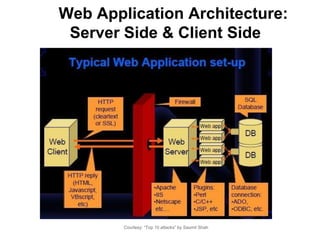
The document discusses web browser security and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. It explains that XSS attacks work by injecting malicious JavaScript code into web pages. This code can then access sensitive data like cookies or modify the page's content. The document outlines the risks of XSS and how attackers use it to steal user information or launch other attacks. It also summarizes some existing approaches to prevent XSS, such as restricting where JavaScript can be placed or limiting its access to sensitive resources.


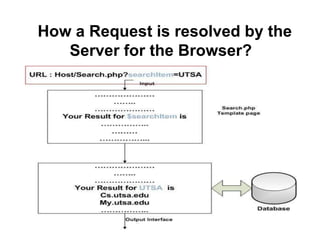
![Http Request (URL) format
"protocol:" "//" host [ ":" port ] [ abs_path [
"?" query ]]
Examples:
1. http://cs.utsa.edu/index.html
2. http://utsa.summon.serialssolutions.com/search/results?
spellcheck=true&q=security
3. http://www.php.net/manual/en/reserved.variables.get.php
4. http://www.amazon.com/s/ref=nb_sb_noss/185-1213459-
6355102 ?url=search-alias%3Daps&field-keywords=iphone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securewebbrowsing-1-120412215533-phpapp02/85/Secure-webbrowsing-1-3-320.jpg)





![How Web Browsing can be
insecure?
• Attacker Steals data [Attack User information]
• Attacker defaces a webpage [Attack markup]
• Inject / Modify JavaScript [Script Based
attack]
• Steal Cookie
• Insert Meta Data on page
• Attack other Resources [ex: Image]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securewebbrowsing-1-120412215533-phpapp02/85/Secure-webbrowsing-1-11-320.jpg)

![Risk That We Do Not Care …
• A website is malicious and an user visits this
site and get infected.
[We can leave it to the discretion of the
visitor]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securewebbrowsing-1-120412215533-phpapp02/85/Secure-webbrowsing-1-13-320.jpg)
![Risk That We Care(2) …
• A website is not intended to be malicious but
attacker has compromised this page and let
everyone who visit it, be compromised.
o [ We do Care for this ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securewebbrowsing-1-120412215533-phpapp02/85/Secure-webbrowsing-1-14-320.jpg)
![Attacking Approach (Client-server
Perspective)
• Attack Servers / Services [ Server side
attack]
o Ex. Website Defacement ,
o SQL injection,
o DoS Attack and others
• Attack Web Client [ Client / Browser based
attack].
o Ex: XSS ( Cross Site Scripting)
o XSRF ( Cross Site Request forgery)
o Phishing ( Social Eng.) and others](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securewebbrowsing-1-120412215533-phpapp02/85/Secure-webbrowsing-1-15-320.jpg)