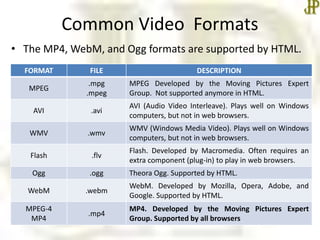
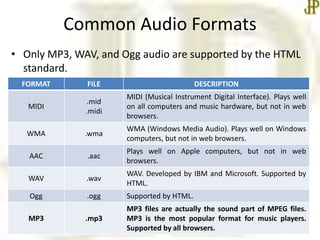
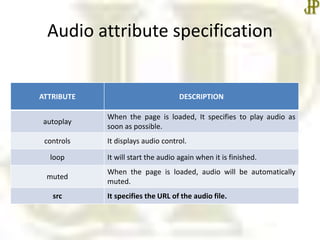
This document provides information about embedding multimedia like video and audio in HTML. It discusses common video formats like MP4, WebM, and Ogg that are supported by HTML, as well as common audio formats like MP3, WAV, and Ogg. It explains how to embed video using the <video> tag and audio using the <audio> tag, including attributes like autoplay, controls, loop, and muted. The document concludes that the next class will cover Cascading Style Sheets in more detail.