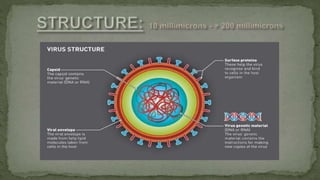
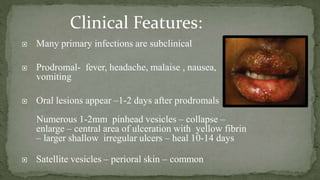
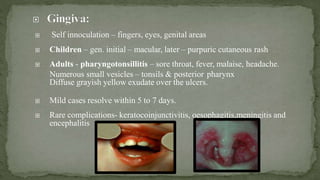
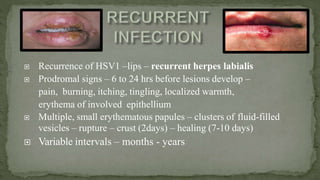
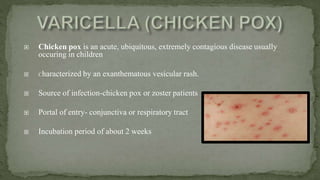
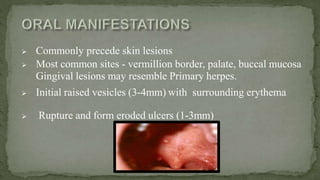
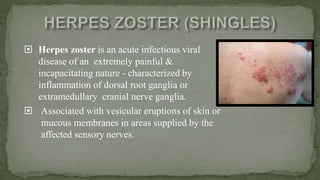
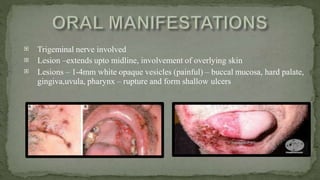
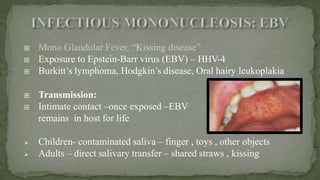
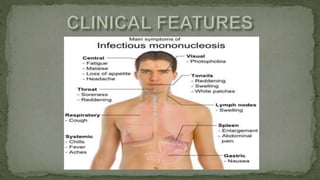
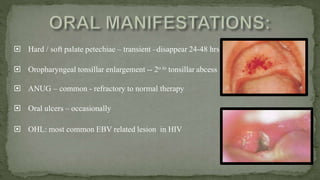
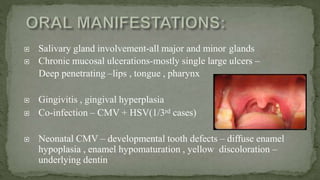
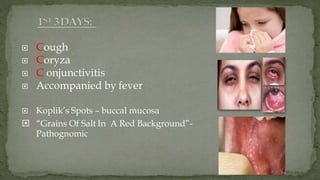
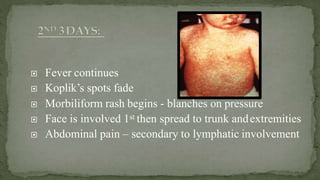
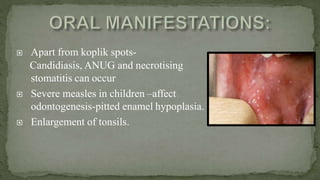
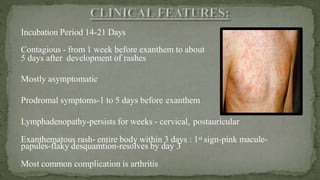
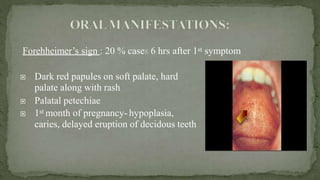
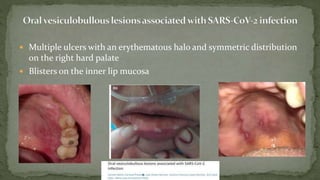
This document provides an overview of various viruses that can cause oral manifestations. It discusses the classification, pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of several viruses including herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, varicella zoster virus, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and others. For each virus, it describes the stages of infection from viral entry and replication to symptoms and shedding as well as approaches to diagnostic testing and management.