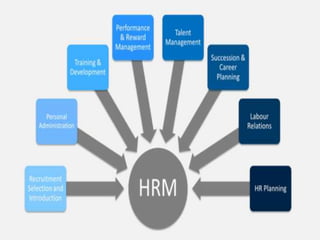
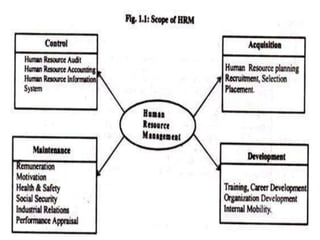
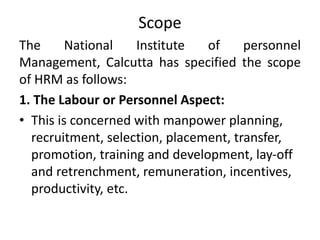
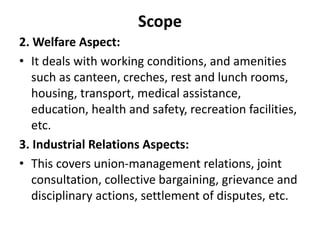
Human resource management involves managing employees in an organization to achieve its goals. It includes recruiting, training, evaluating performance, and resolving disputes. HRM aims to optimize the workforce to efficiently and effectively accomplish objectives. It benefits organizations through increased productivity and profits, and benefits individuals through career growth opportunities and job satisfaction. The scope of HRM encompasses all aspects of managing employees from hiring to retirement. Its importance is seen at the enterprise, individual, societal, and national levels. HRM has evolved from traditional personnel management approaches to focus more on human values and development.