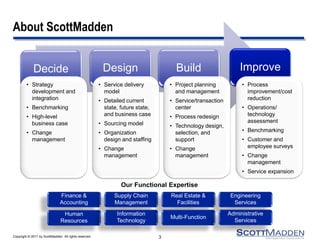
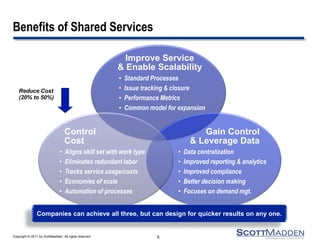
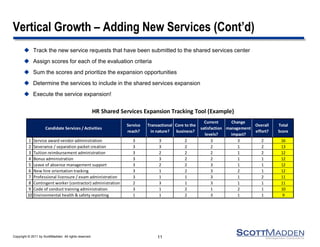
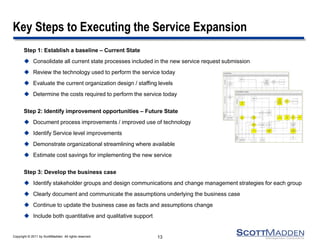
This document discusses strategies for expanding HR shared services. It outlines four key steps: 1) establishing a current state baseline, 2) identifying future state improvement opportunities, 3) developing a business case, and 4) creating a transition and training plan. Expansion can occur horizontally by adding new customers, business units, or geographic areas, or vertically by adding new HR services like recruiting, training, or vendor management. Benefits include reduced costs, improved control and data leverage, and enhanced service and scalability. Careful planning is needed to successfully execute a service expansion.