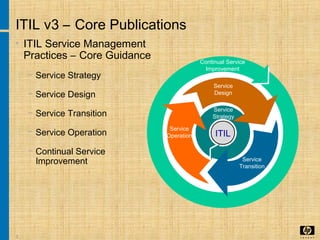
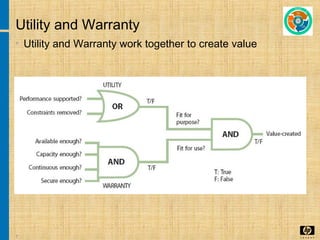
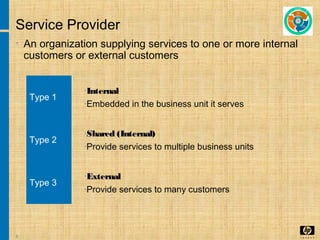
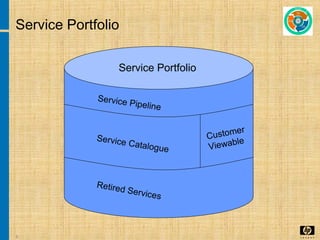
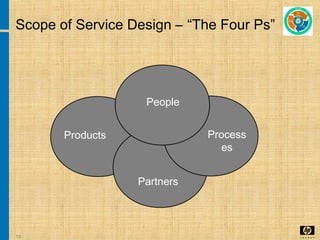
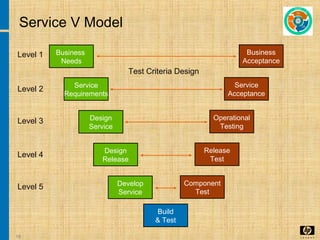
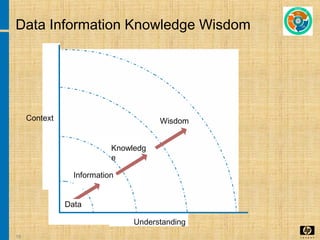
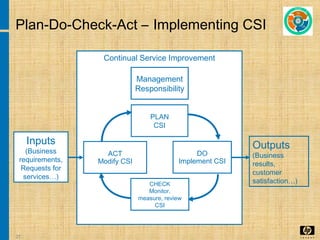
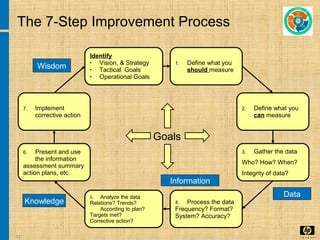
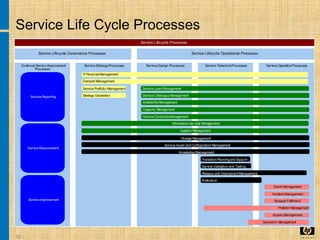
The document discusses the key concepts and processes in the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) framework. ITIL describes best practices for IT service management and is broken down into five core publications: Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation, and Continual Service Improvement. Each publication focuses on a different stage of the service lifecycle to help align IT services with business needs and ensure quality service delivery.