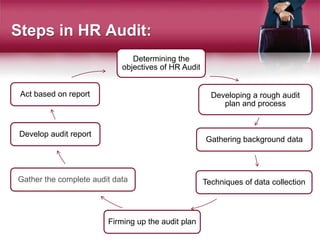
This document discusses the purpose and process of conducting an HR audit. It begins by defining an HR audit as an examination of HR policies, procedures, and practices to evaluate the effectiveness of personnel management. The objectives of an HR audit are to review all aspects of HR management to determine the effectiveness of programs and policies, seek explanations for successes and failures, and evaluate employee and HR staff performance. Key sections to review include hiring, benefits, compensation, performance evaluations, termination processes, and job descriptions. The document then outlines five common approaches to conducting an HR audits, including comparative, outside authority, statistical, compliance, and management by objectives approaches. It concludes by listing the typical steps in an HR audit process from determining objectives to gathering data