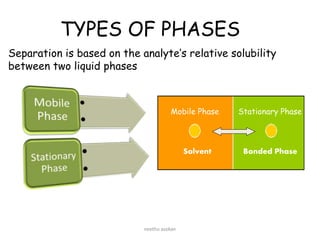
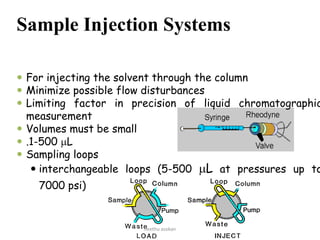
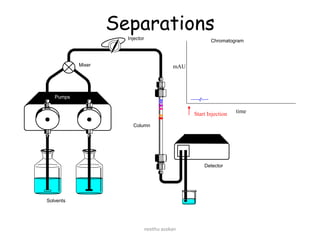
The document discusses High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). It provides background on the origins and development of HPLC from the early 1900s. By the 1980s, HPLC was commonly used for separation, identification, purification and quantification of chemical compounds. The document then discusses the basic principles, components, and instrumentation of HPLC systems. It explains how HPLC uses high pressure to force a mobile phase through a column containing a stationary phase to separate compounds based on their interactions with the phases. Common applications of HPLC across various fields like pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, forensics and food are also summarized.