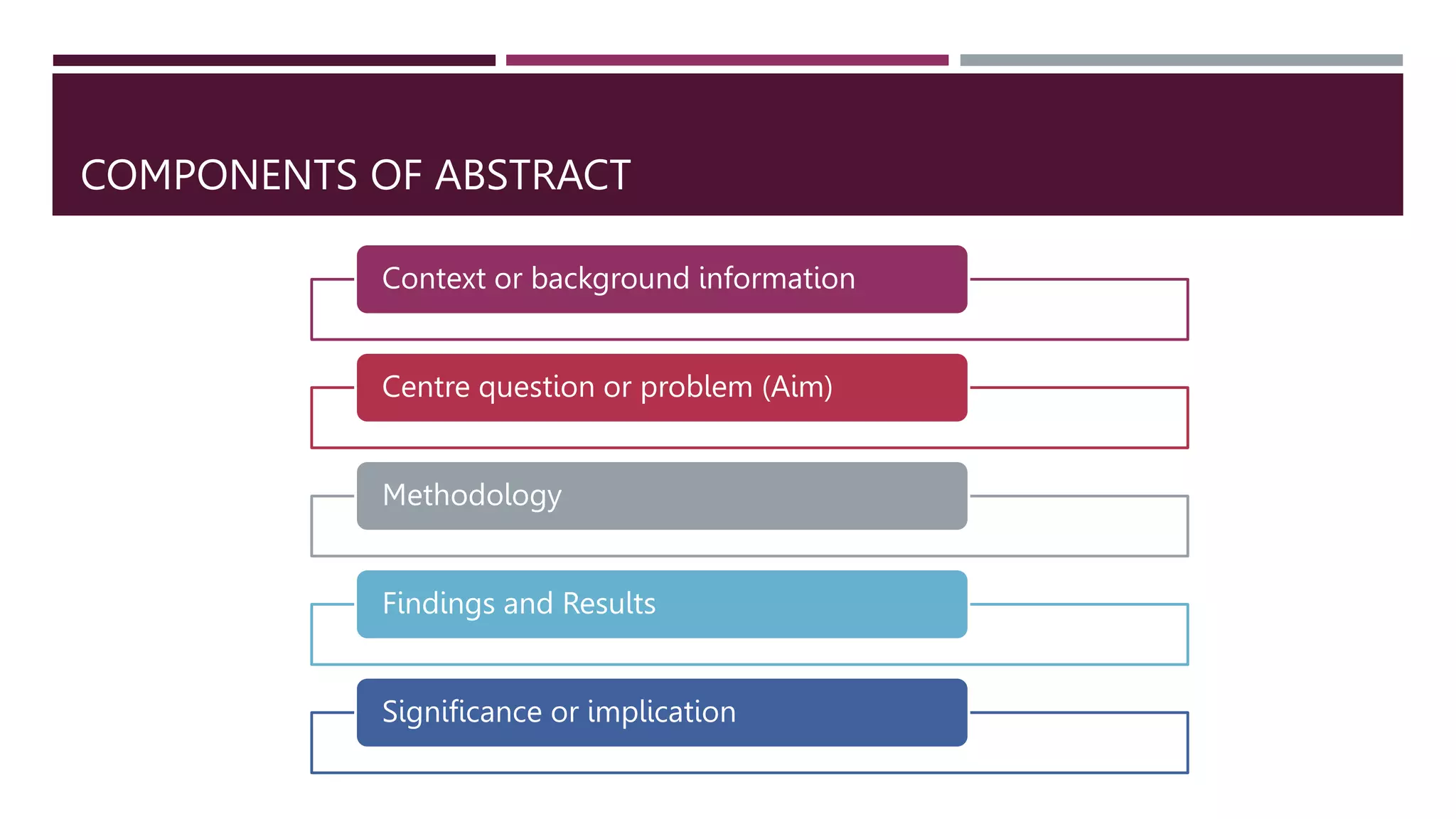
The document provides guidance on writing an abstract for a research paper. It explains that an abstract is a short summary, around 150-250 words, that is written after completing the paper. The abstract should provide an overview of the paper's context, research question, methodology, main findings and conclusions in a coherent and concise manner. It should allow the reader to understand the essence and significance of the paper without referring to the main text. The document outlines the key components and 4 C's (complete, concise, clear, cohesive) that an effective abstract should possess. It also highlights best practices for structuring an abstract and common issues to avoid.