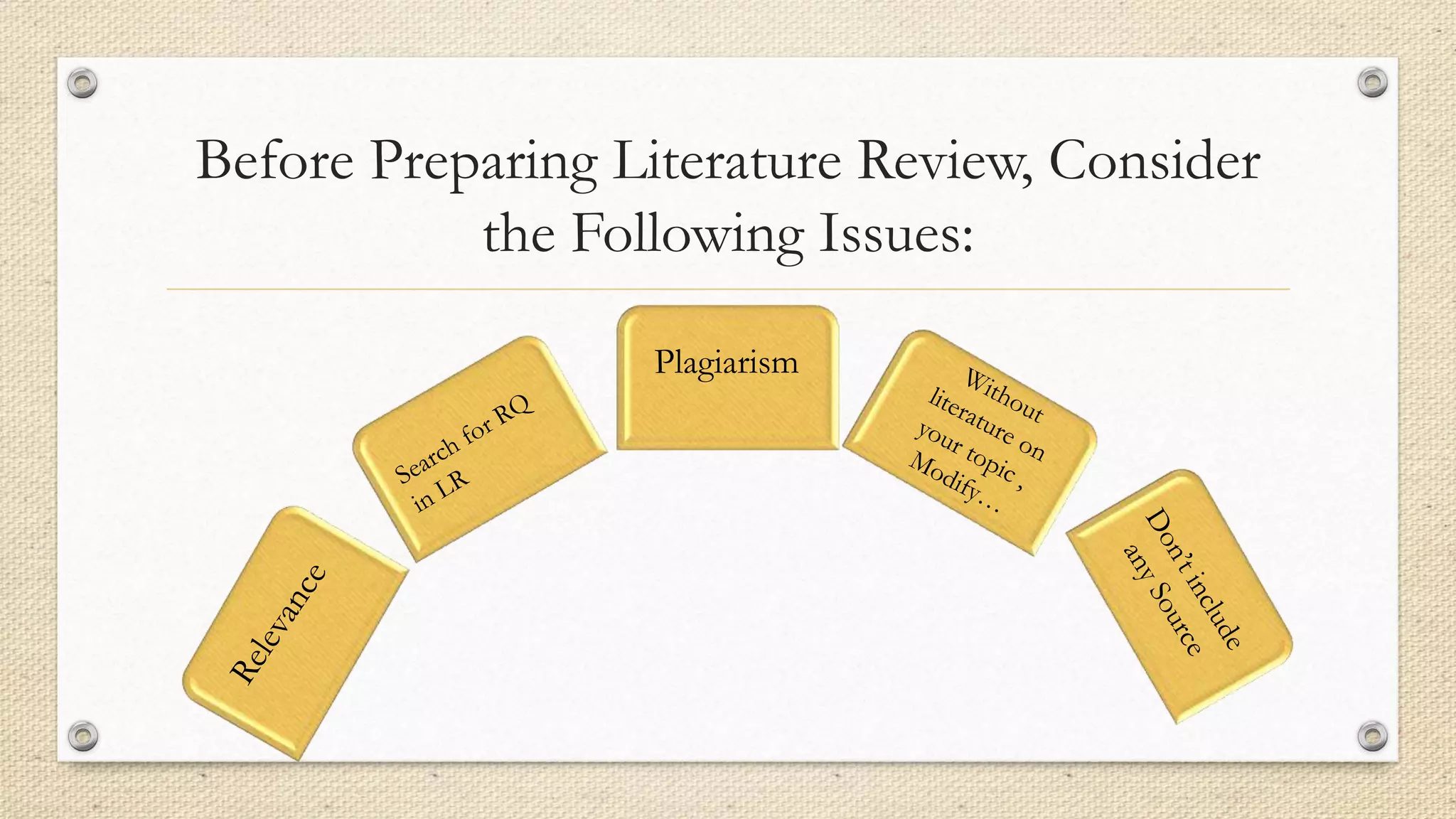
This document outlines the key components of conducting a literature review. It discusses defining a literature review and its purpose, issues to consider, and how it relates to other research components. The document also provides guidance on organizing a literature review, including locating relevant literature, critically reading sources, preparing to write, writing an introduction and sub-sections, and indicating gaps. Steps and strategies are provided for each part of the writing process, such as identifying key terms, authors, and journals; avoiding plagiarism; and using the review to lead into research questions.