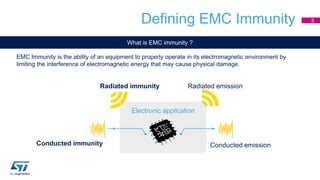
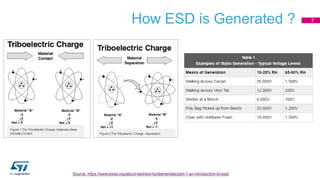
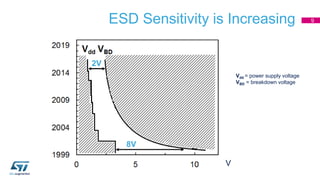
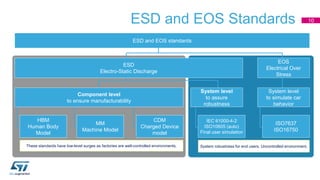
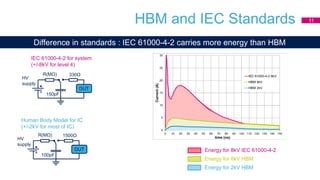
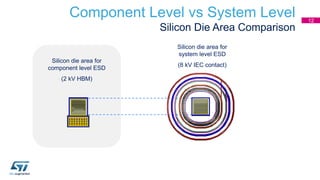
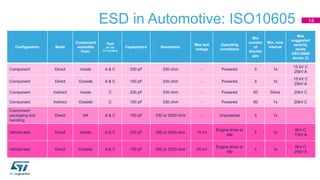
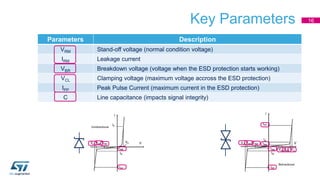
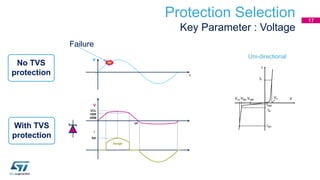
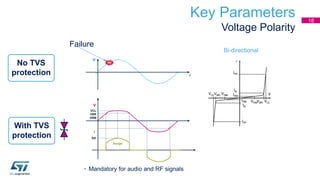
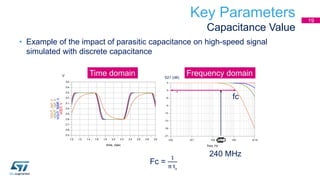
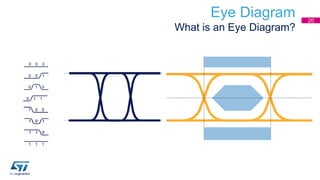
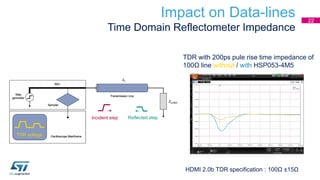
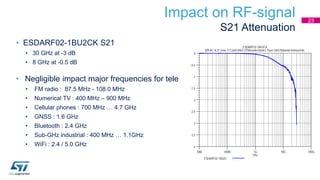
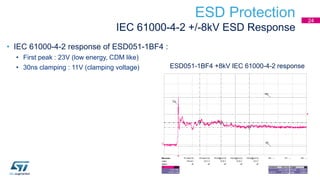
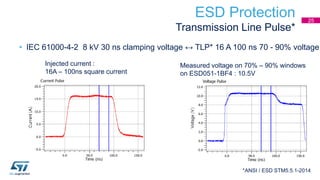
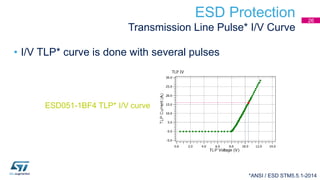
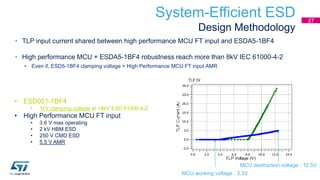
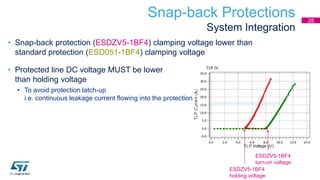
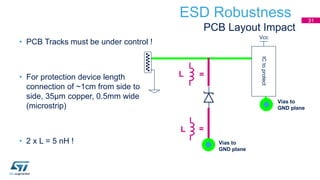
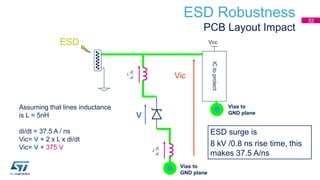
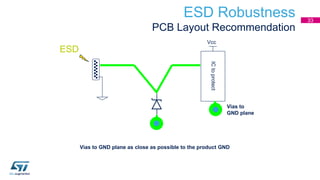
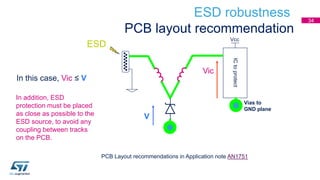
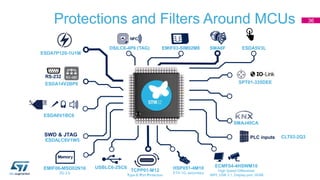
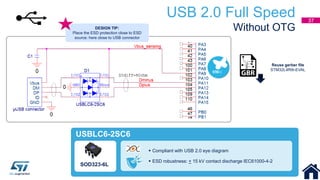
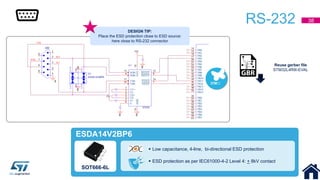
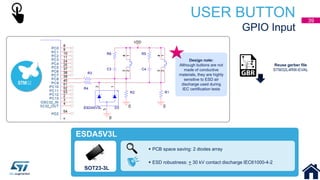
This document discusses Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) immunity, focusing on the ability of electronic systems to function properly amidst electromagnetic interference. It details ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) protection methods, standards, and guidelines, highlighting the significance of component and system-level ESD protection. Additionally, it covers practical examples of ESD protection devices and PCB layout recommendations for effective implementation.