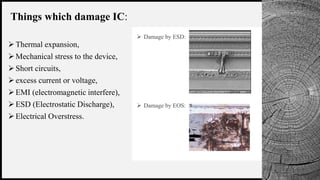
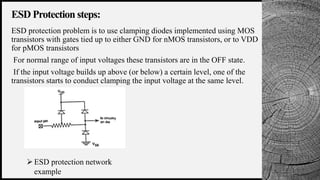
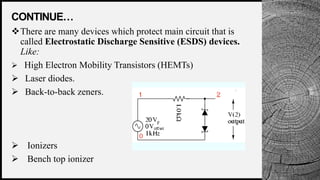
The document discusses electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection in VLSI design, detailing the causes and effects of ESD on integrated circuits (ICs). It differentiates between direct and latent failures caused by ESD, emphasizing the need for protective measures such as clamping diodes and ESD-sensitive devices. Various tools and techniques for ESD protection are also mentioned, including high electron mobility transistors and ionizers.