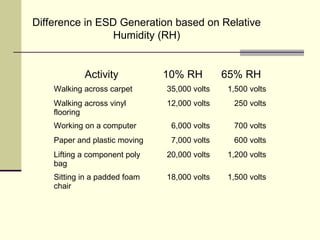
The document provides an overview of electrostatic discharge (ESD), explaining its causes, importance, and potential damages to electronic components. It emphasizes the need for preventative measures such as using ESD wrist straps, mats, and maintaining humidity to reduce risks. It also details proper handling techniques and the use of anti-static bags for storing sensitive components.