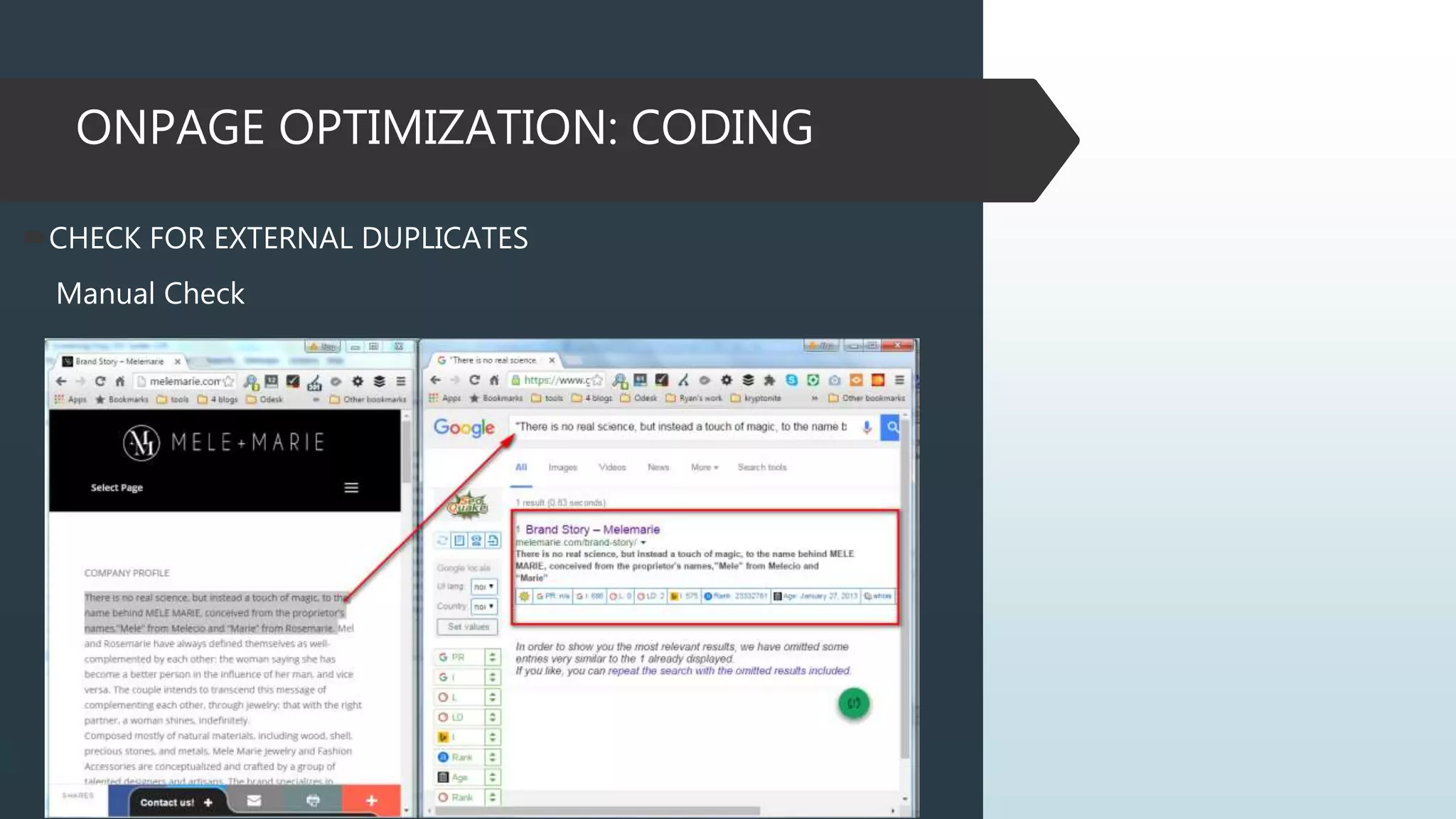
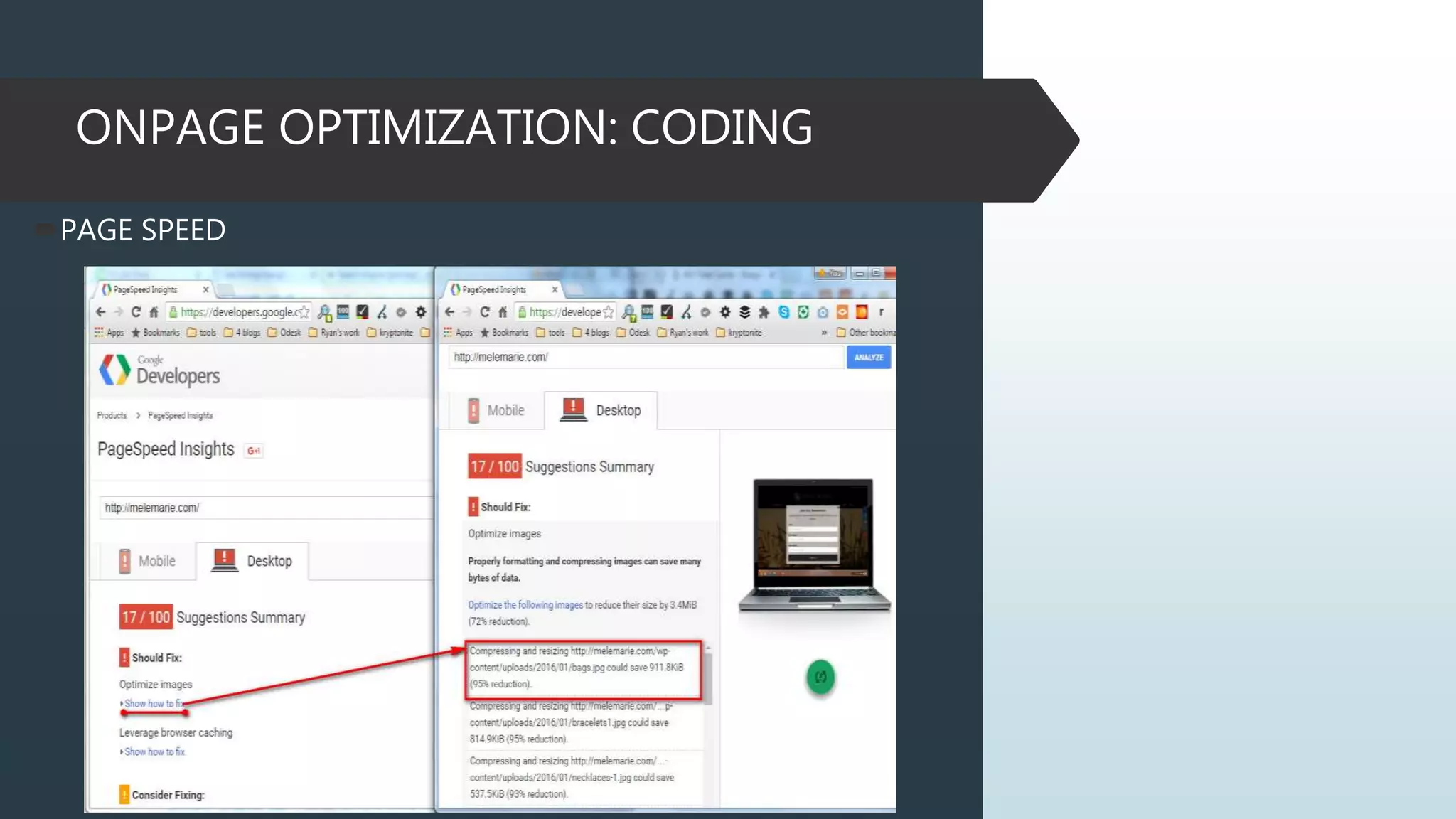
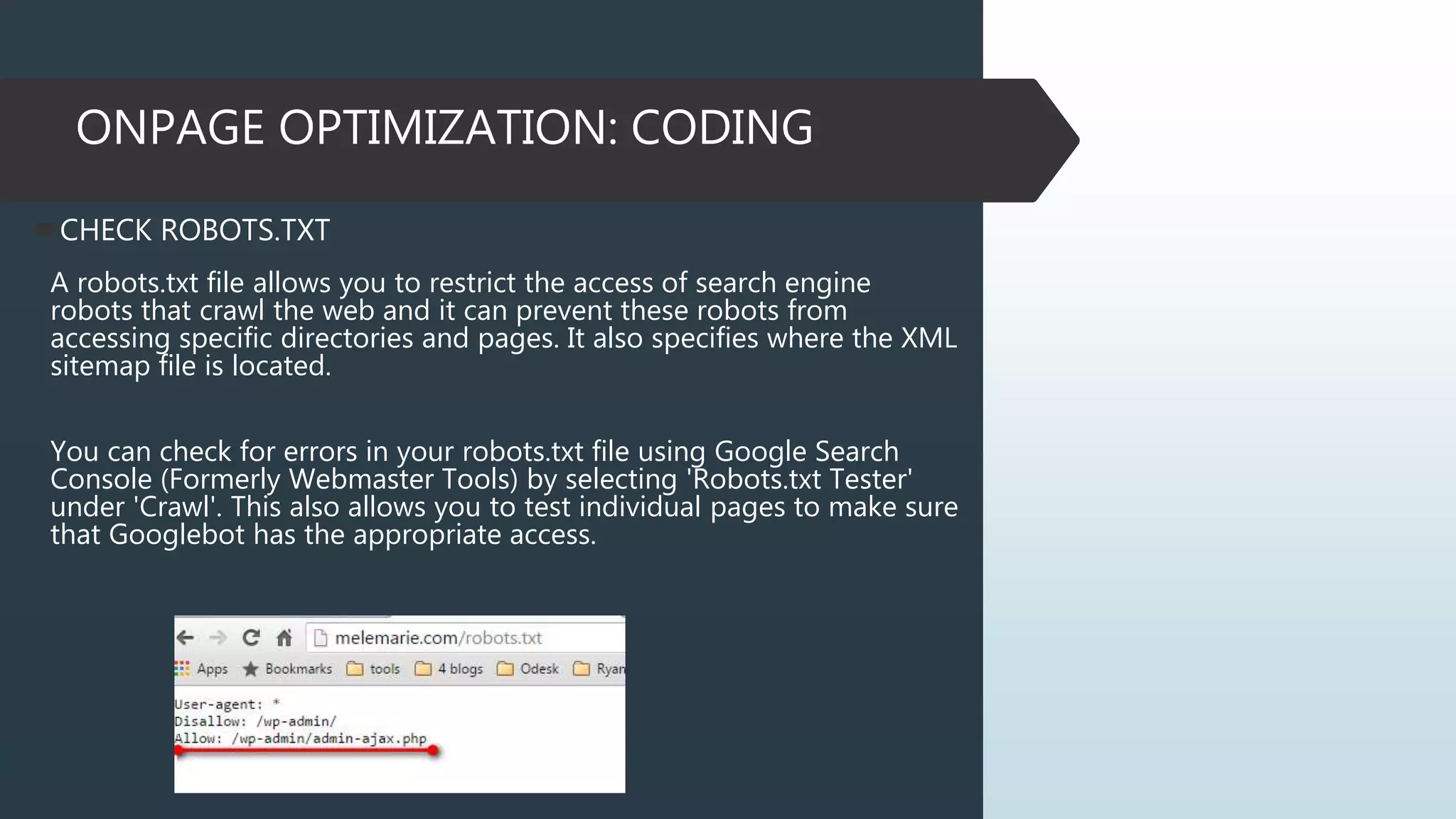
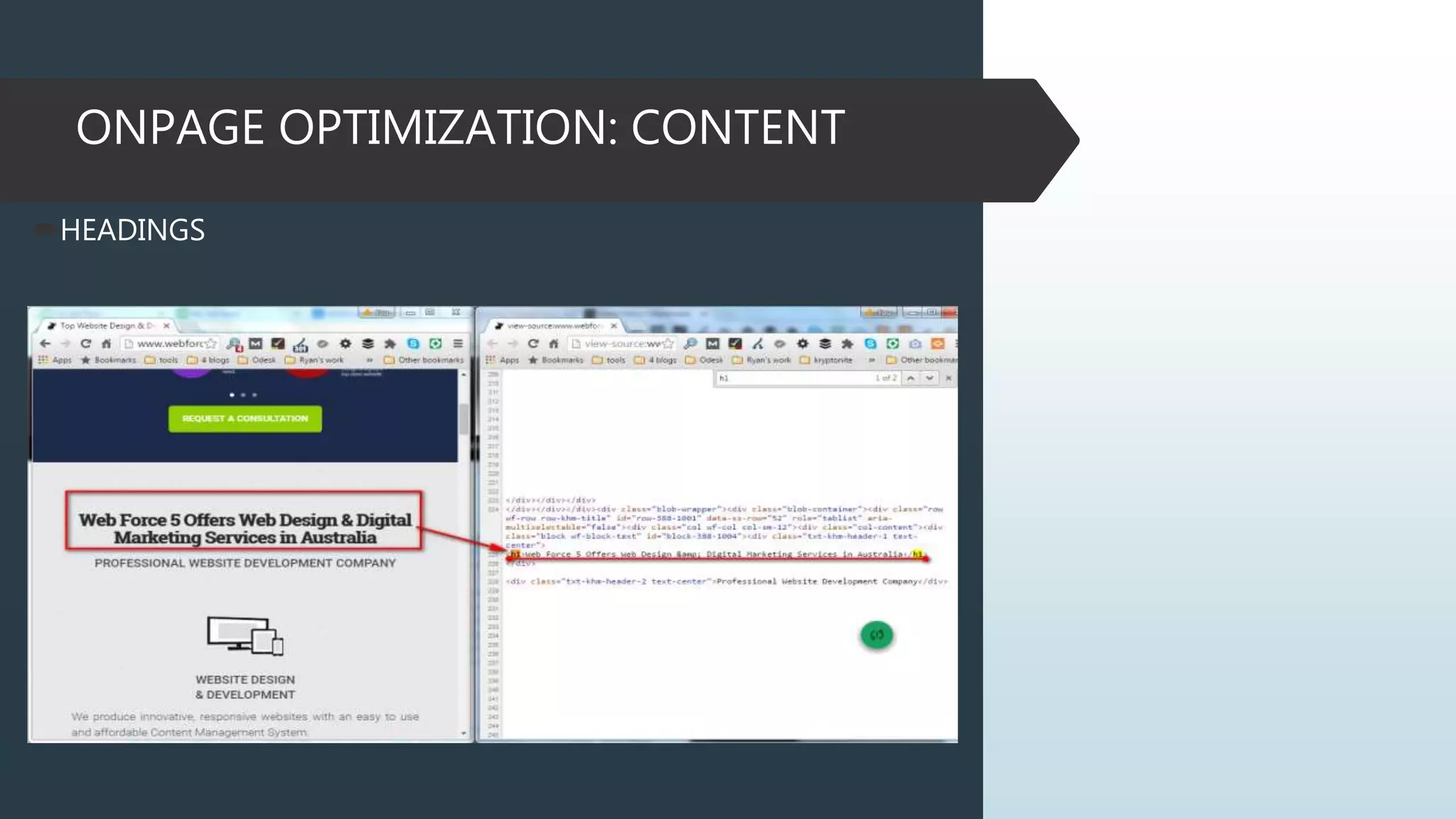
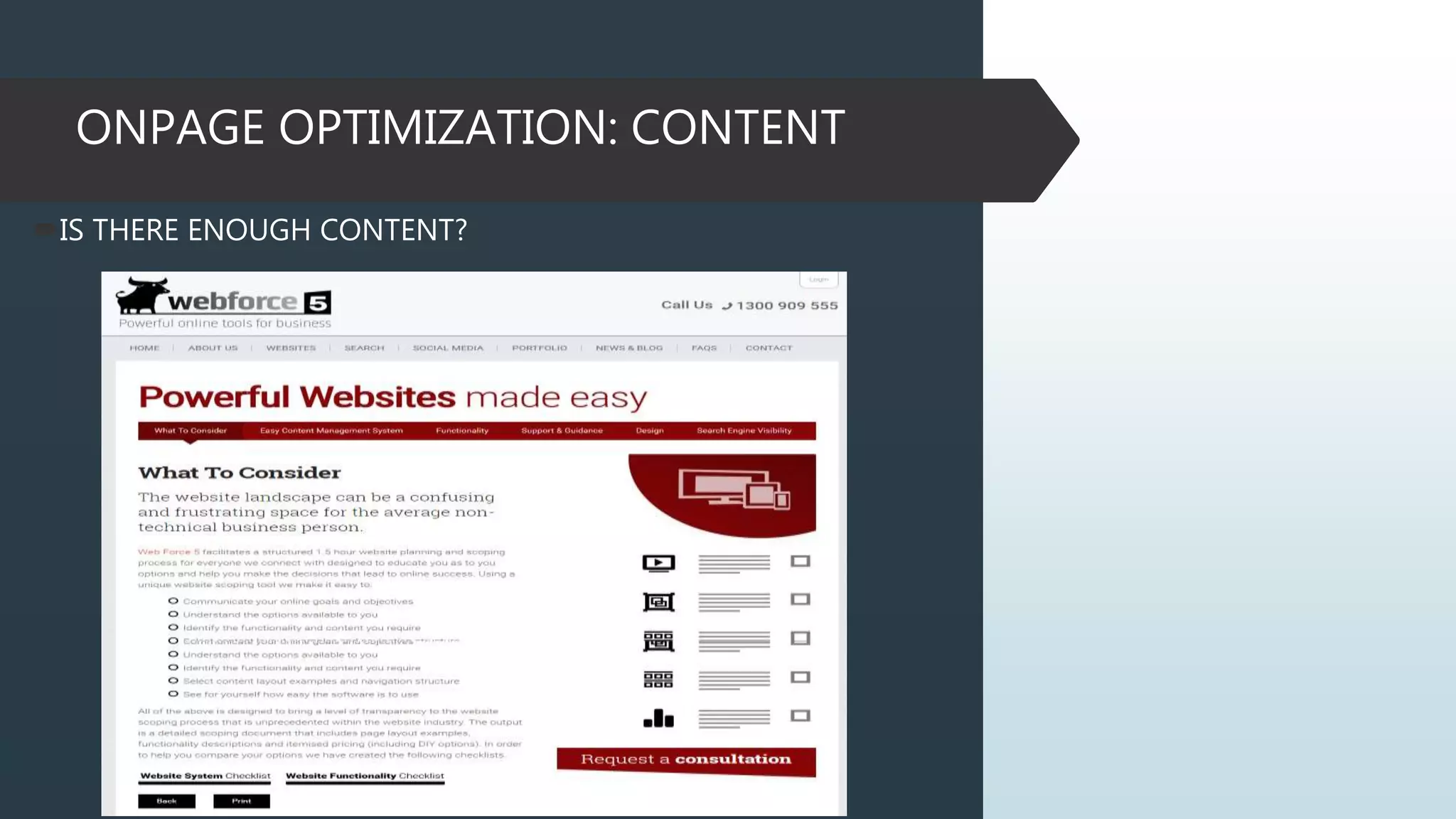
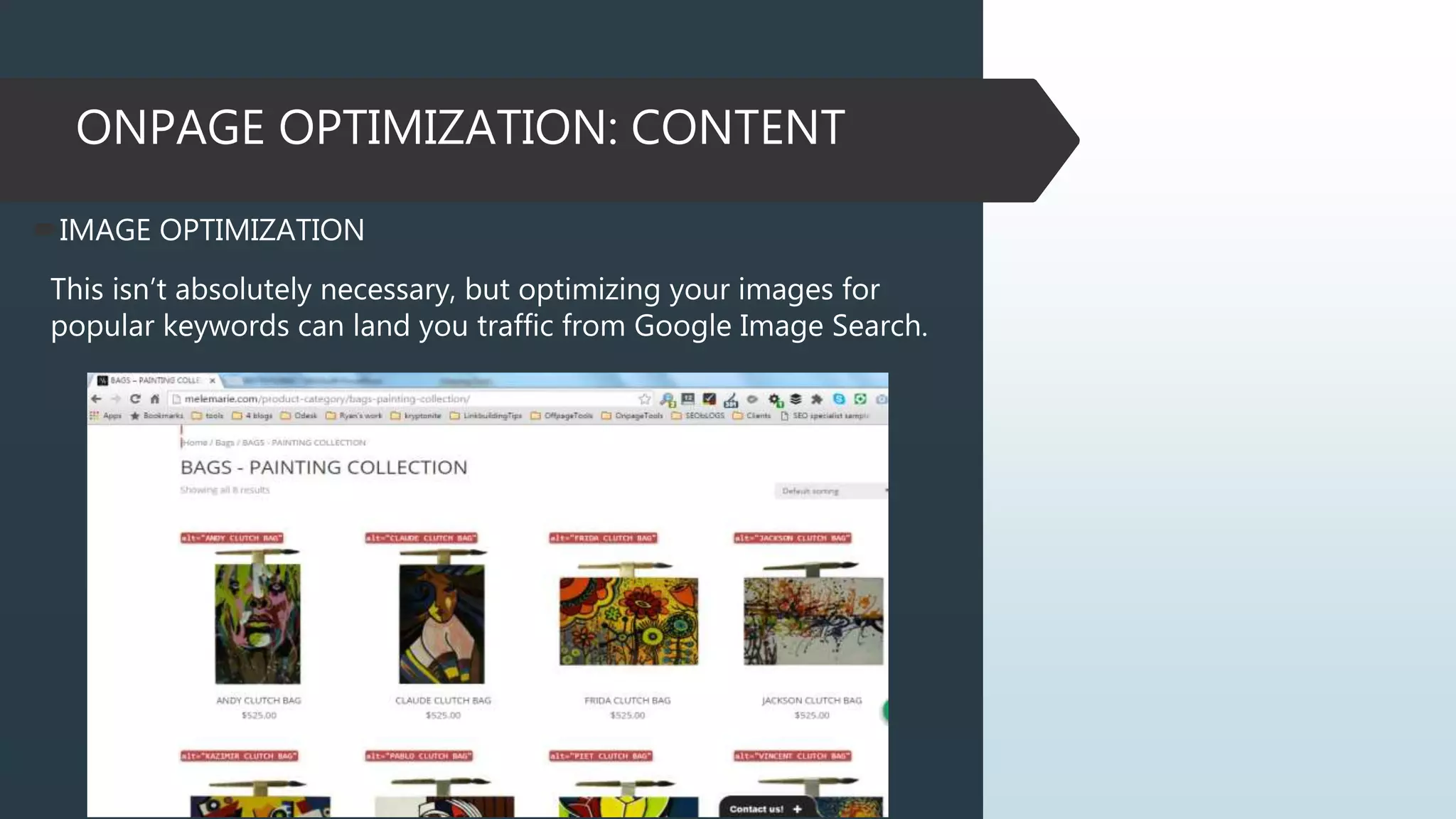
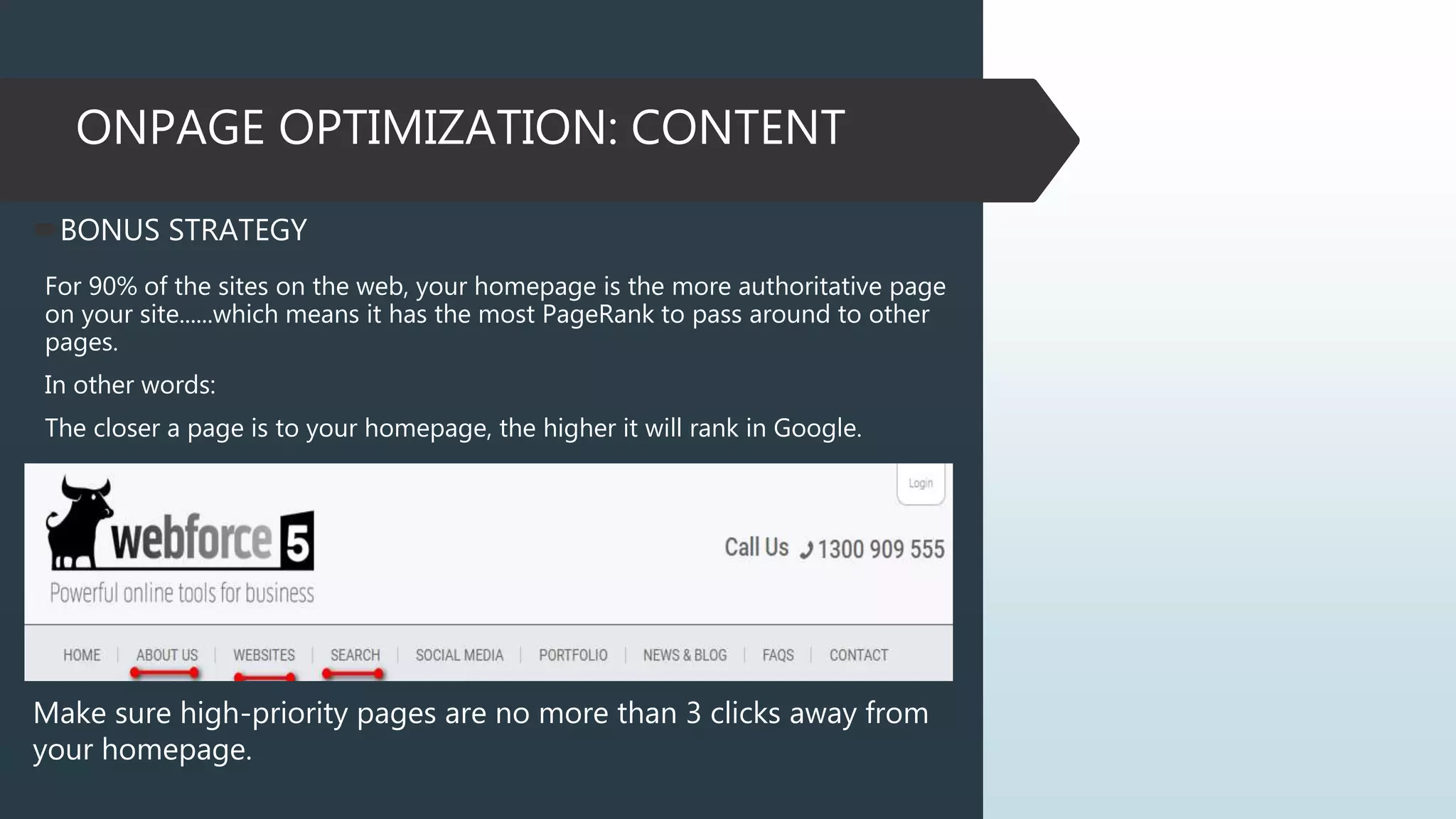
This document provides information on how to properly analyze a website for search engine optimization (SEO) purposes. It discusses key aspects of on-page optimization that should be analyzed, including coding elements like URLs, Google Analytics implementation, and page speed, as well as content elements like titles, meta descriptions and headings. The document also provides background information on search engines, SEO, and ranking factors to help inform the audit process.