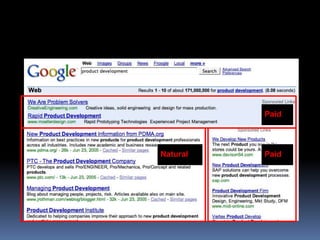
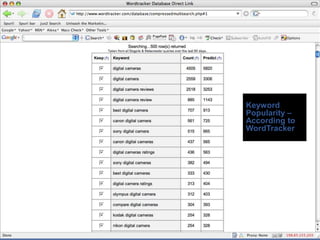
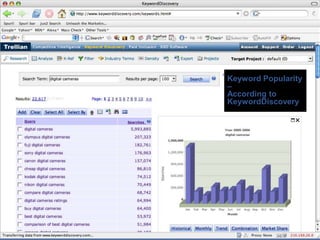
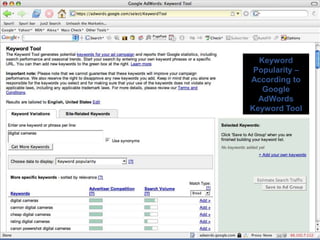
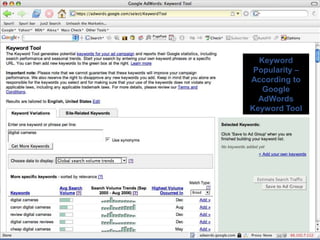
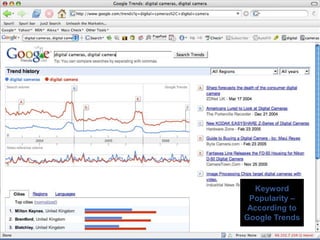
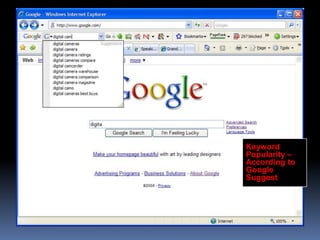
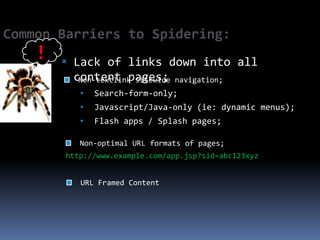
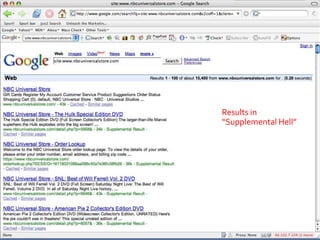
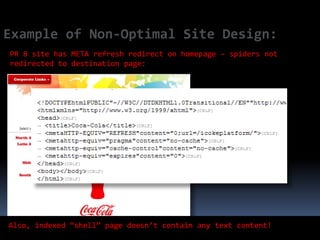
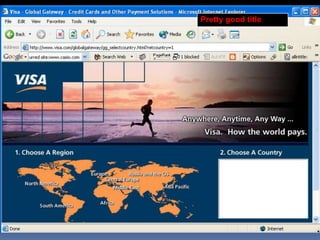
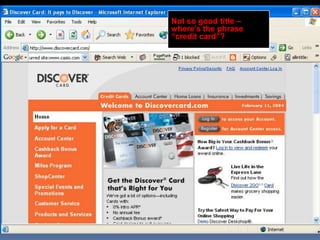
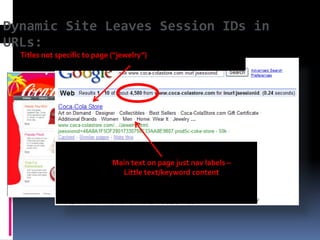
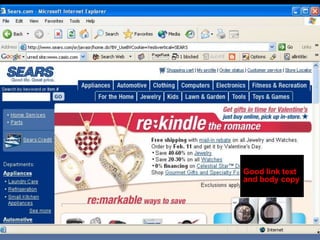
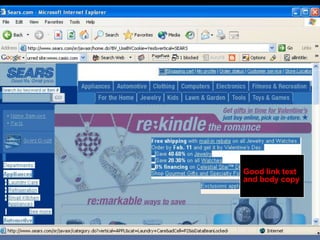
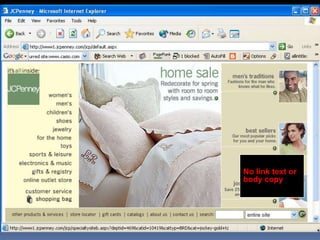
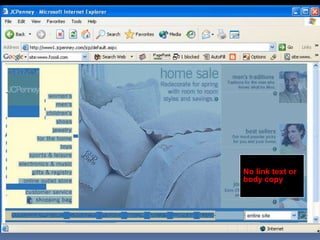
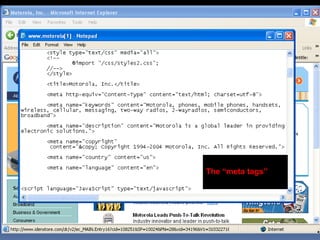
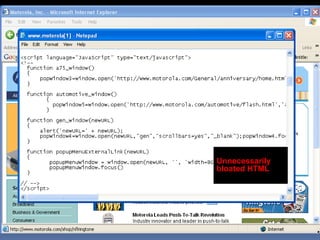
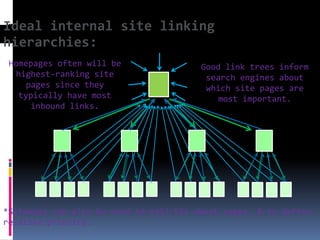
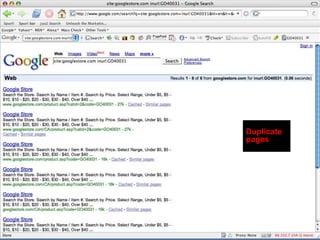
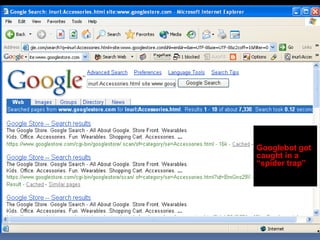
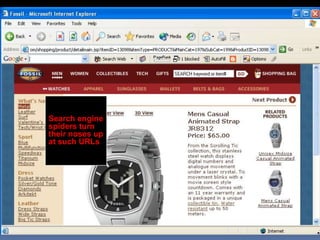
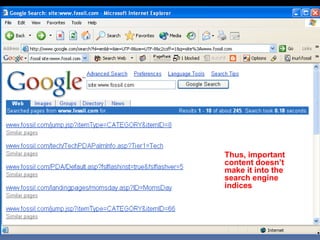
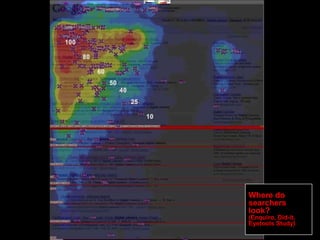
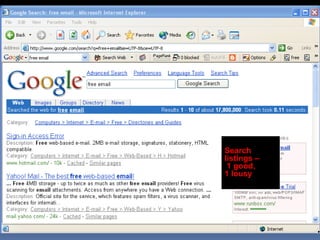
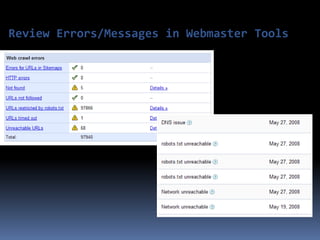
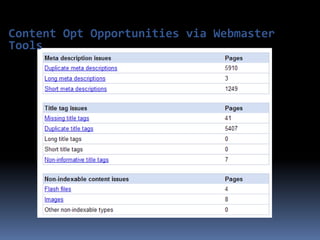
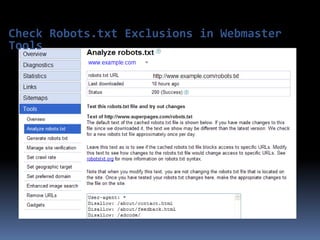
This document provides an overview of search engine optimization (SEO) strategies and best practices. It discusses the importance of SEO given that most internet users begin their sessions through search engines. The document then outlines a seven step process for improving search engine rankings, including getting a site fully indexed, optimizing page content and structure, building links, leveraging PageRank, encouraging clicks, tracking metrics, and avoiding bad practices. Specific techniques are provided for each step, such as optimizing title tags and meta descriptions. The presentation warns against spammy techniques and emphasizes creating useful, relevant content.