This document outlines a webinar on avoiding pitfalls in big data analytics, featuring speakers from Datameer and MapR, who emphasize the importance of Apache Hadoop for handling large data sets. Key topics include types of analytics, common pitfalls in implementations, and tips for optimizing the use of Hadoop. It highlights the need for proper planning, governance, and user-friendly platforms to maximize the effectiveness of big data initiatives.







![Types of Analytics for Hadoop [2]"
▪ Predictive – what will happen
– Cross-sell/up-sell (recommendations), fraud/
anomaly detection
▪ Prescriptive – what should I do
– Preventative maintenance,
smart meter analysis
Better with
more data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-howtoavoidpitfallsinbigdataanalyticsss-140512131212-phpapp01/85/How-to-Avoid-Pitfalls-in-Big-Data-Analytics-Webinar-8-320.jpg)



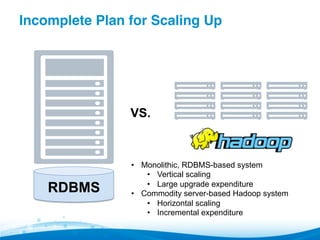
![Incomplete Plan for Scaling Up [2]"
▪ Relatively easy to extrapolate existing data
load to future
▪ But, must also factor in:
– Larger time windows of data
• Expanding beyond 3-month time window broke system
• Now can store 18-months, results in more accurate
analytics
– More data sources
• Typically, new sources that could not be added before
– More use cases and users
• More divisions want to join system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-howtoavoidpitfallsinbigdataanalyticsss-140512131212-phpapp01/85/How-to-Avoid-Pitfalls-in-Big-Data-Analytics-Webinar-14-320.jpg)
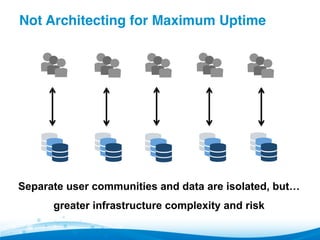
![Not Architecting for Maximum Uptime [2]"
▪ Separate physical clusters for separate
“tenants” appears easy
▪ Multiple clusters lead to:
– Infrastructural complexity, more risk of error
– More points of failure
▪ Instead, leverage software components to
help logically separate users/data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-howtoavoidpitfallsinbigdataanalyticsss-140512131212-phpapp01/85/How-to-Avoid-Pitfalls-in-Big-Data-Analytics-Webinar-16-320.jpg)
![Not Architecting for Maximum Uptime [3]"
▪ Global Storage Solutions Company
▪ Deployed file-serving HBase application
▪ Introduce ad-hoc analytics in same cluster
▪ No resource fencing, poor workload mgmt.
▪ Result: Significant downtime](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-howtoavoidpitfallsinbigdataanalyticsss-140512131212-phpapp01/85/How-to-Avoid-Pitfalls-in-Big-Data-Analytics-Webinar-17-320.jpg)