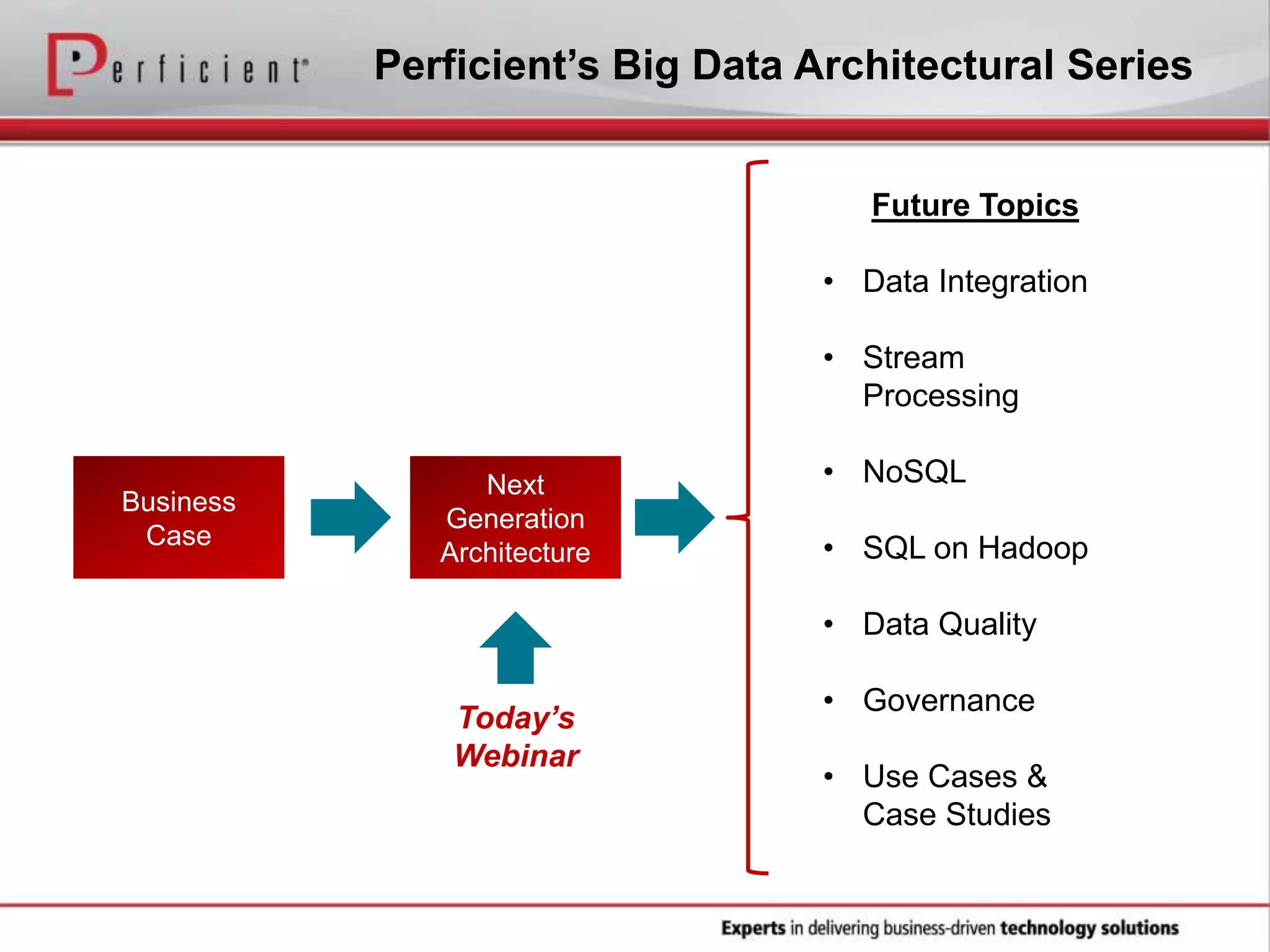
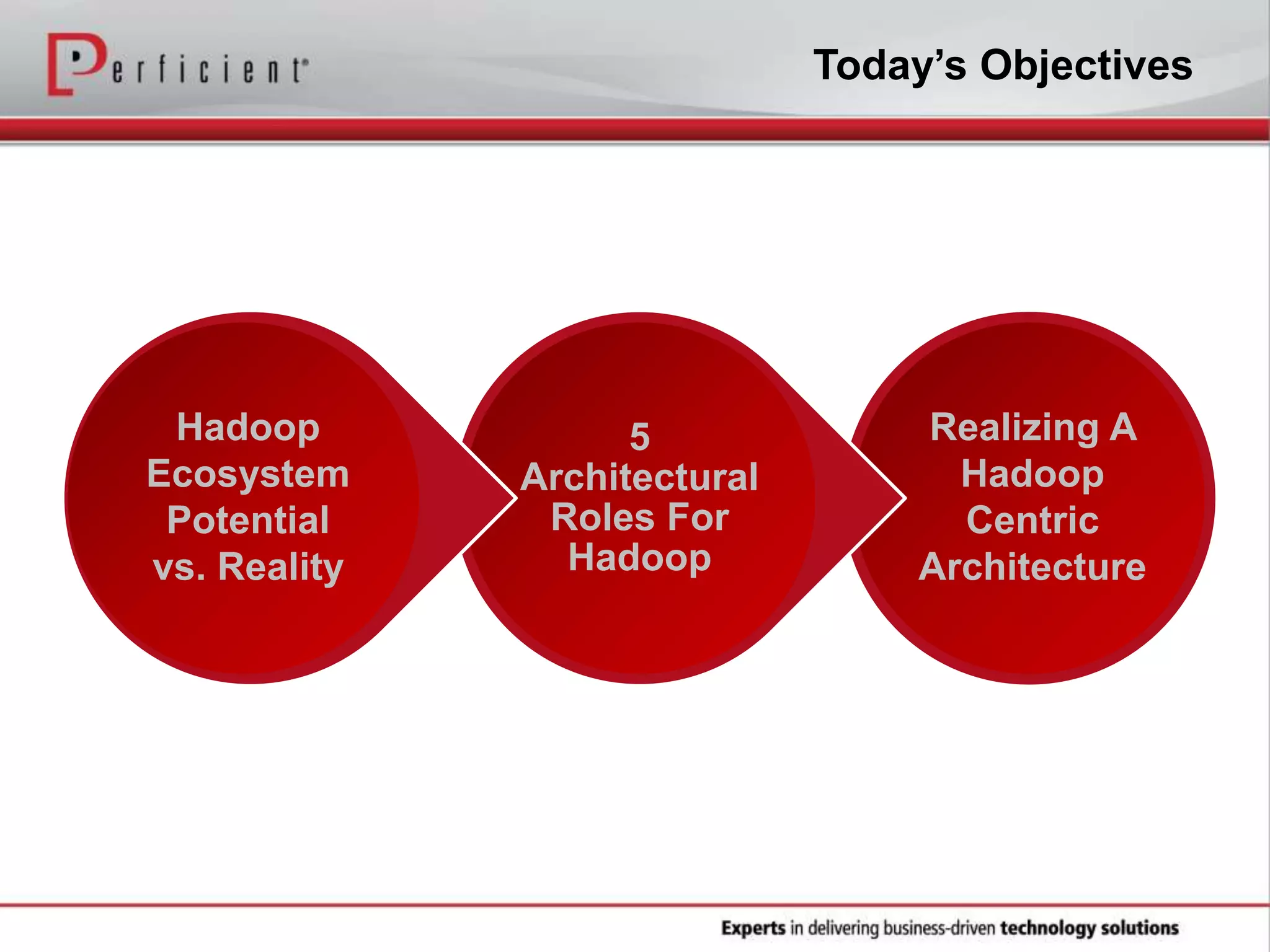
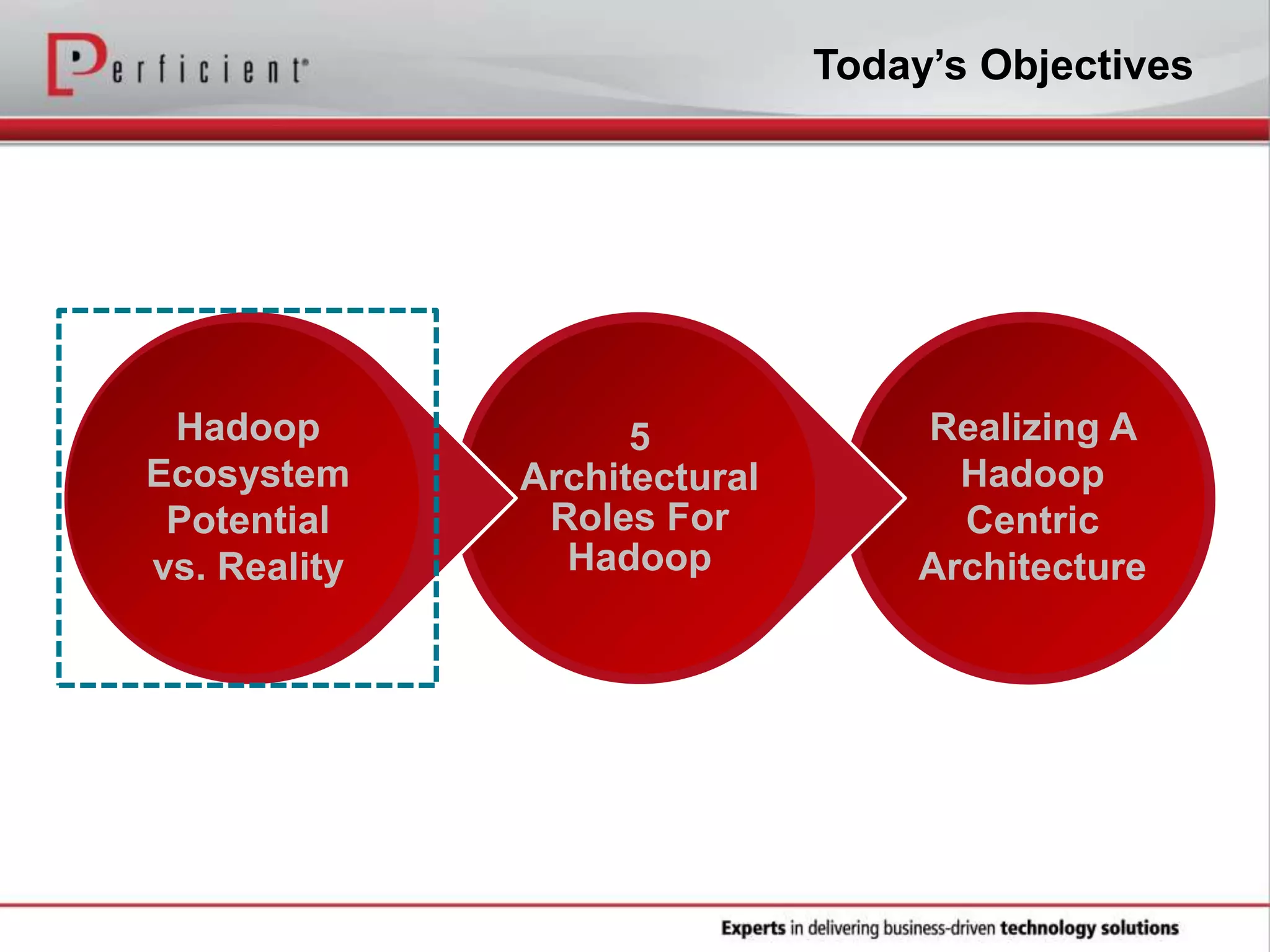
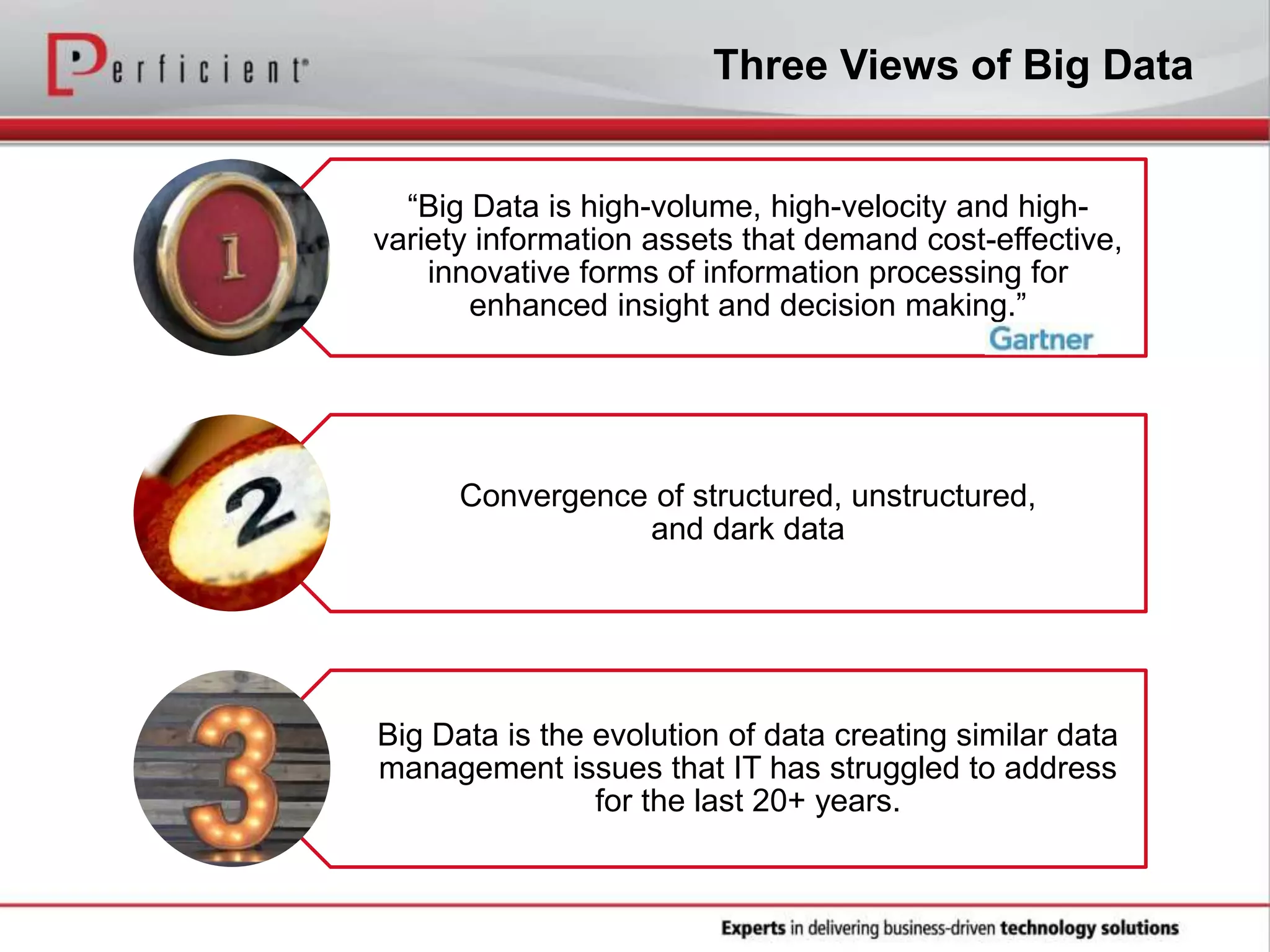
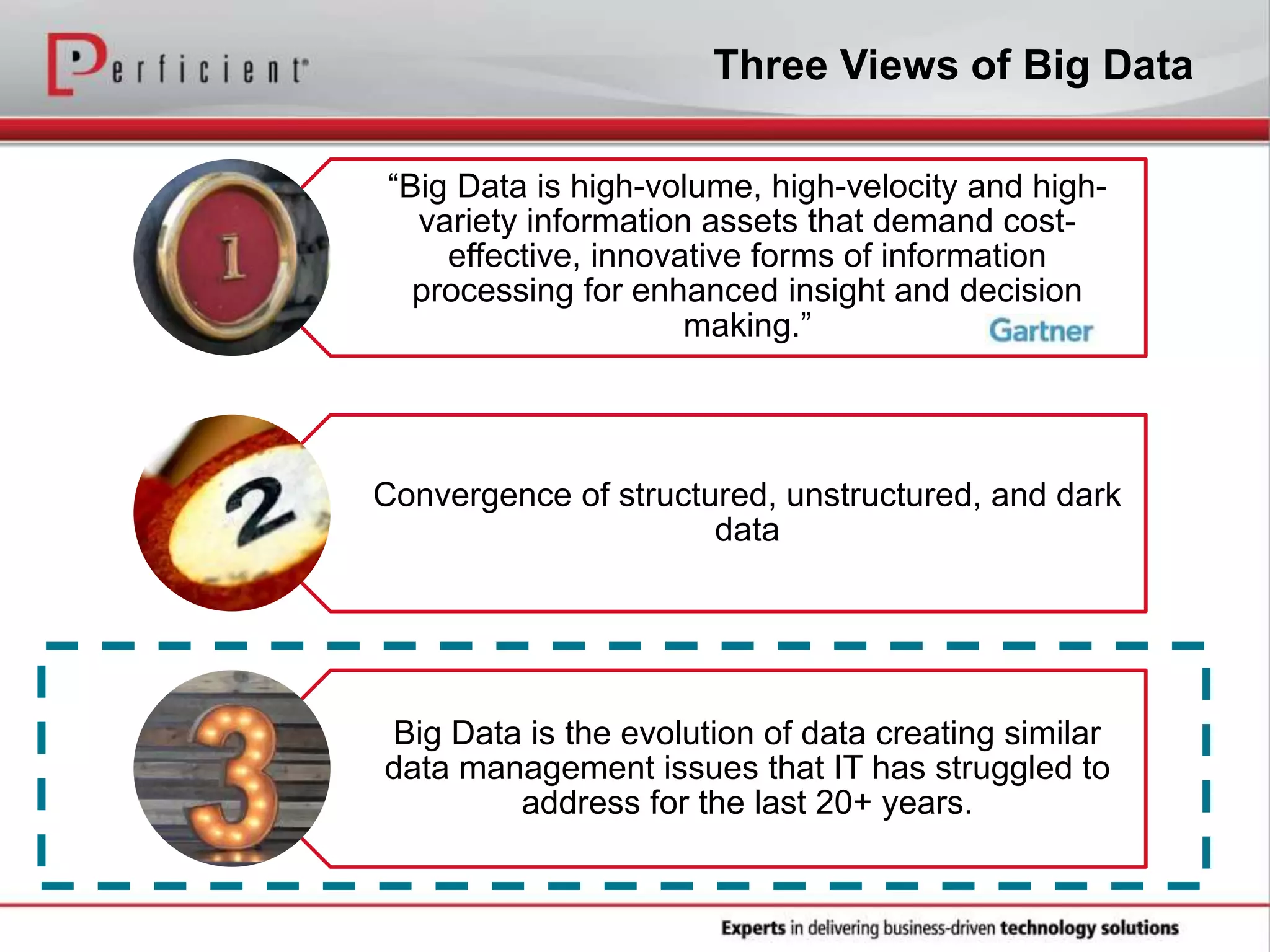
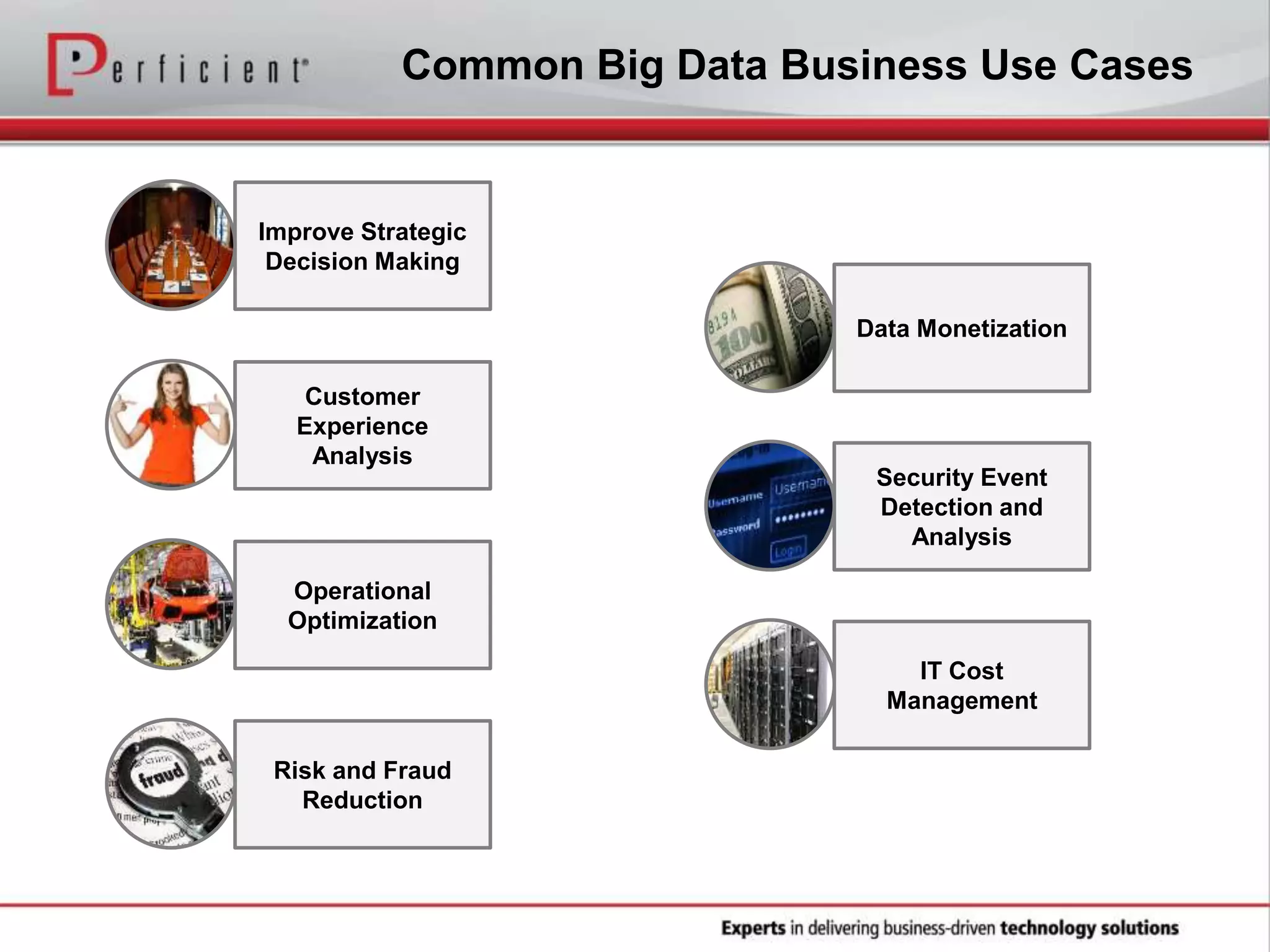
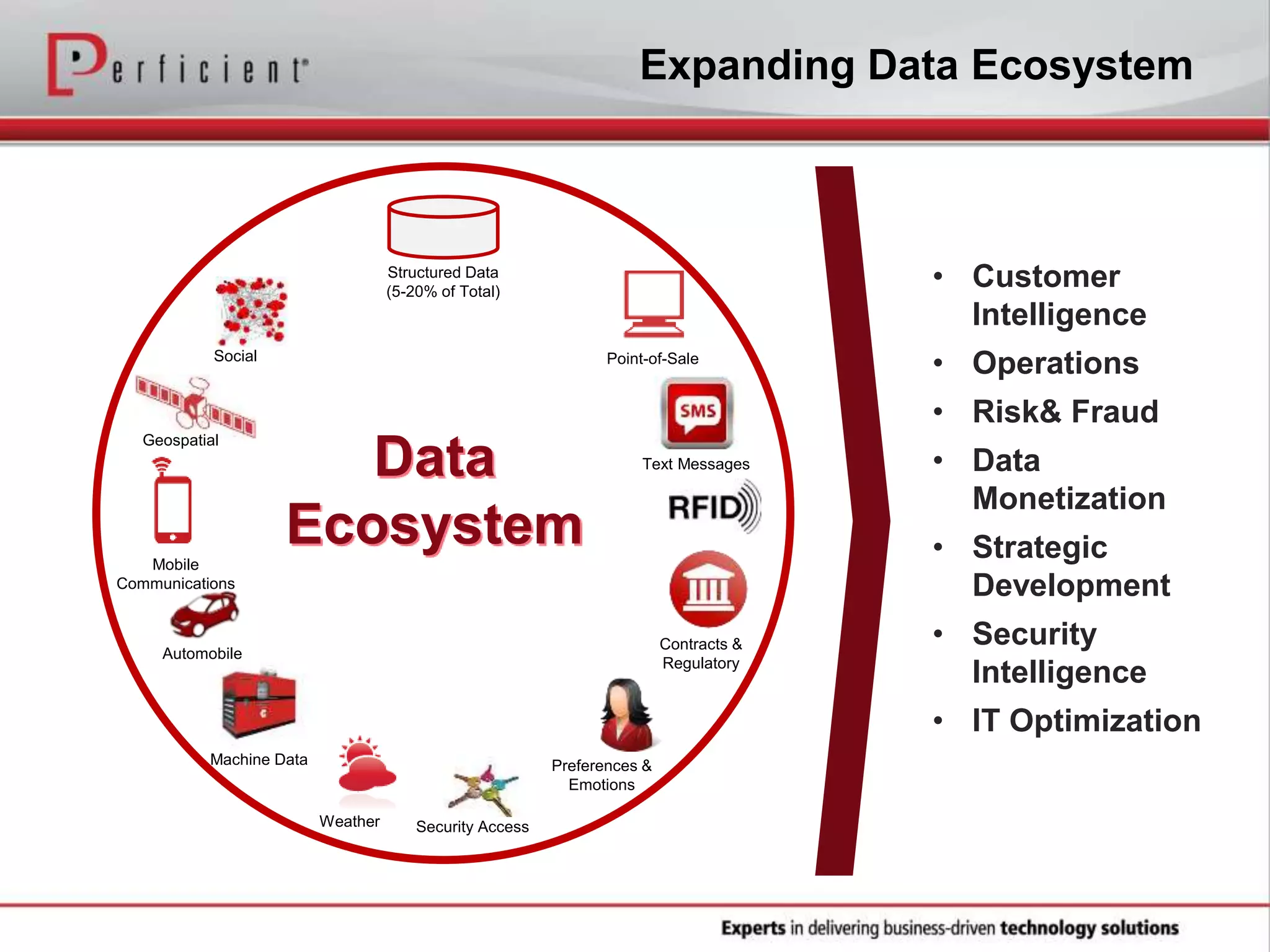
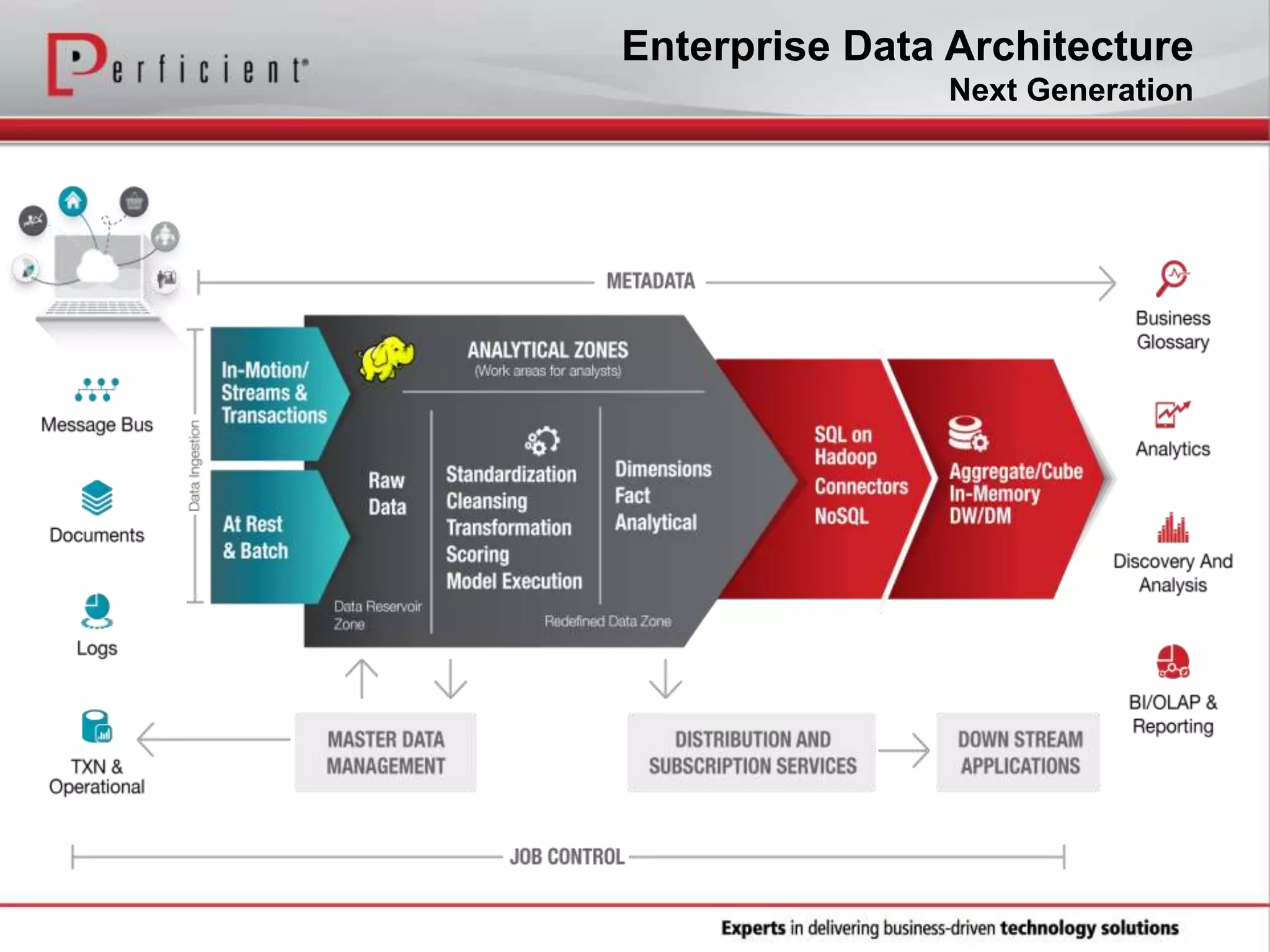
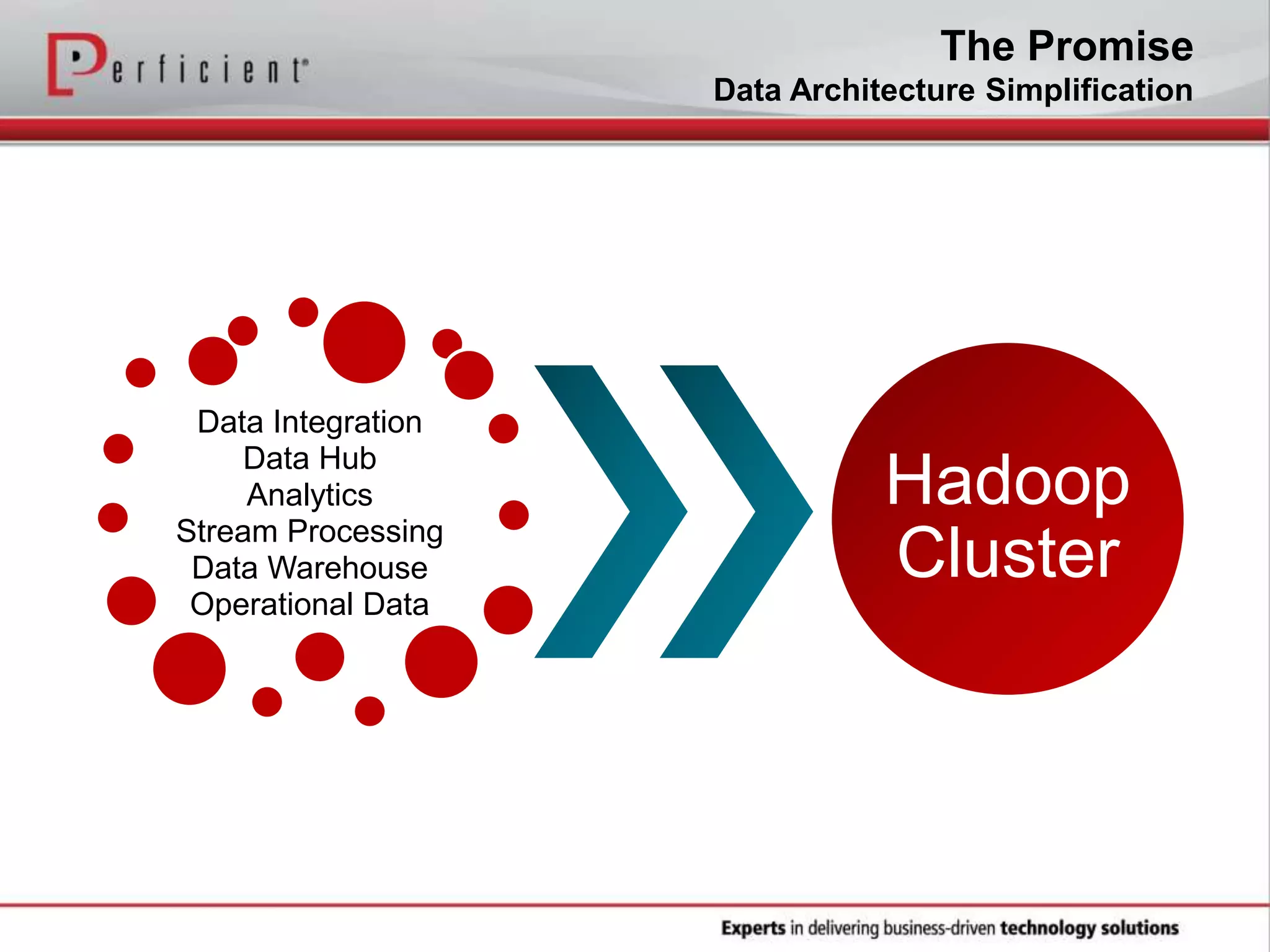
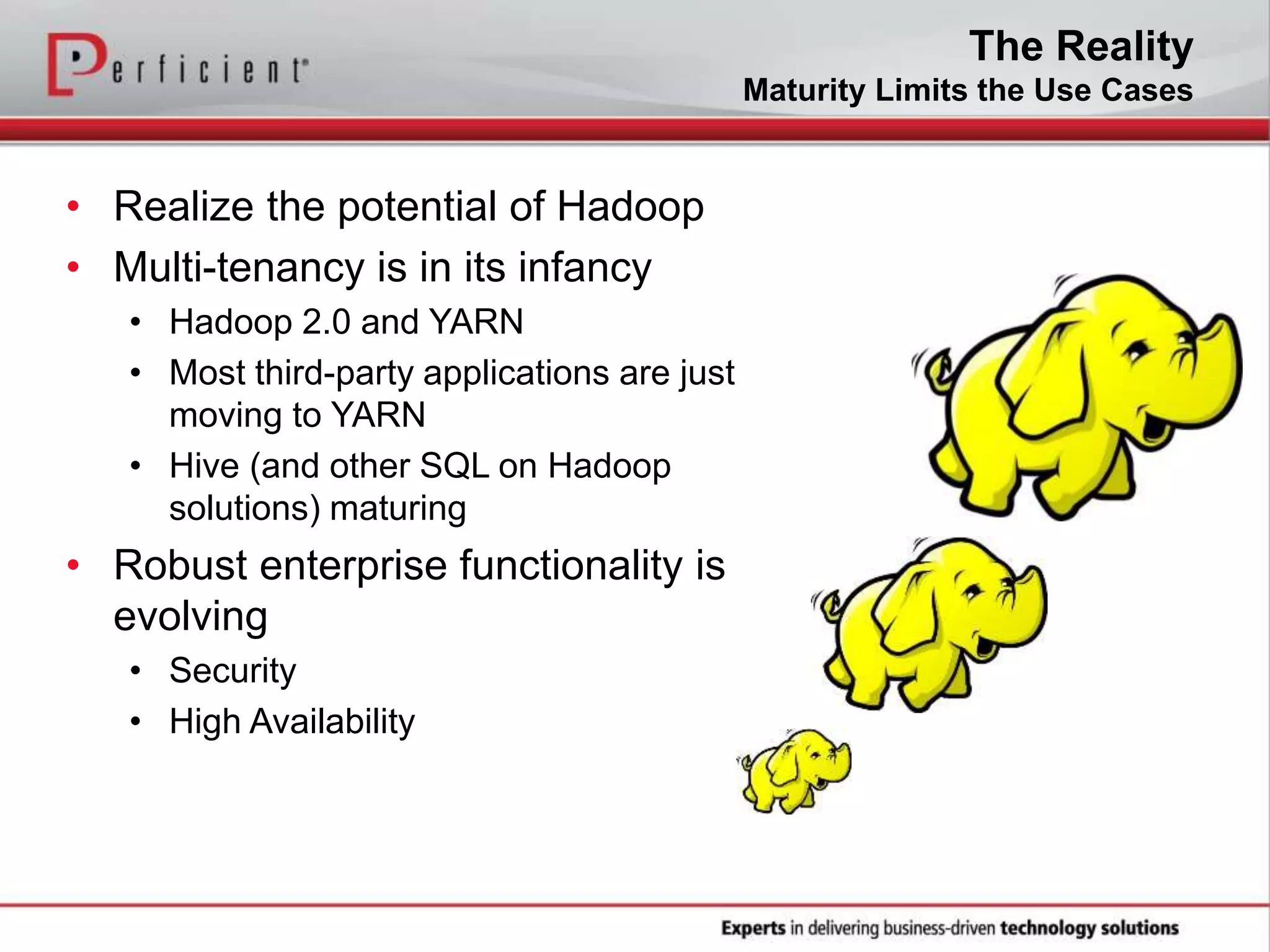
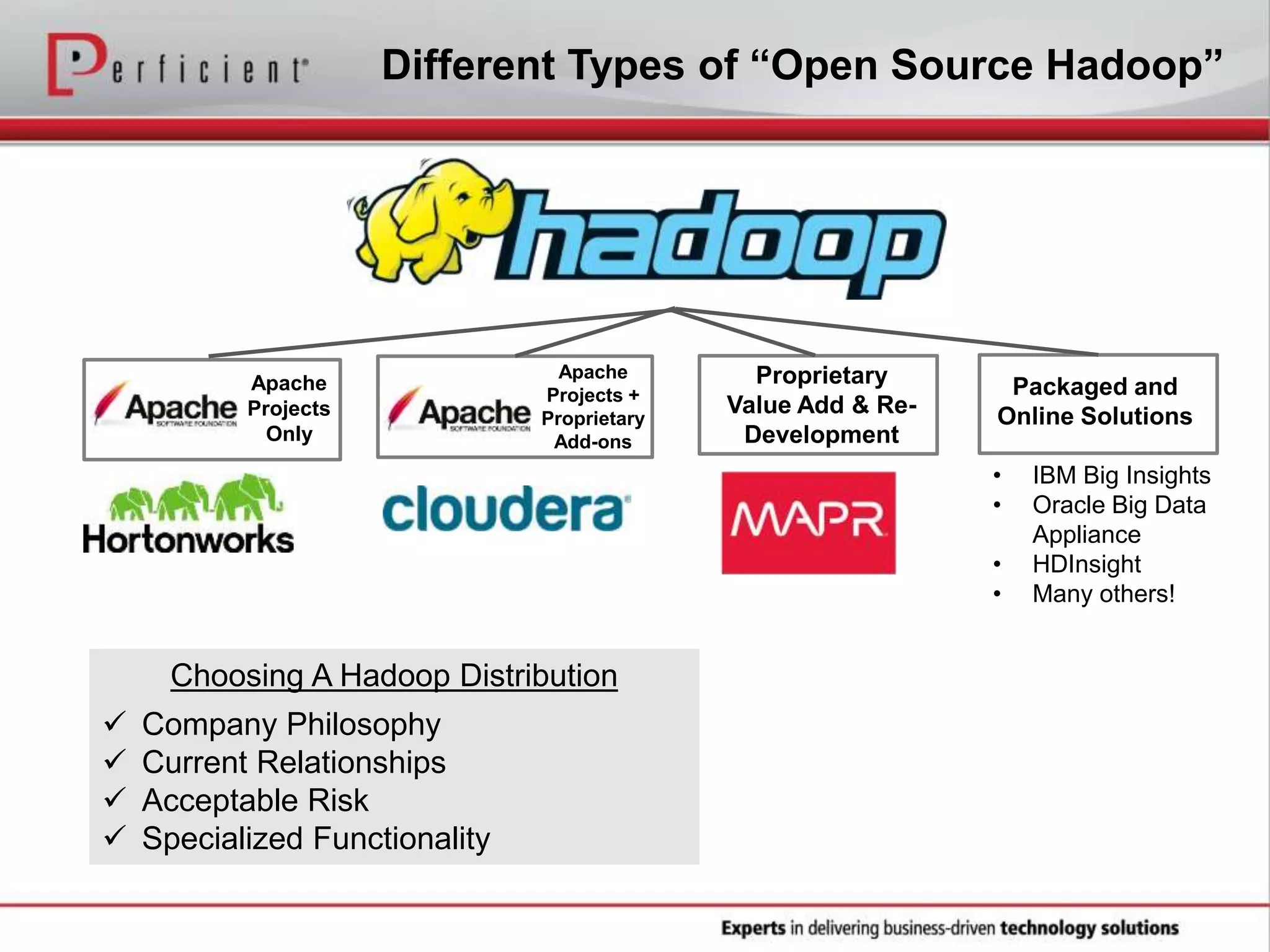
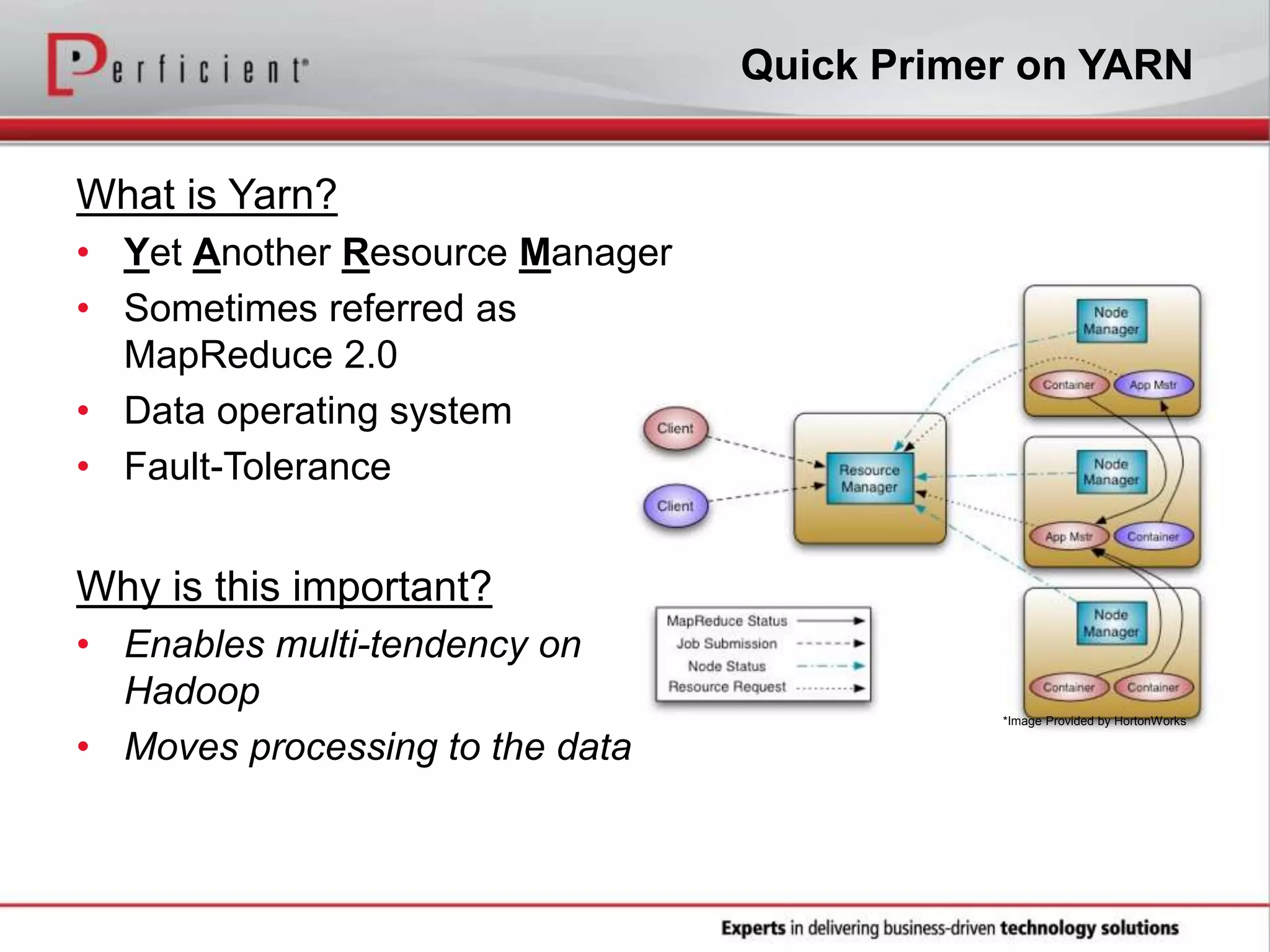
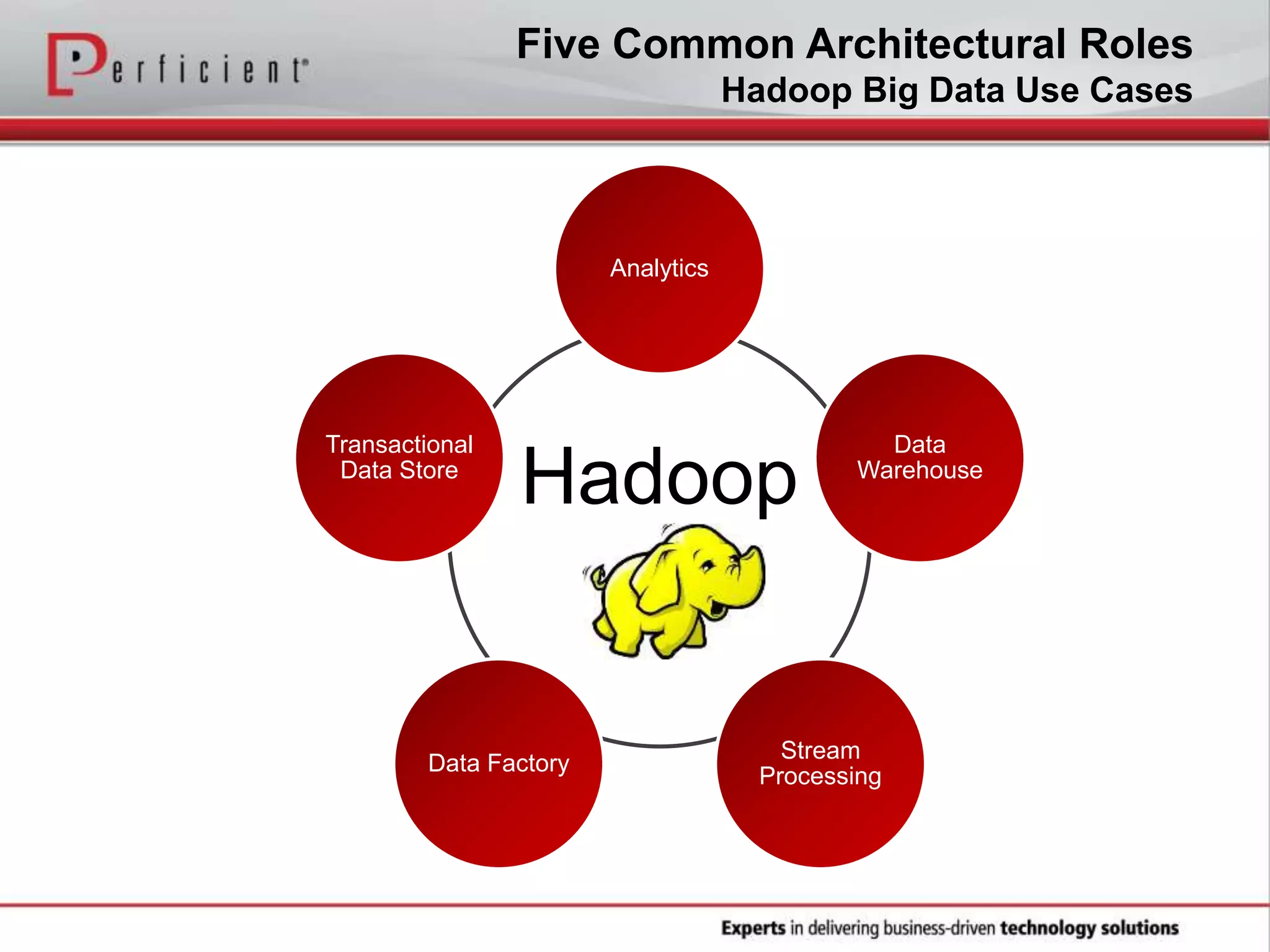
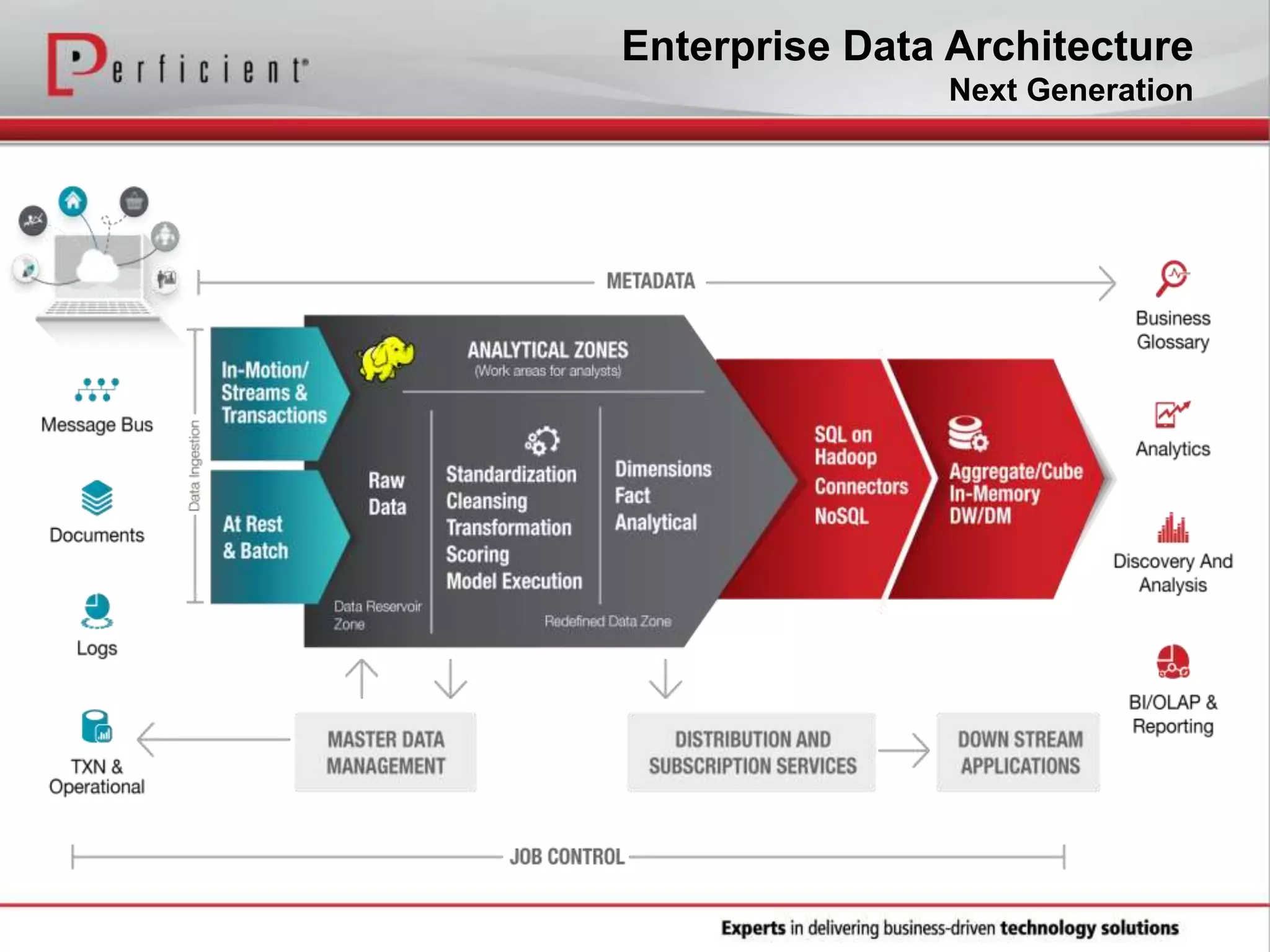
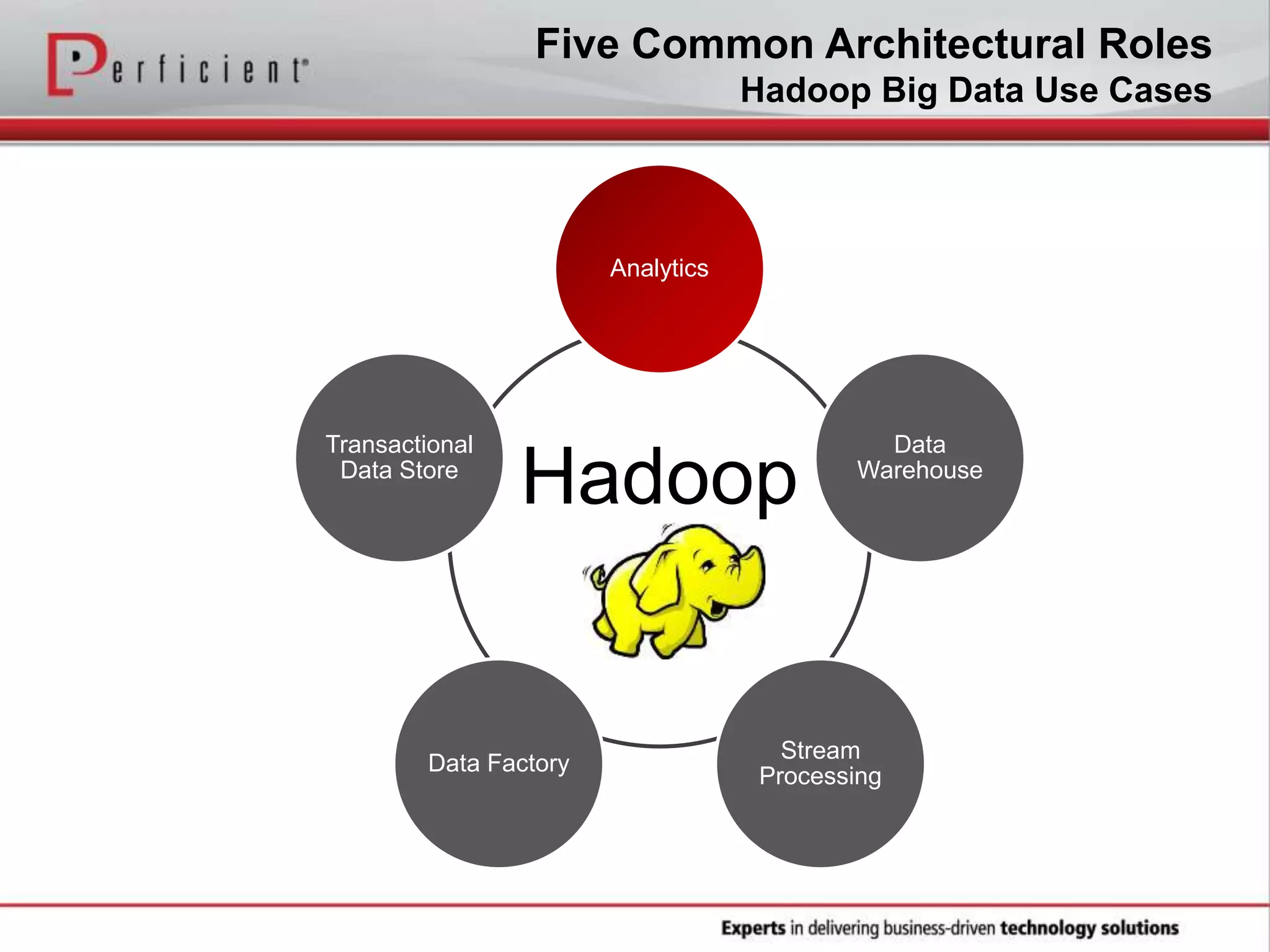
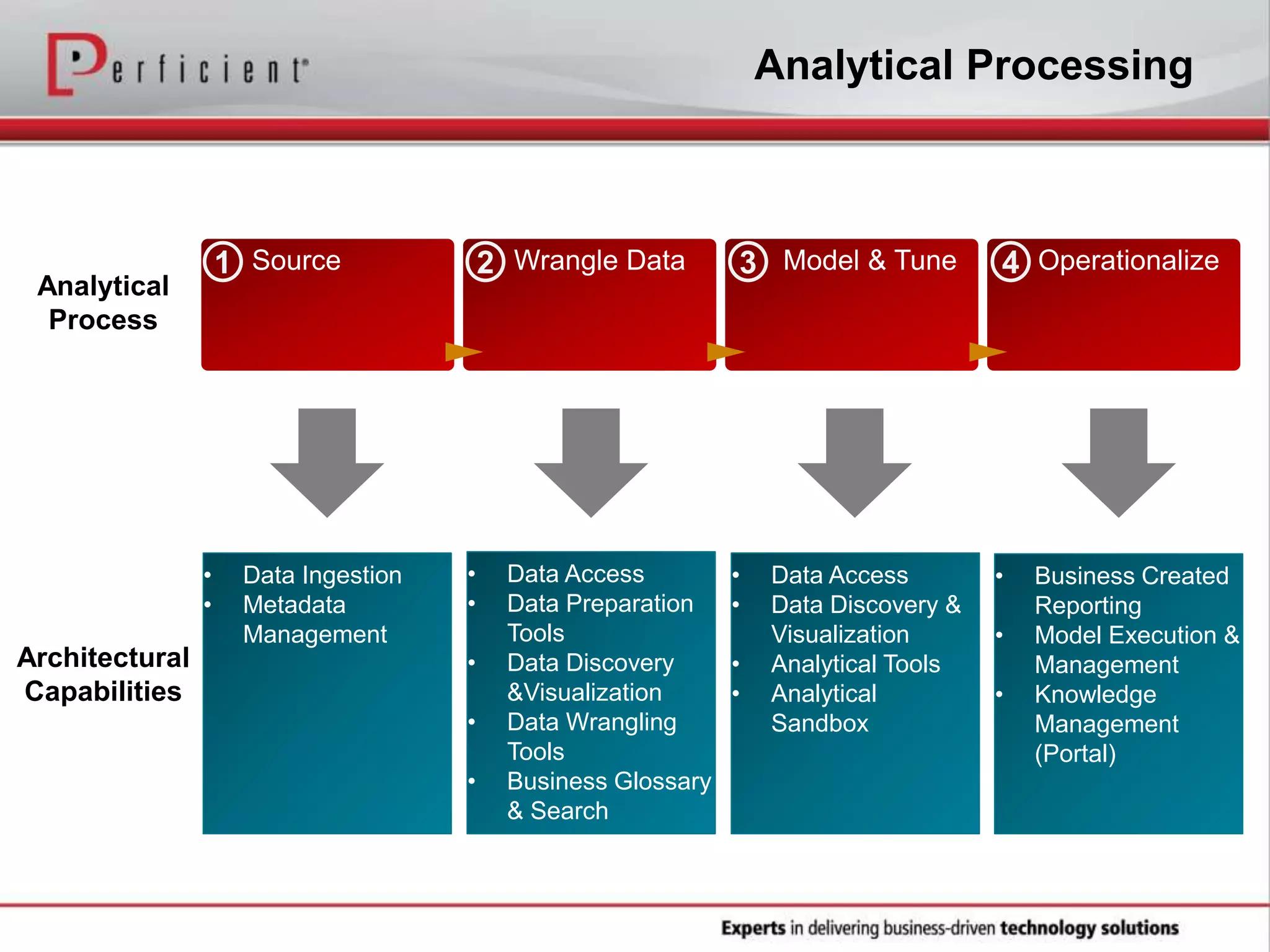
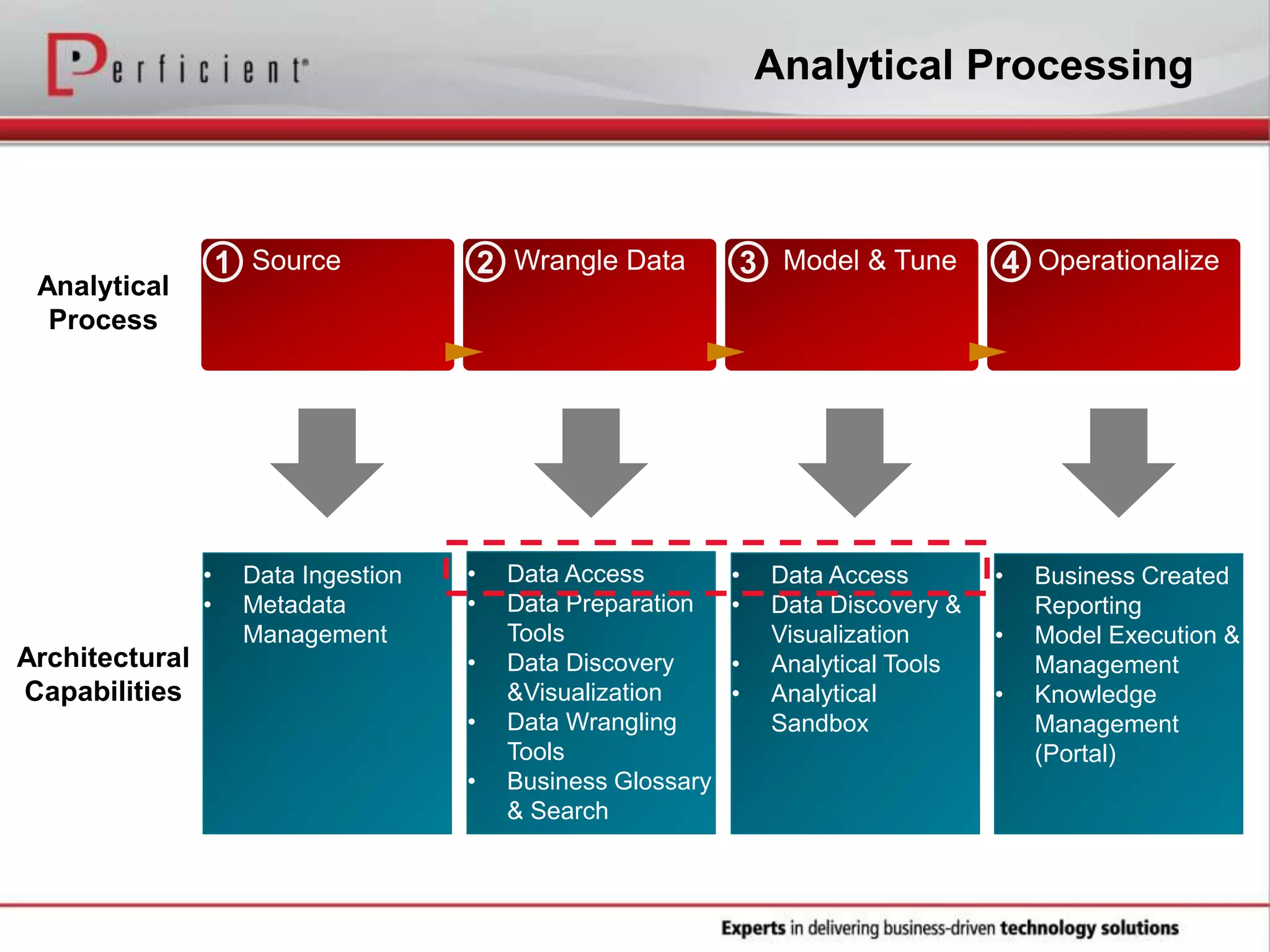
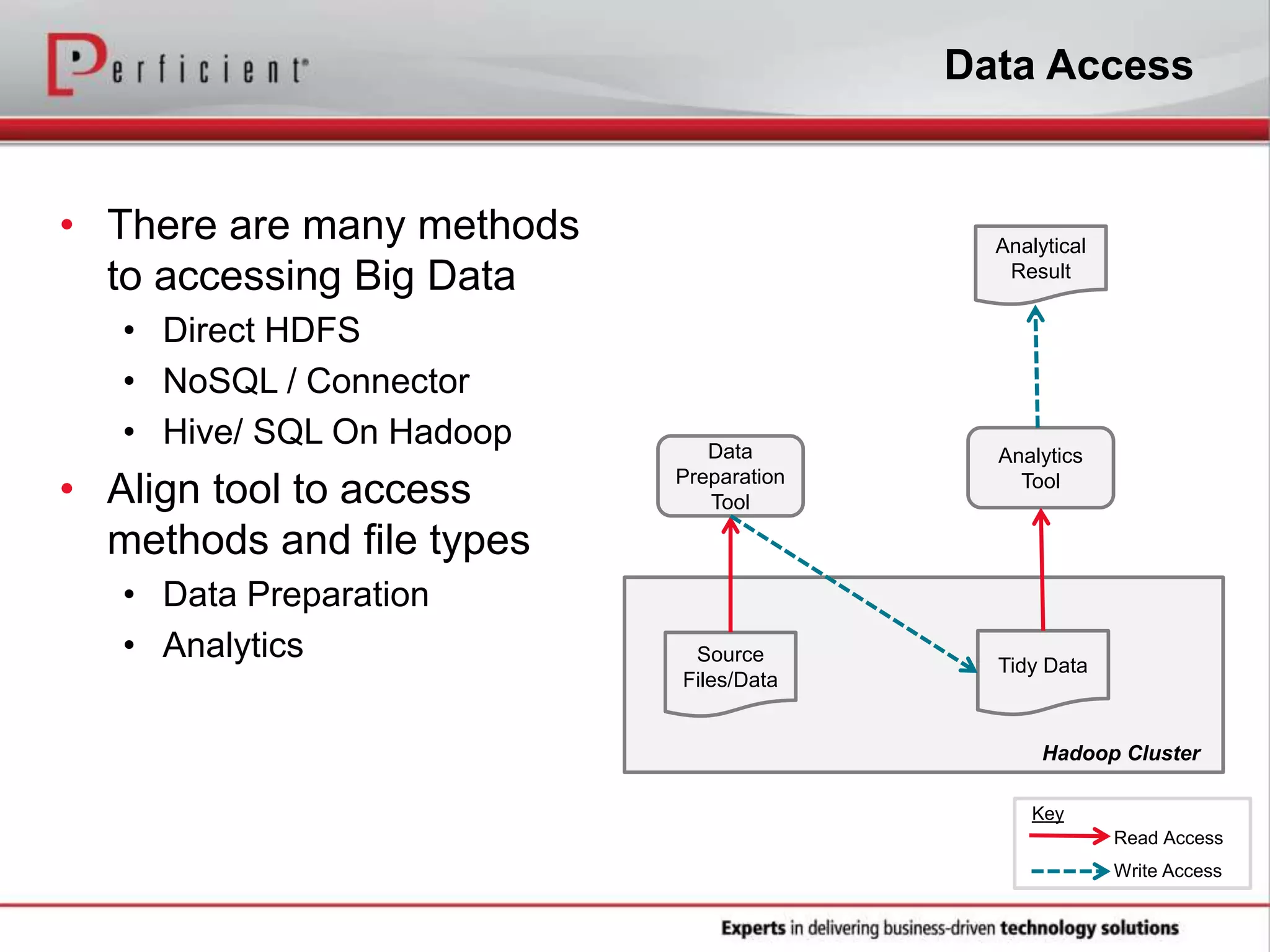
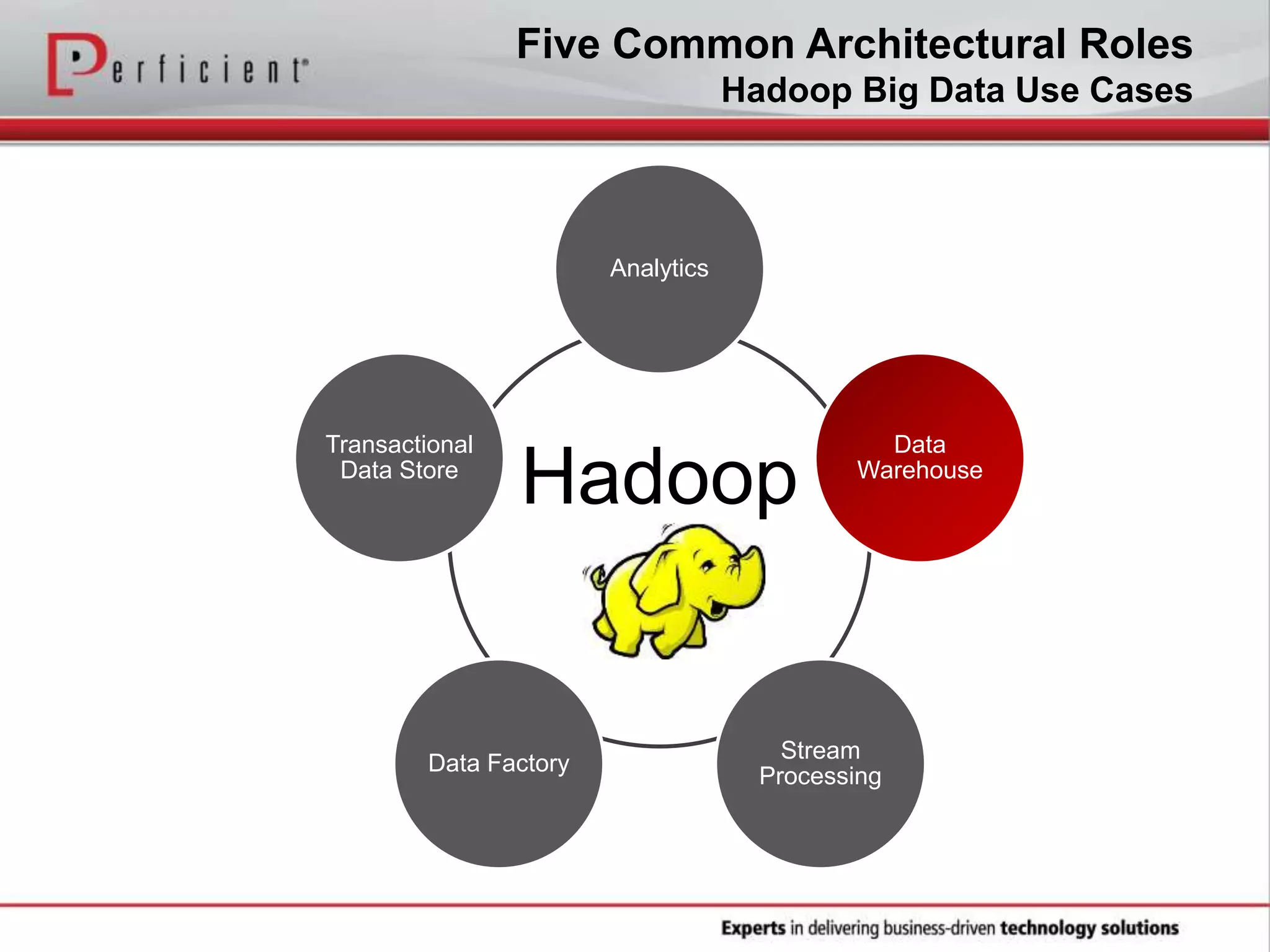
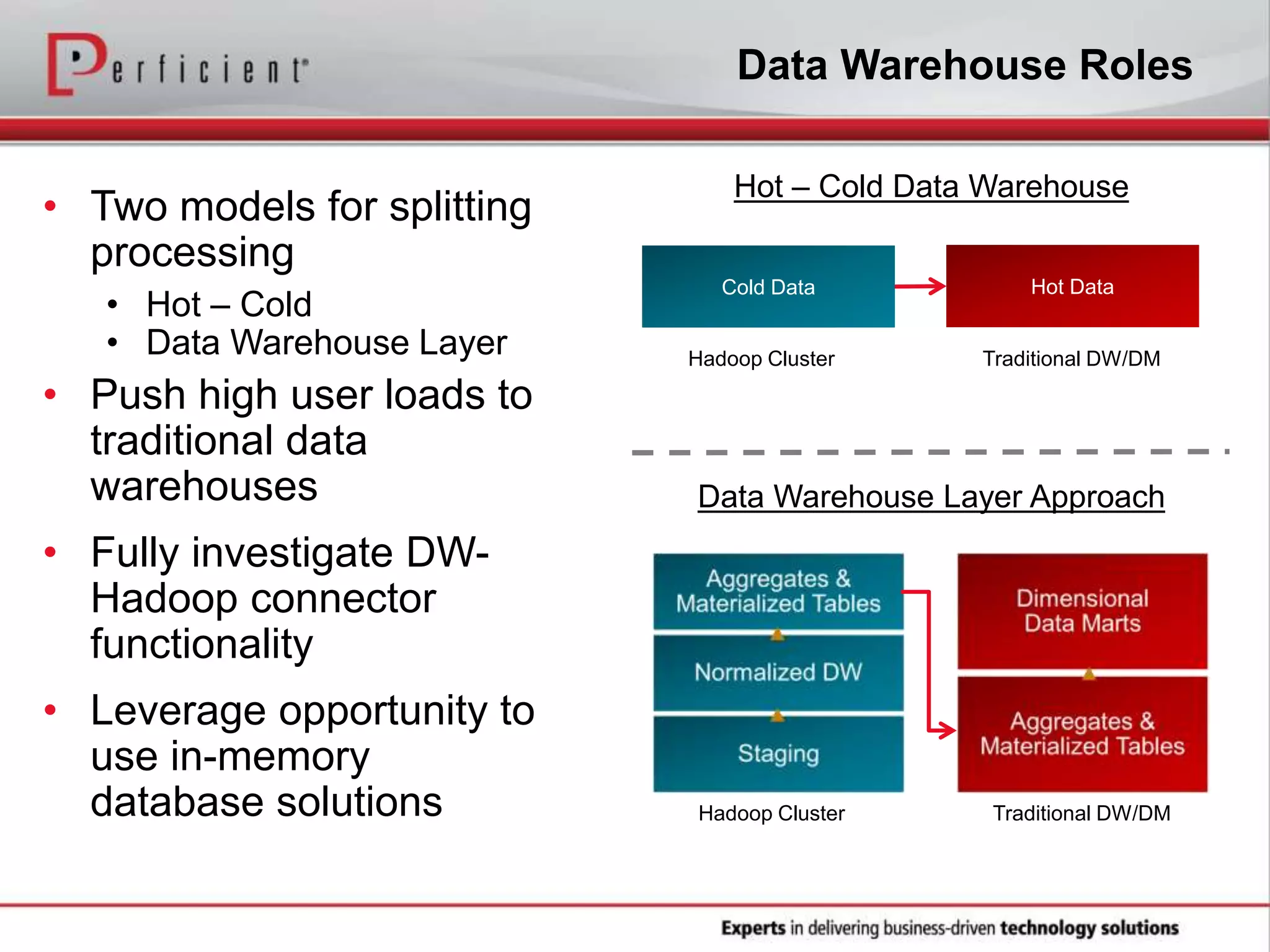
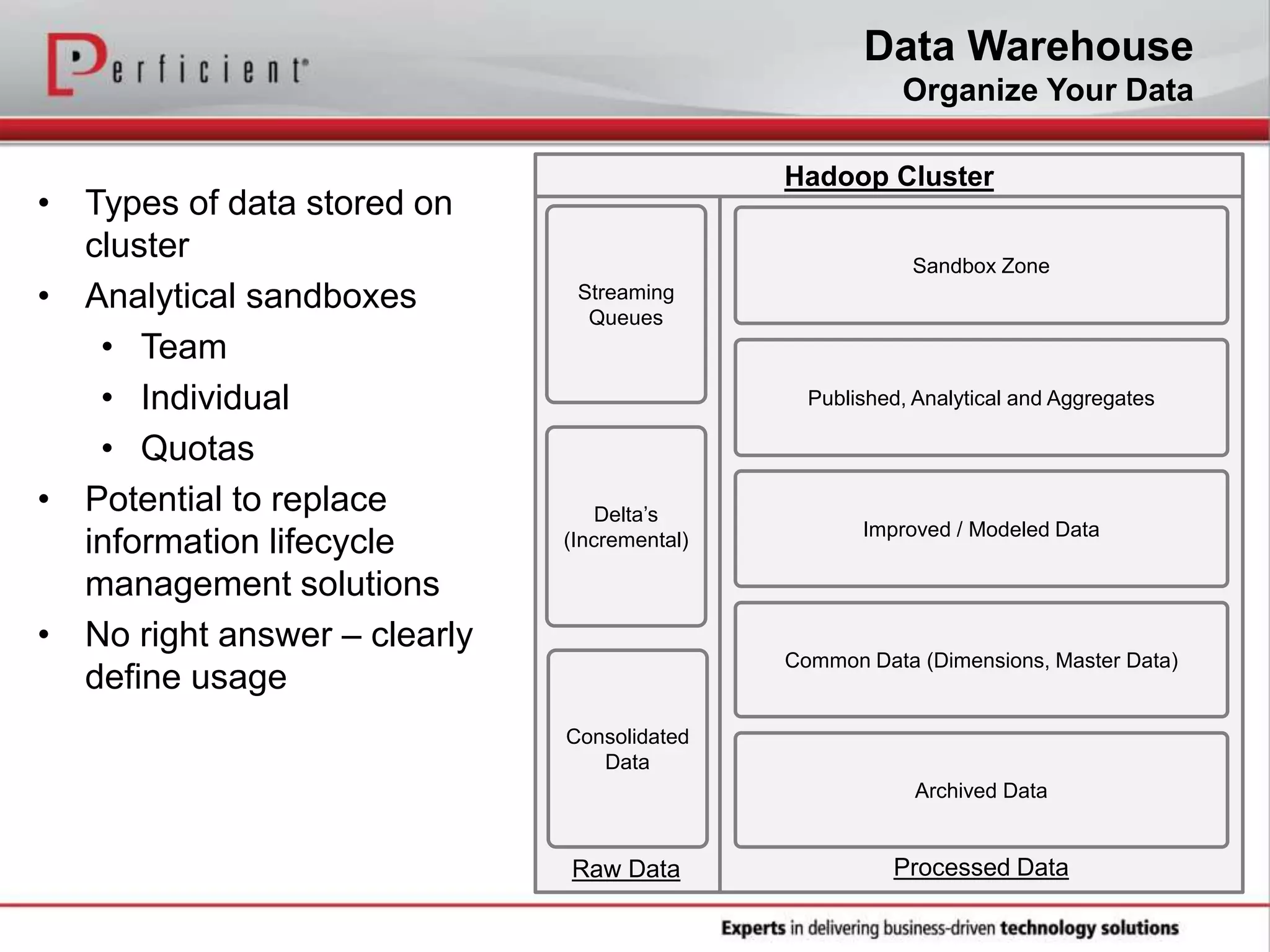
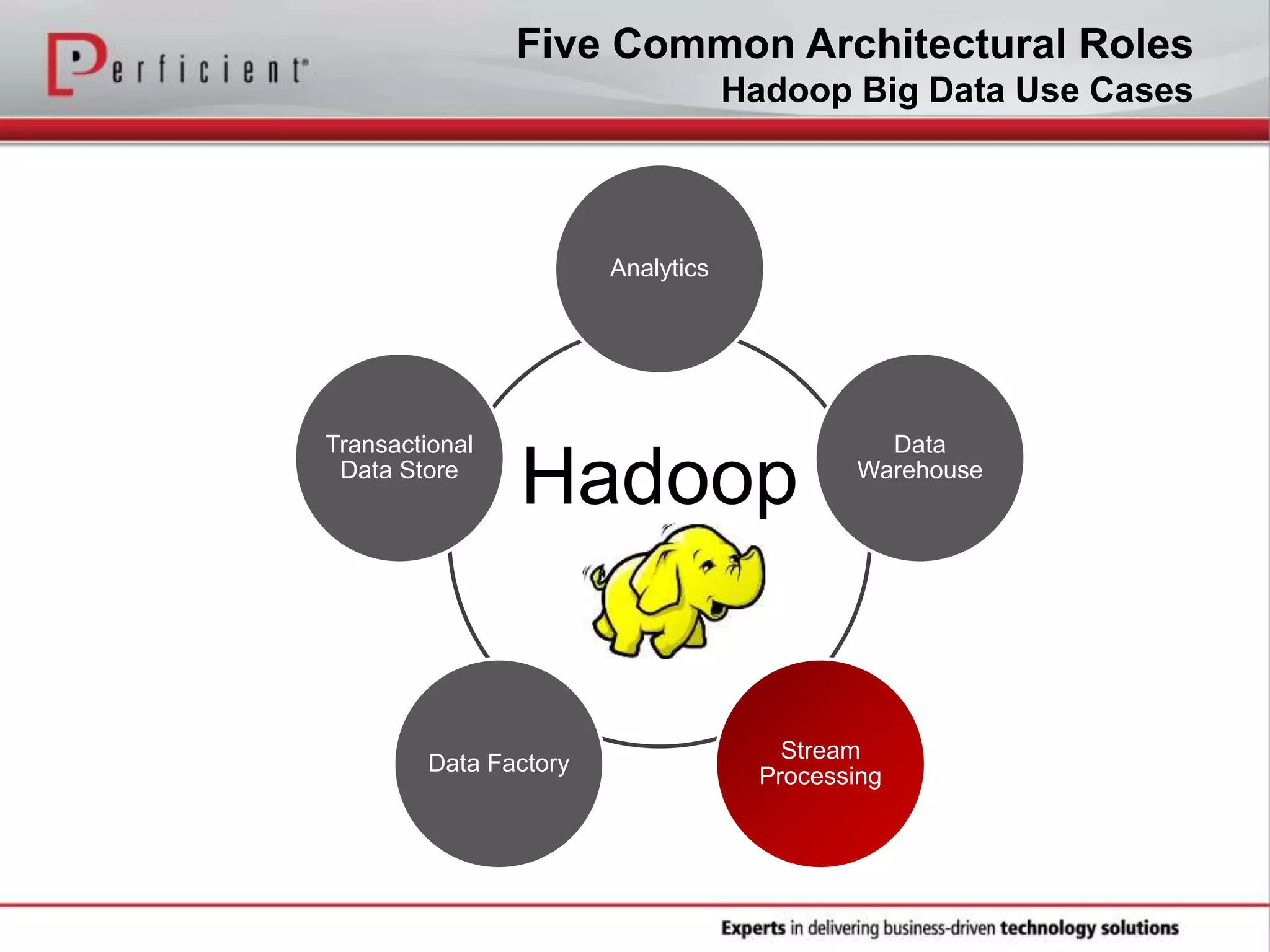
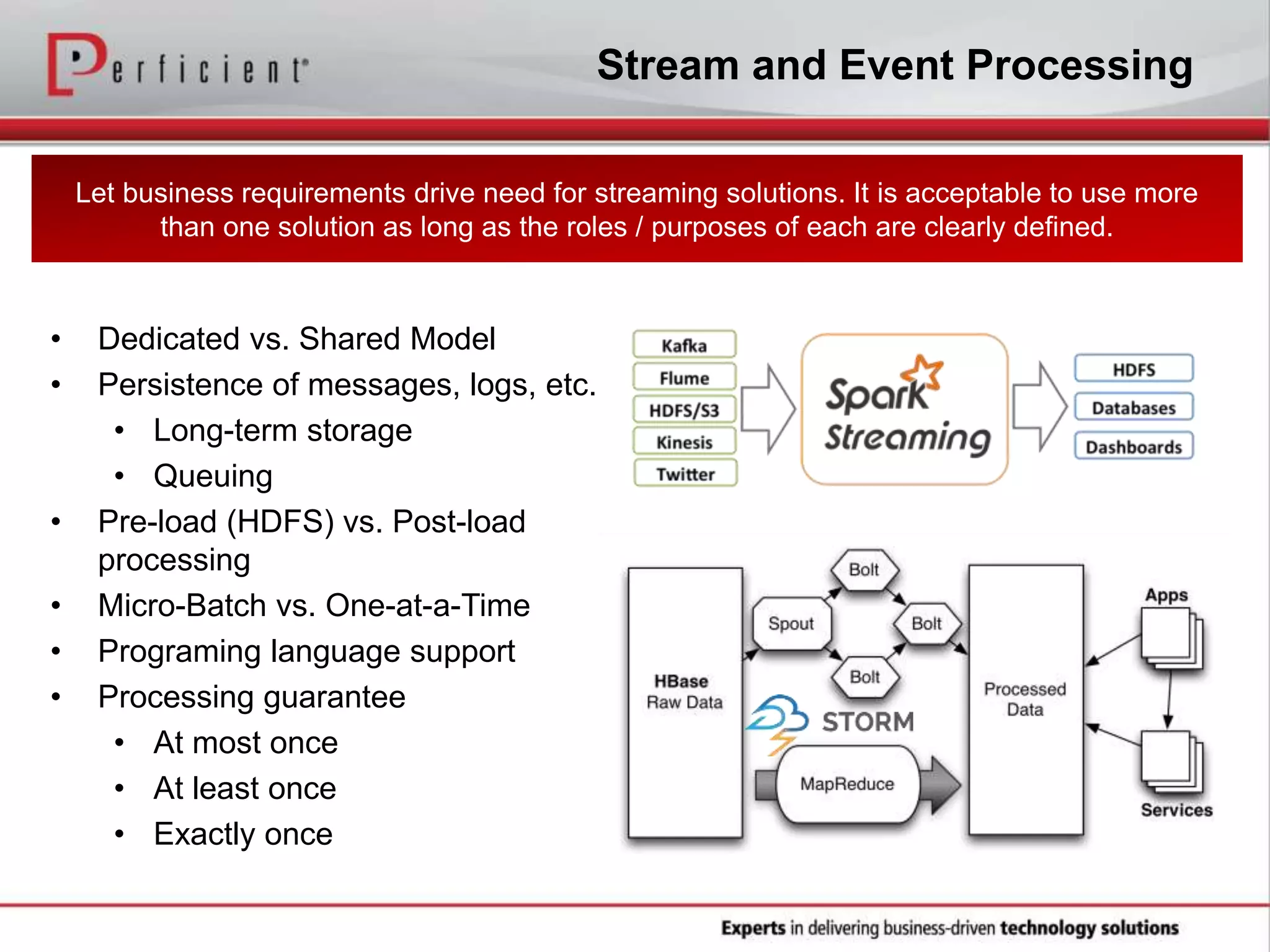
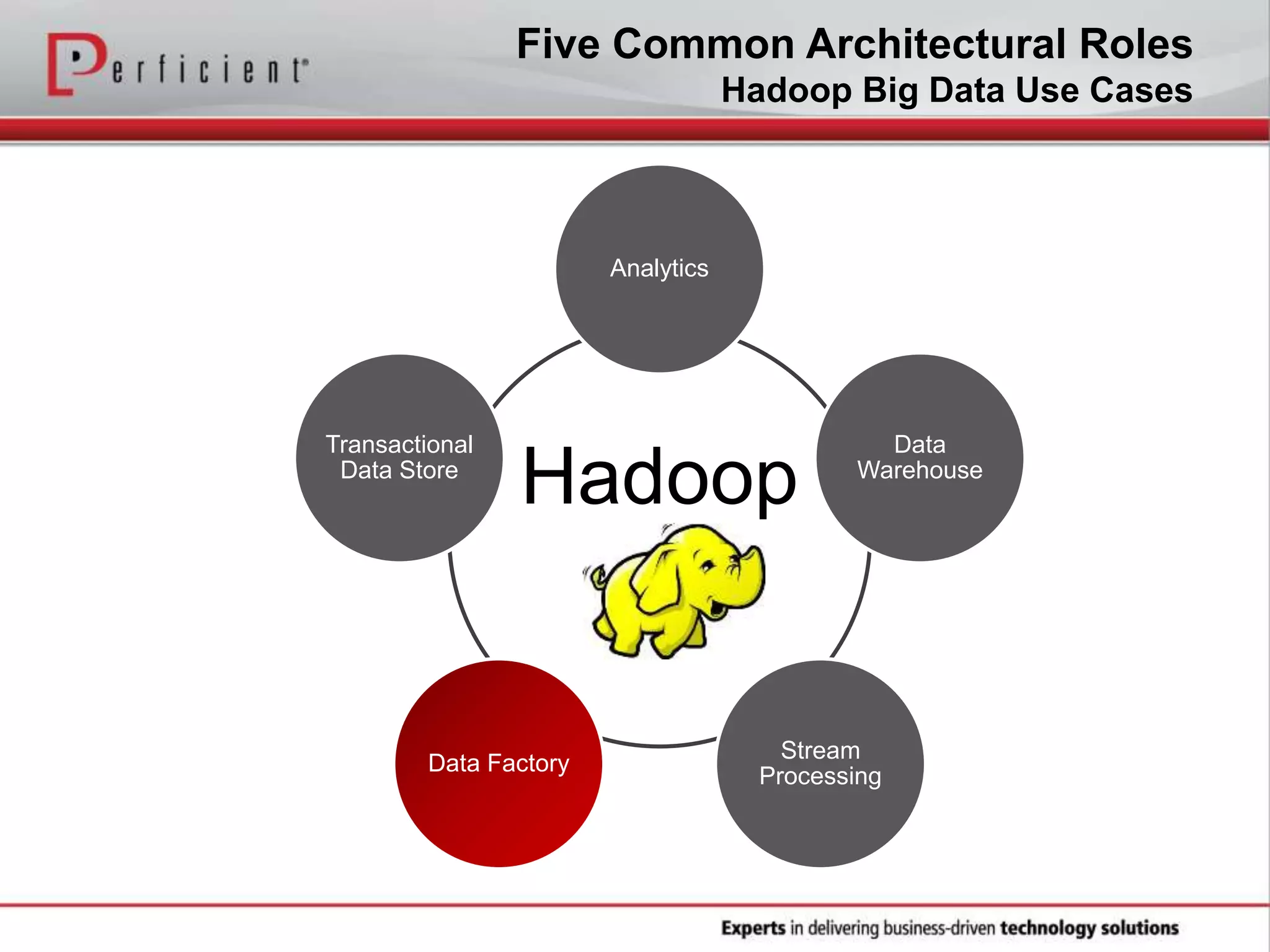
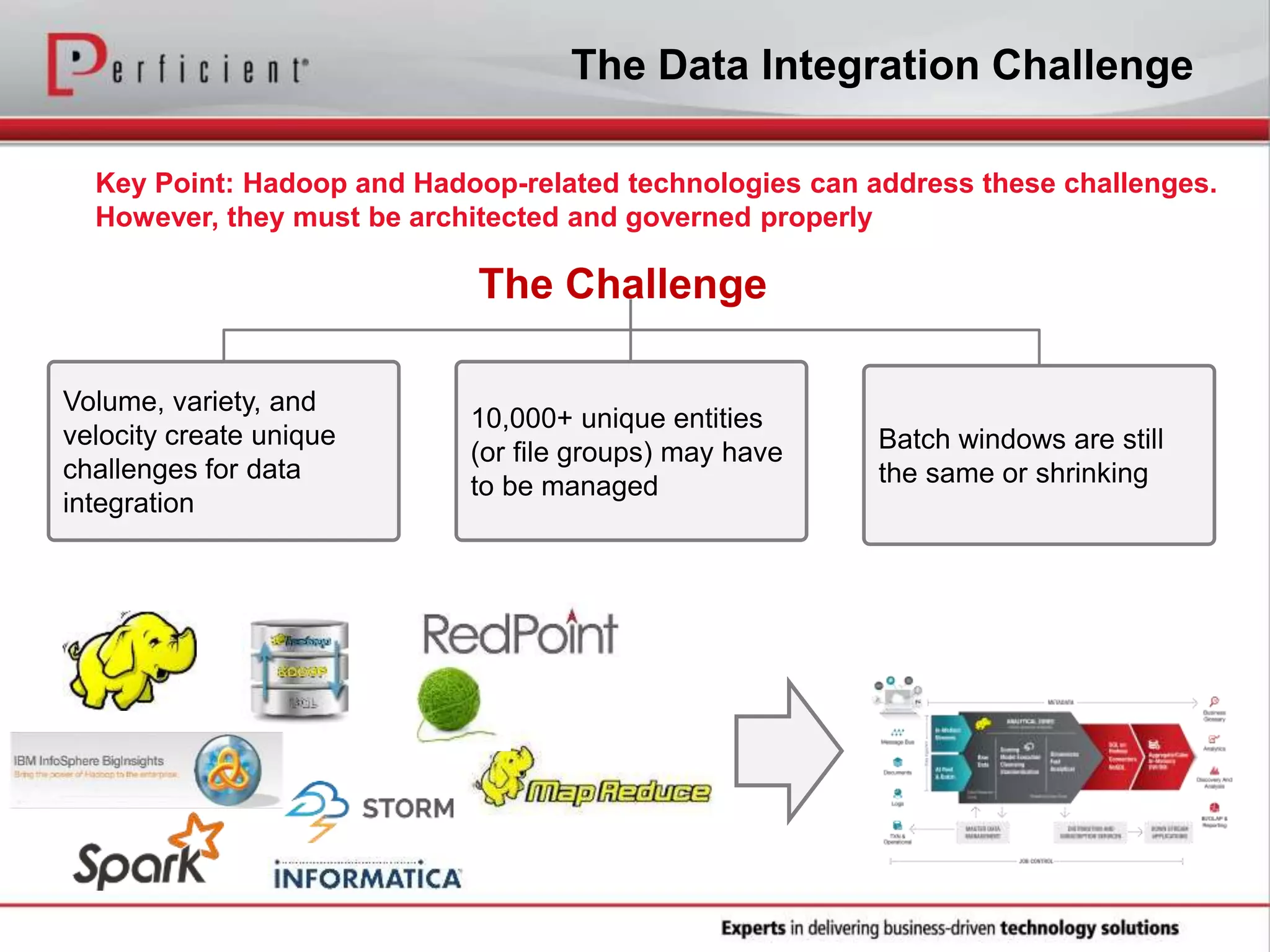
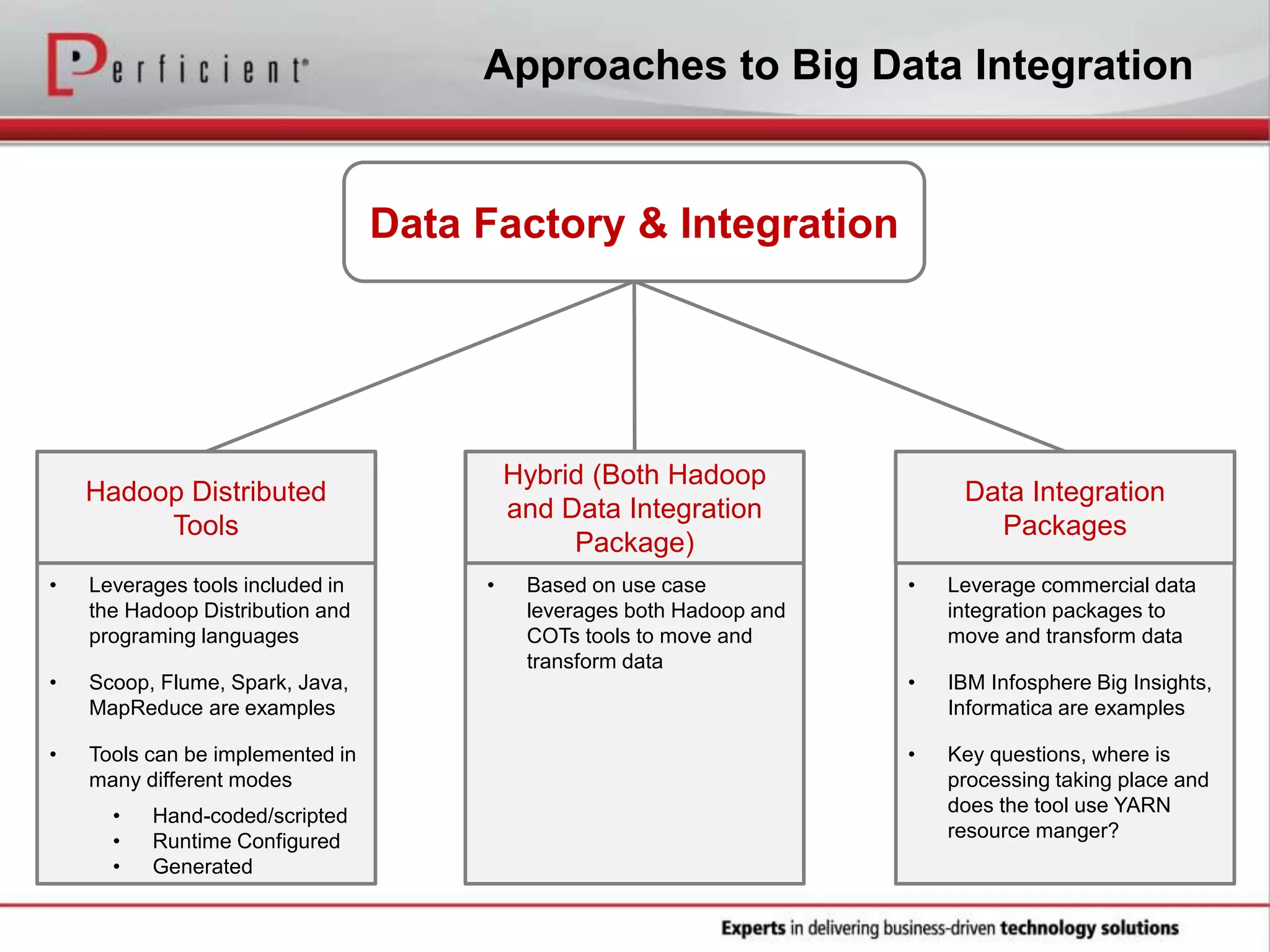
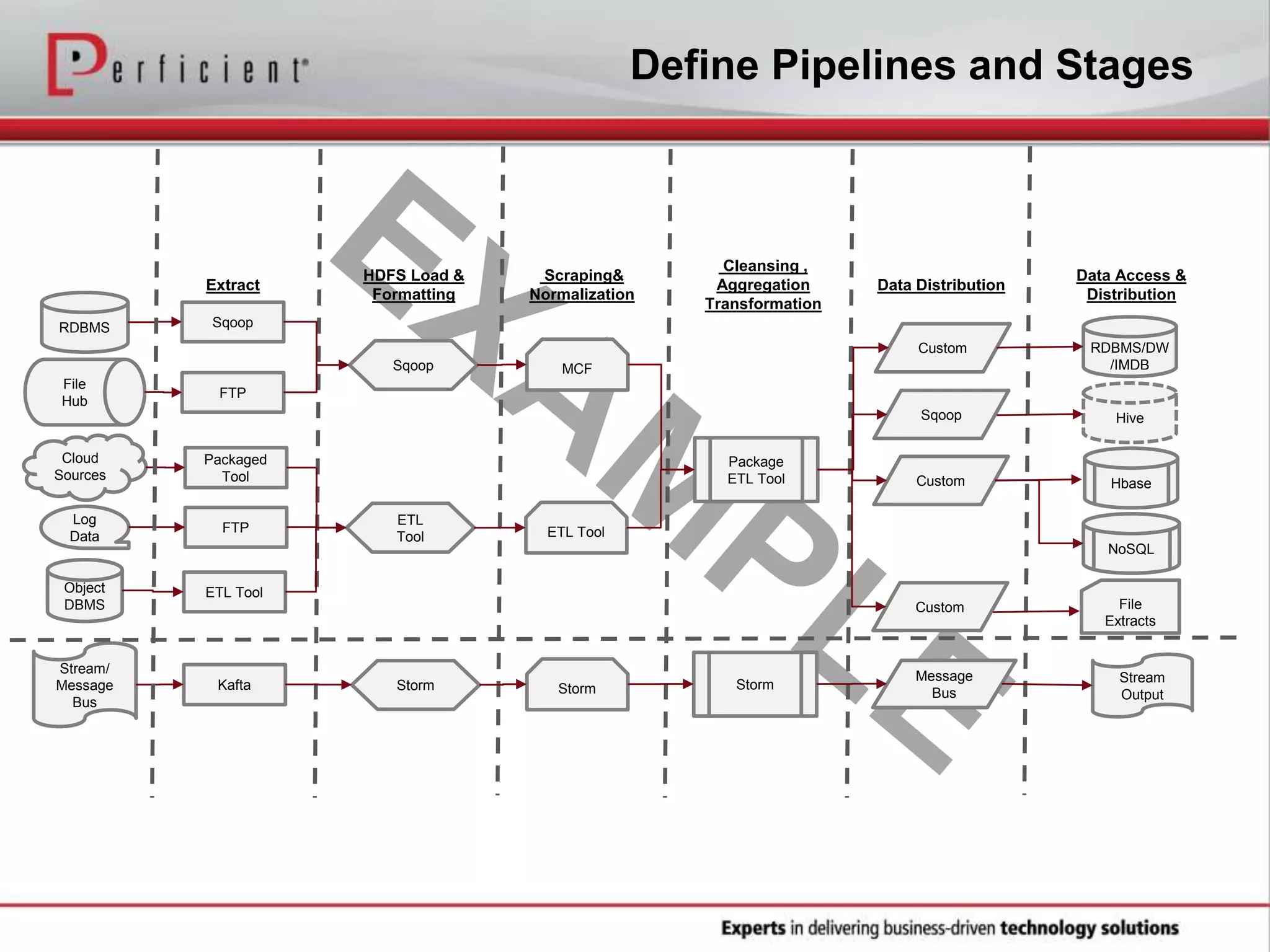
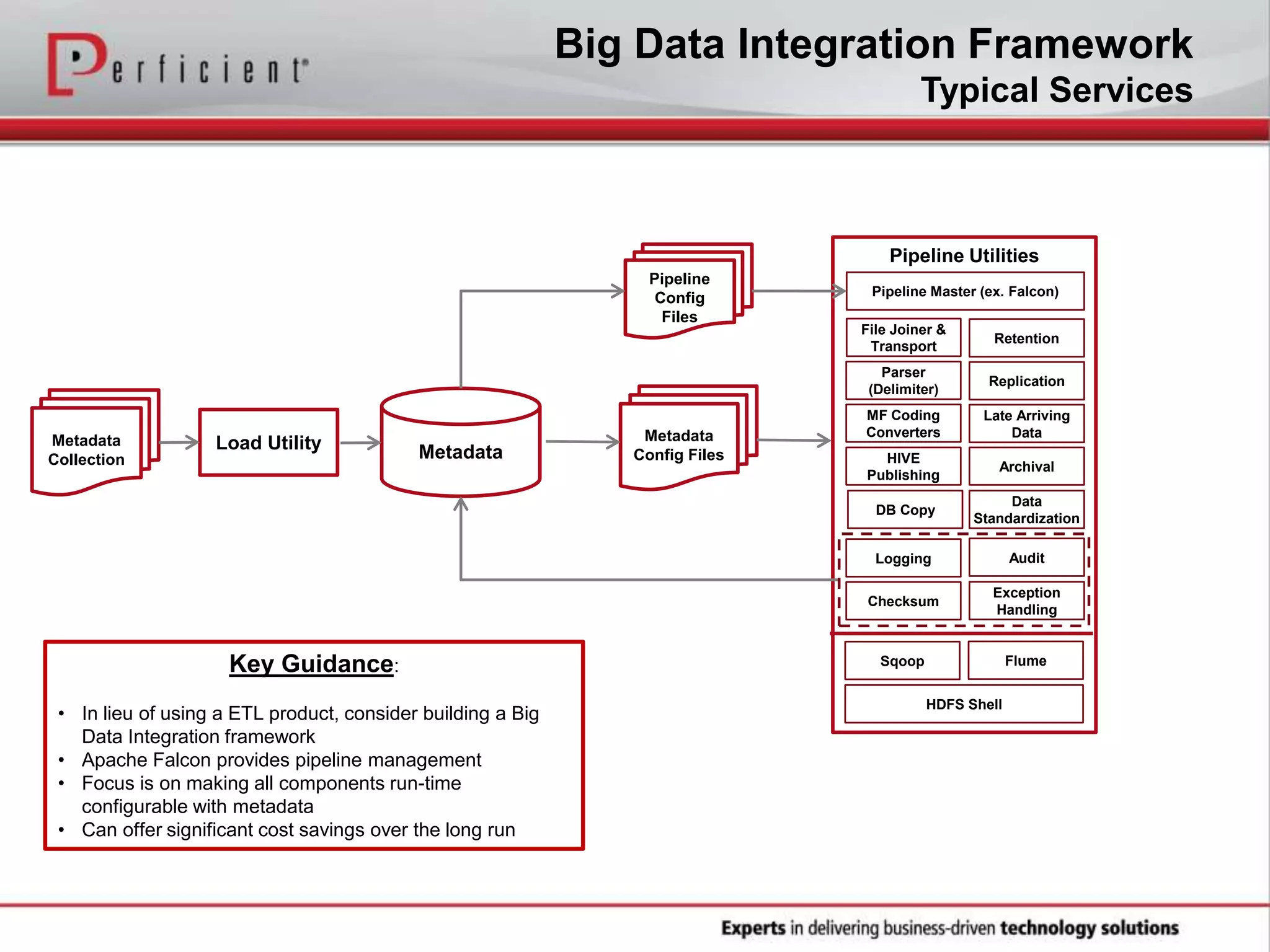
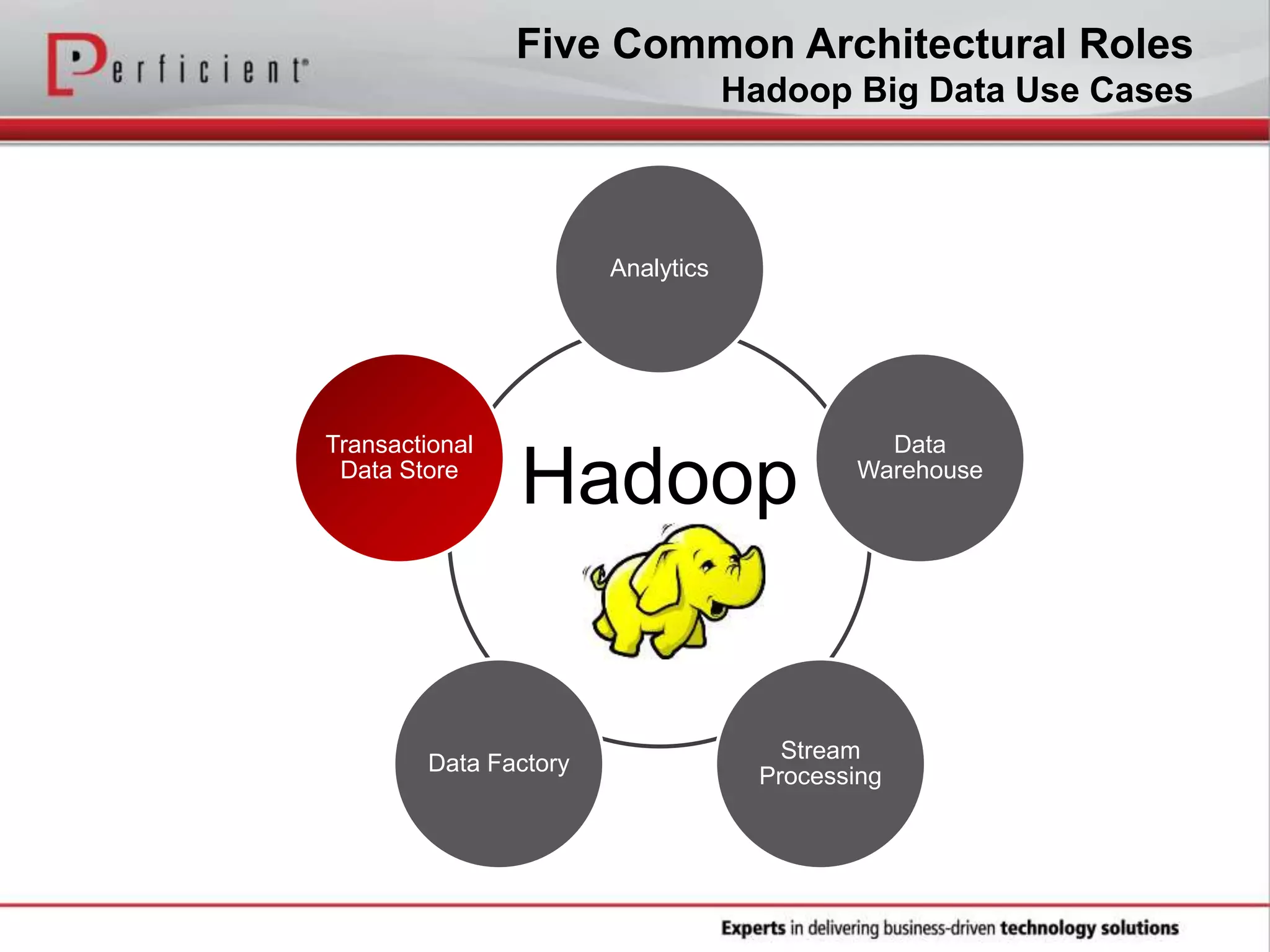
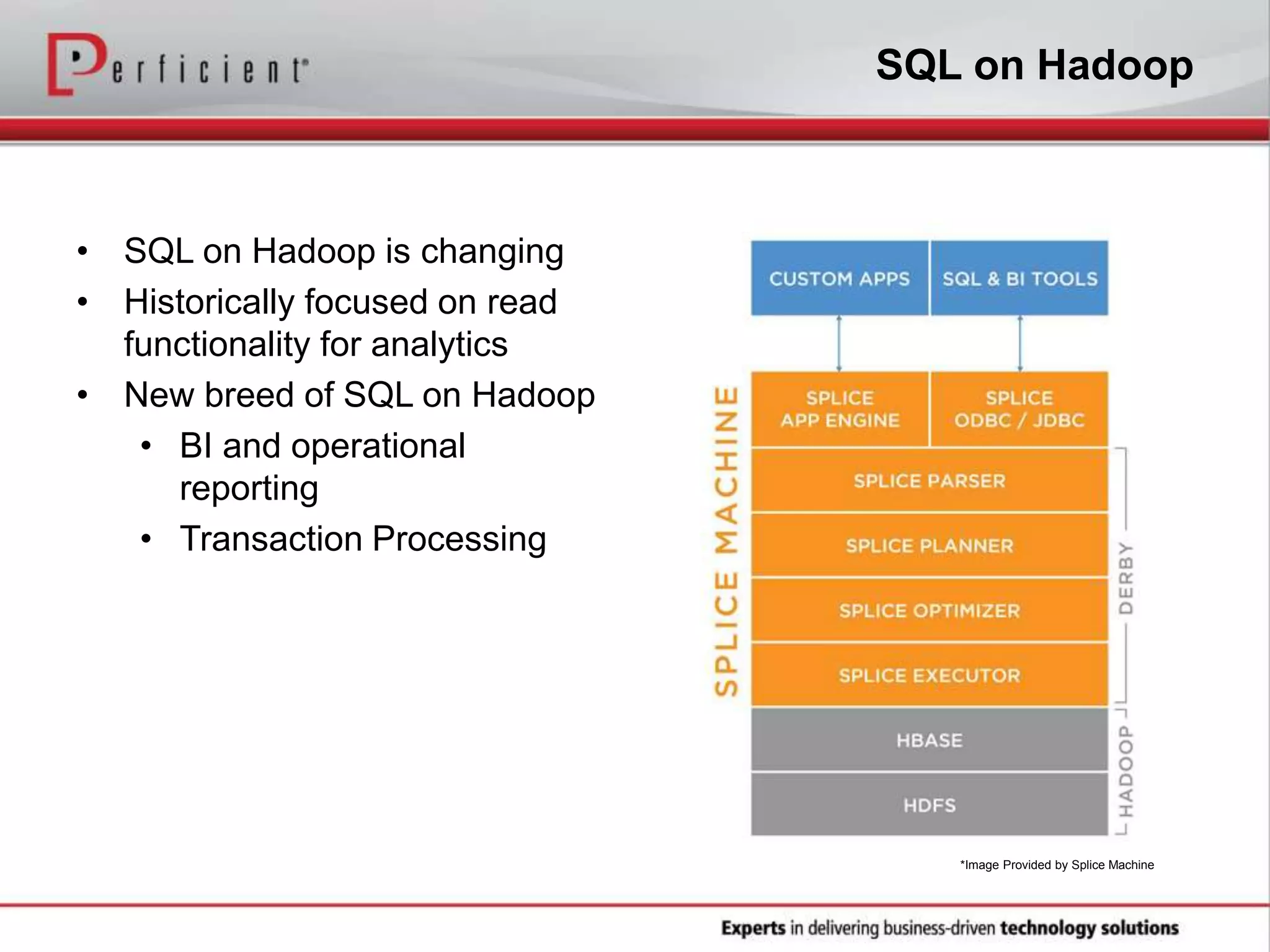
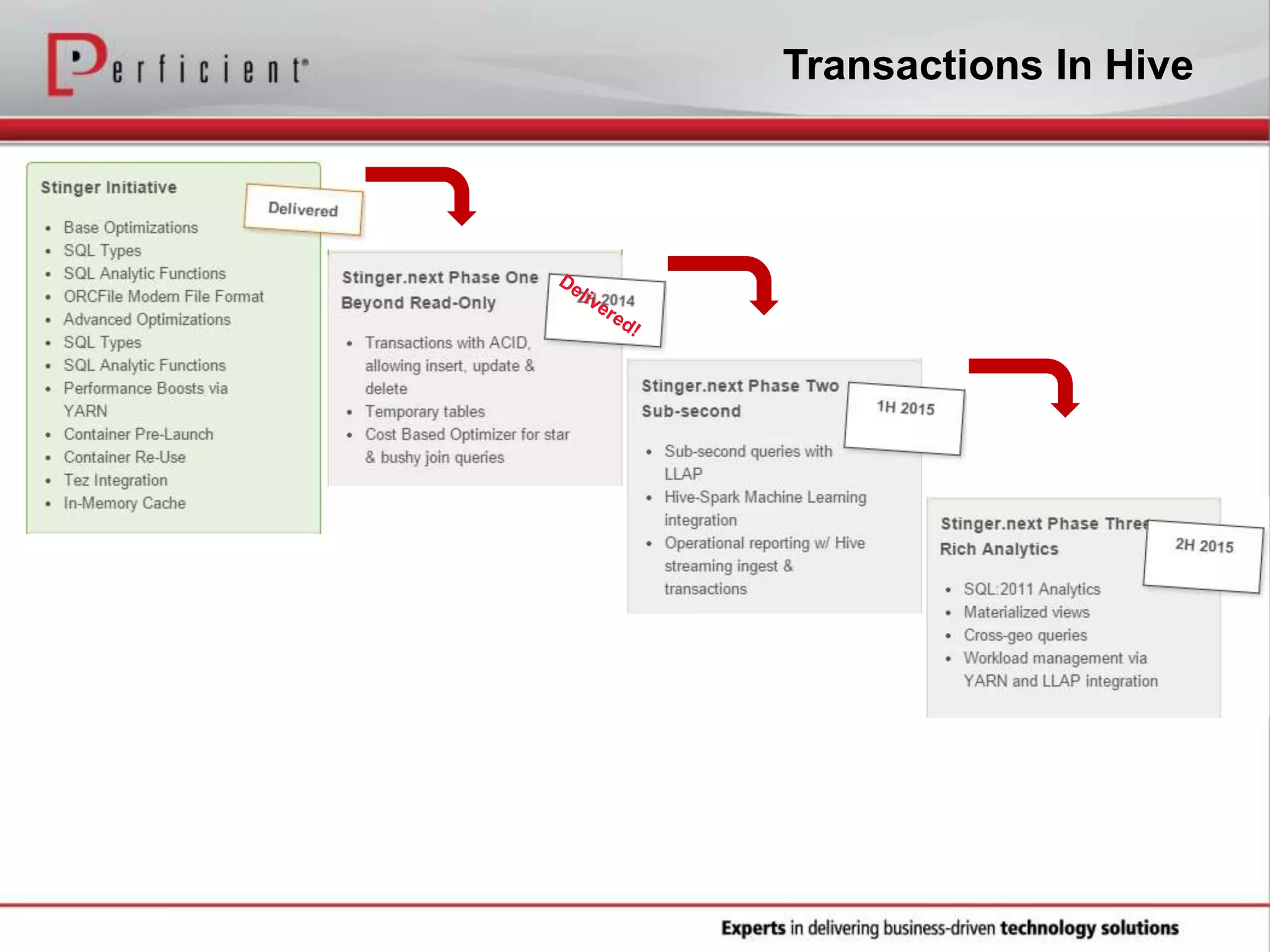
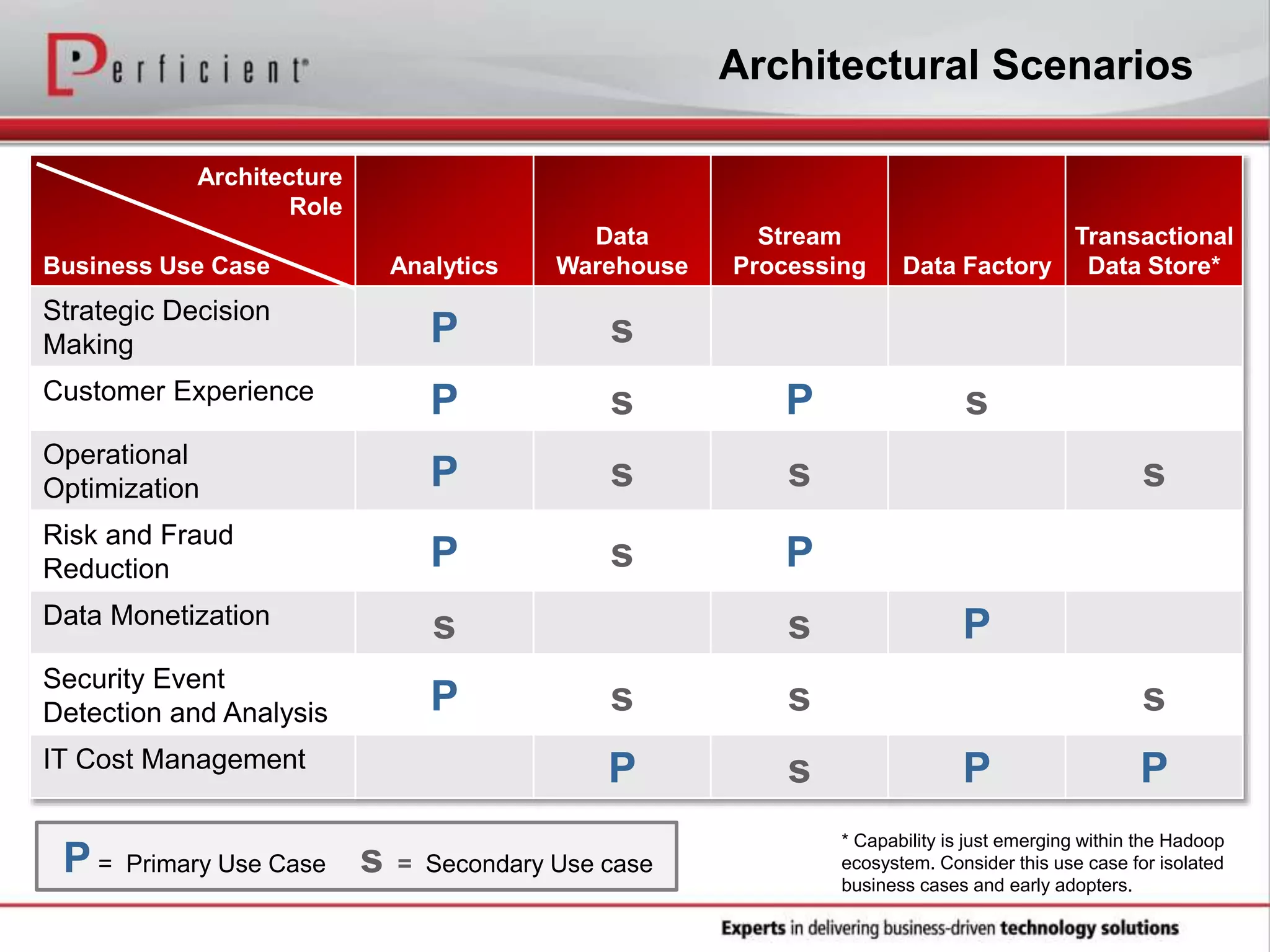
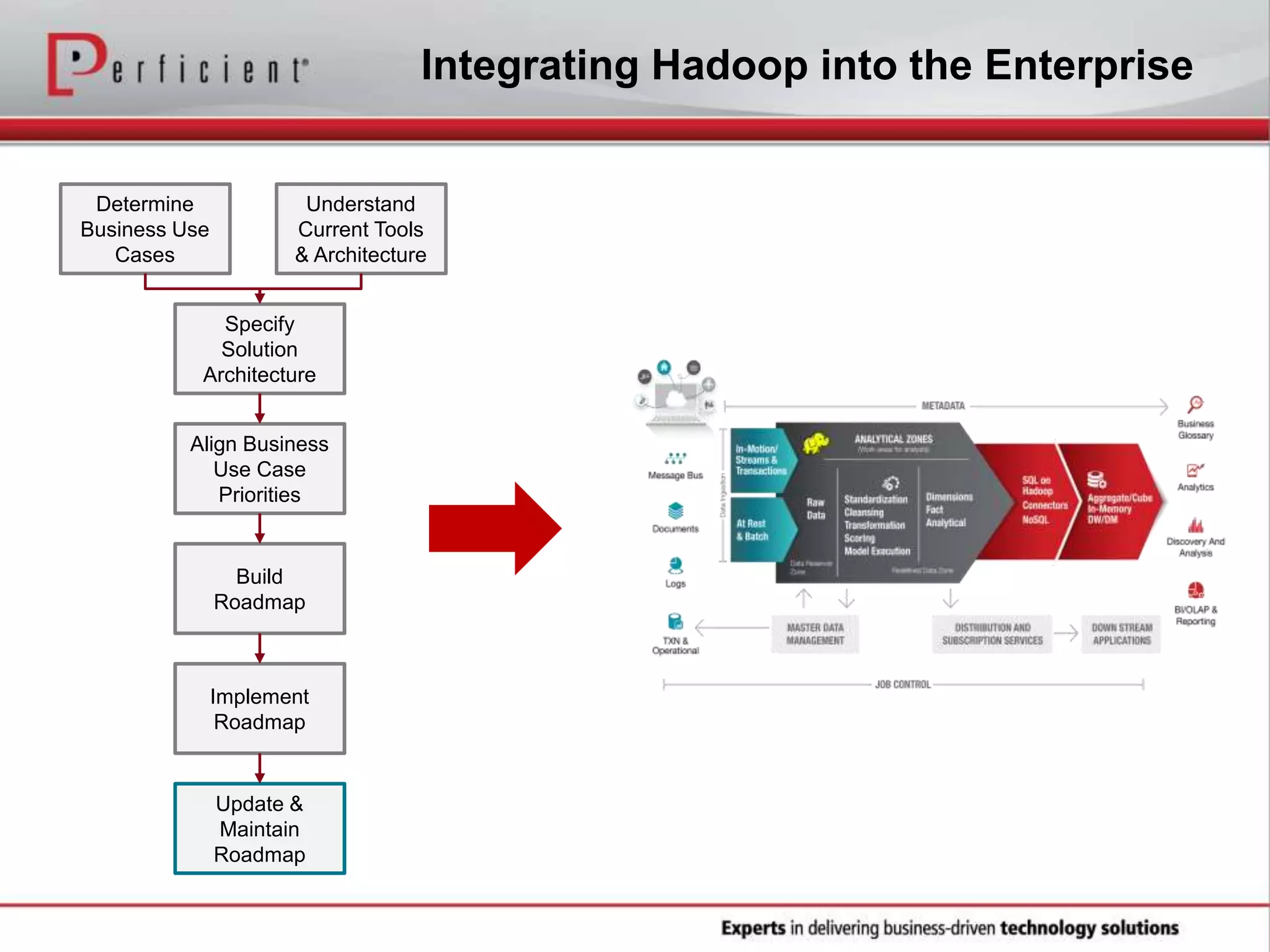
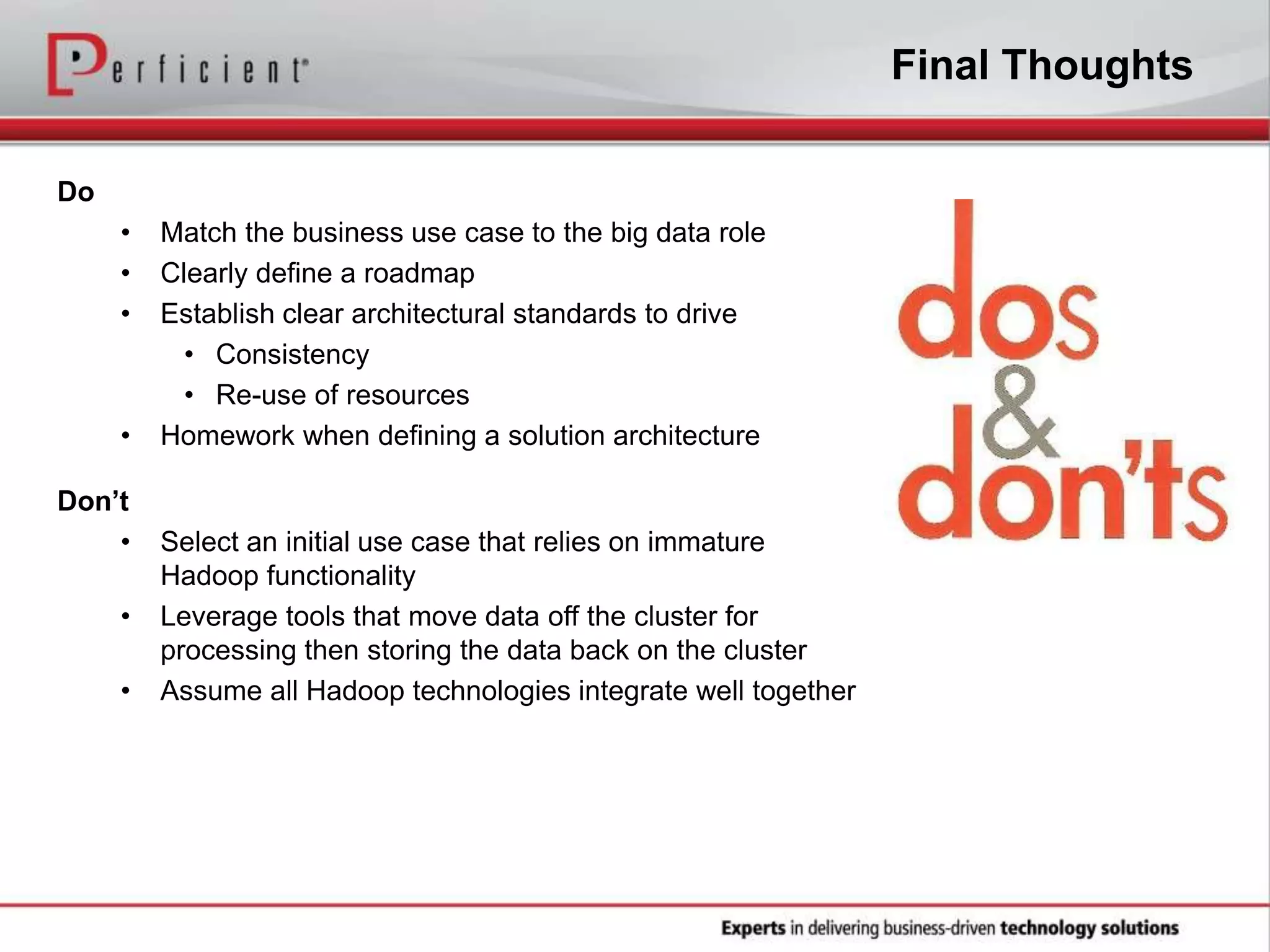
The document provides an overview of Perficient, a leading information technology consulting firm, and their big data architectural series webinar on creating a next-generation big data architecture. The webinar discusses big data business use cases, the Hadoop ecosystem, realizing a Hadoop-centric architecture through different architectural roles for Hadoop including analytics, data warehousing, stream processing, data integration and transactional data stores. It also covers challenges in moving from potential to reality and provides recommendations for integrating Hadoop into the enterprise.