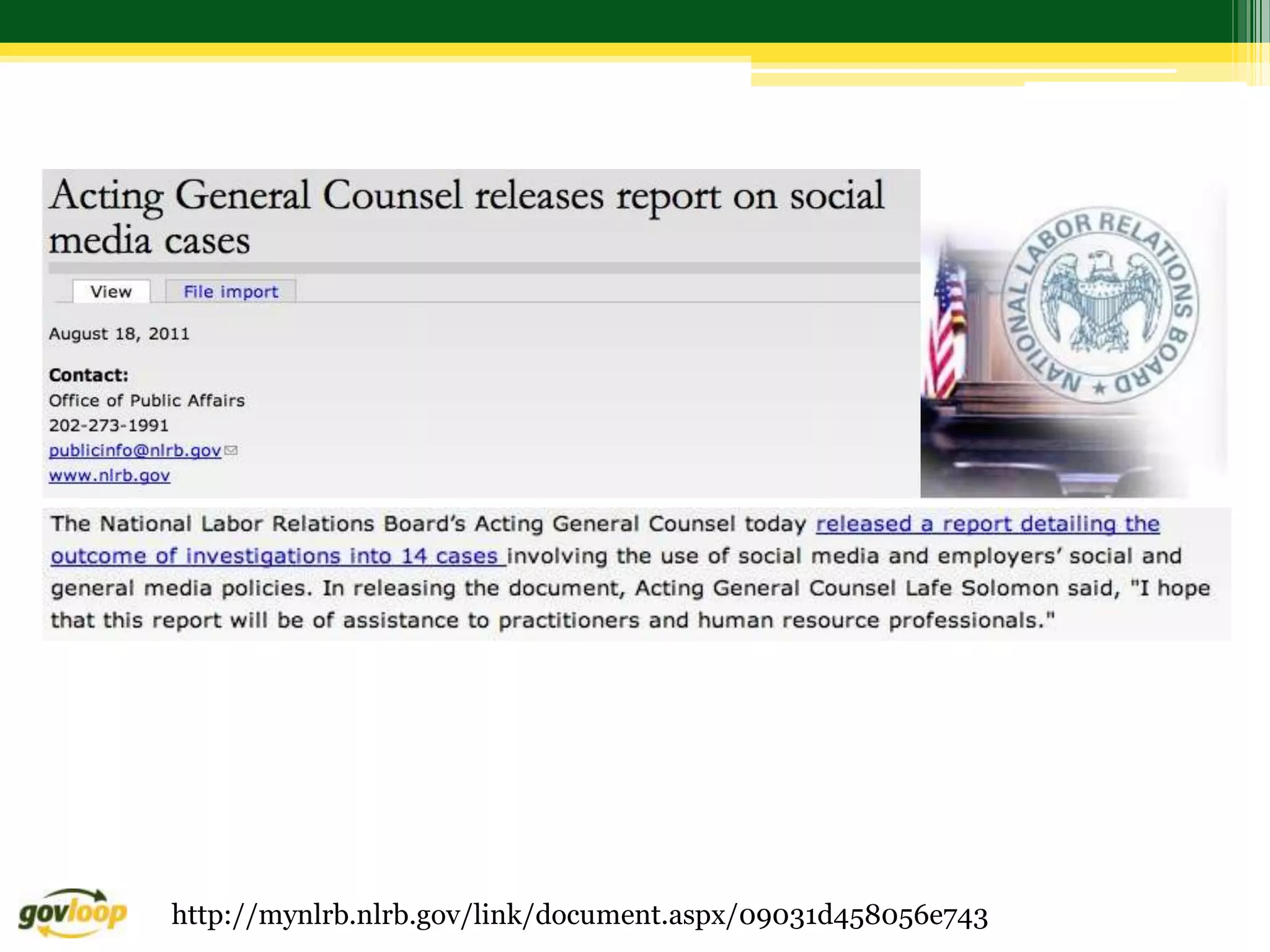
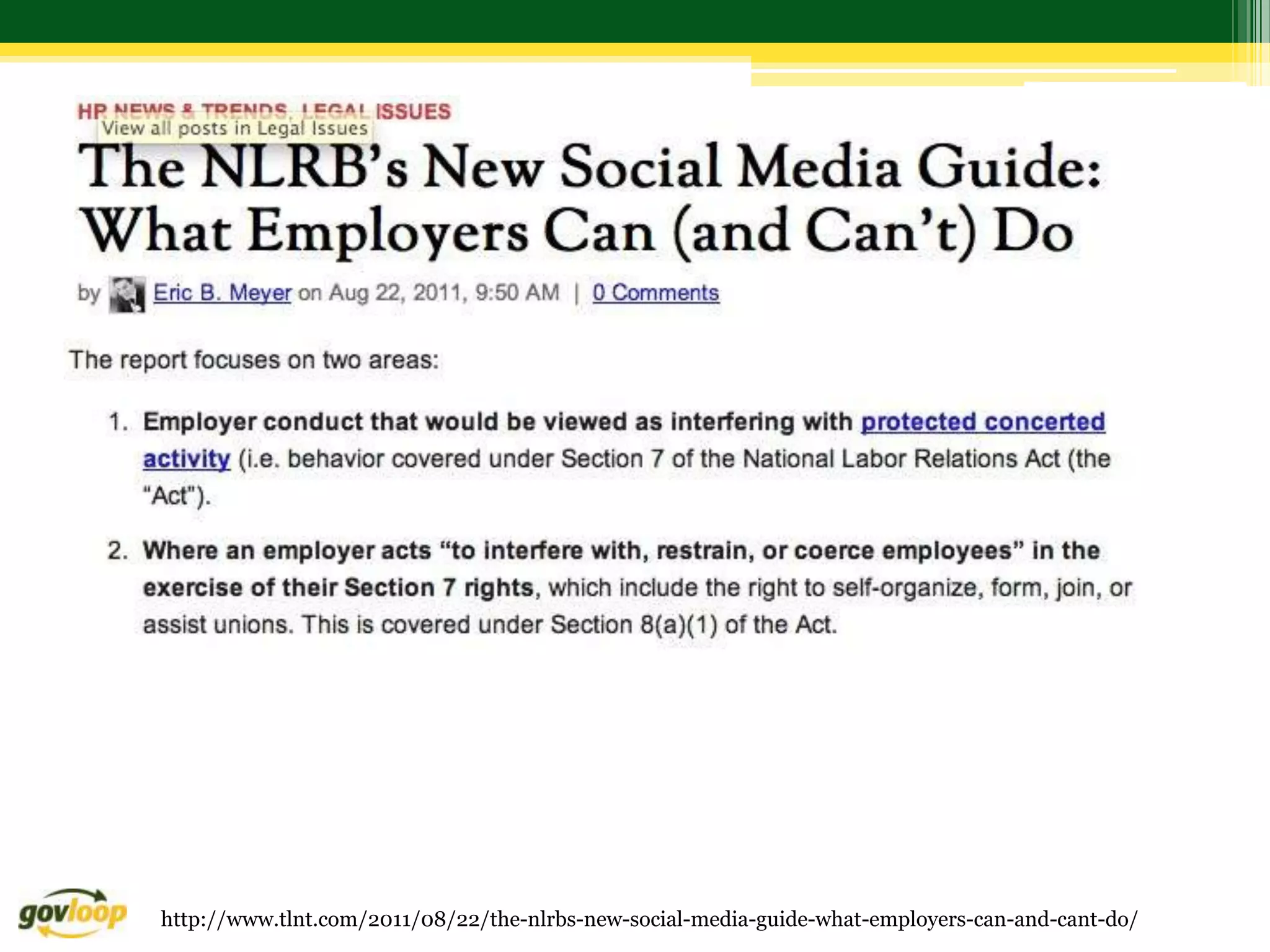
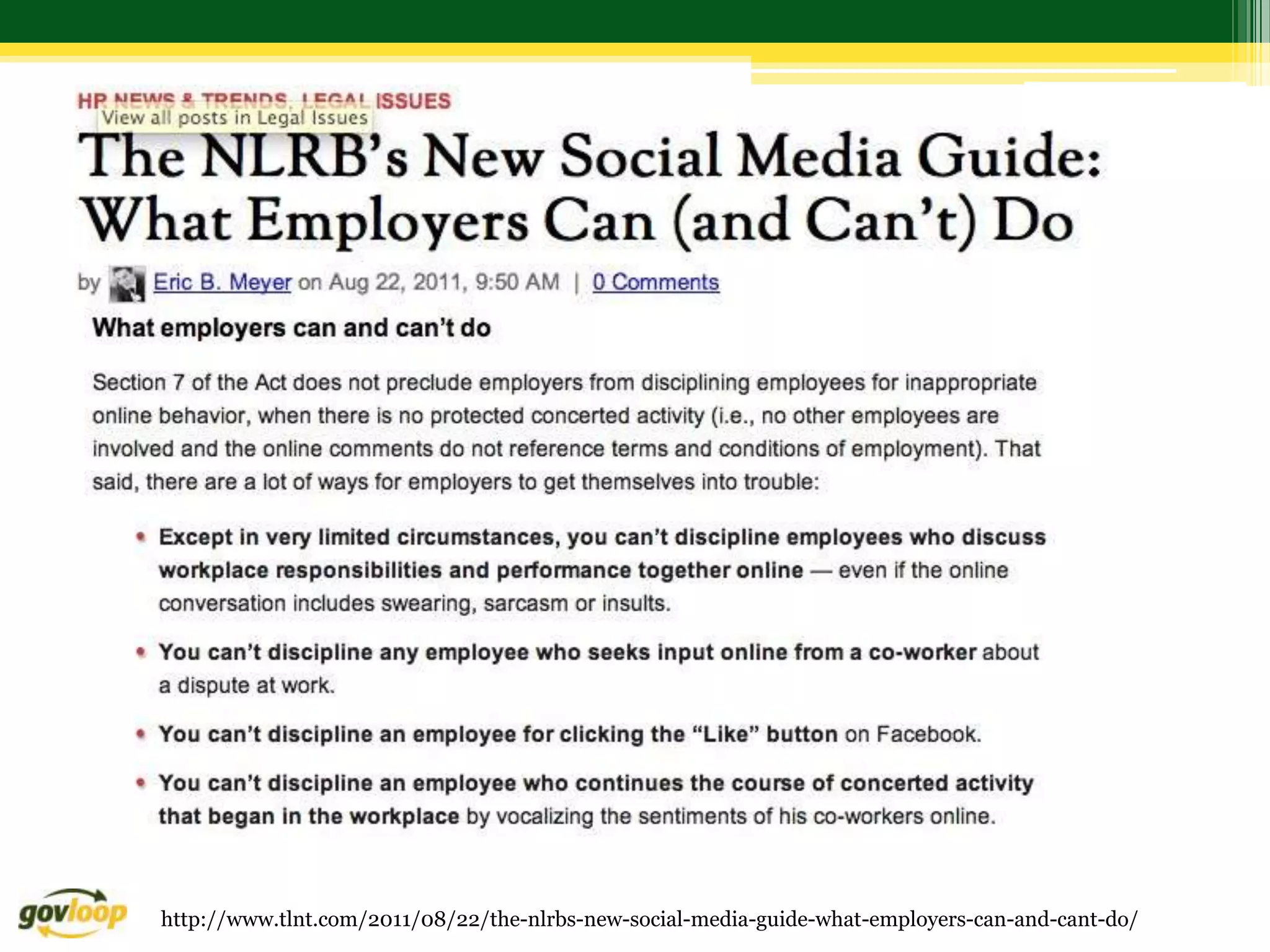
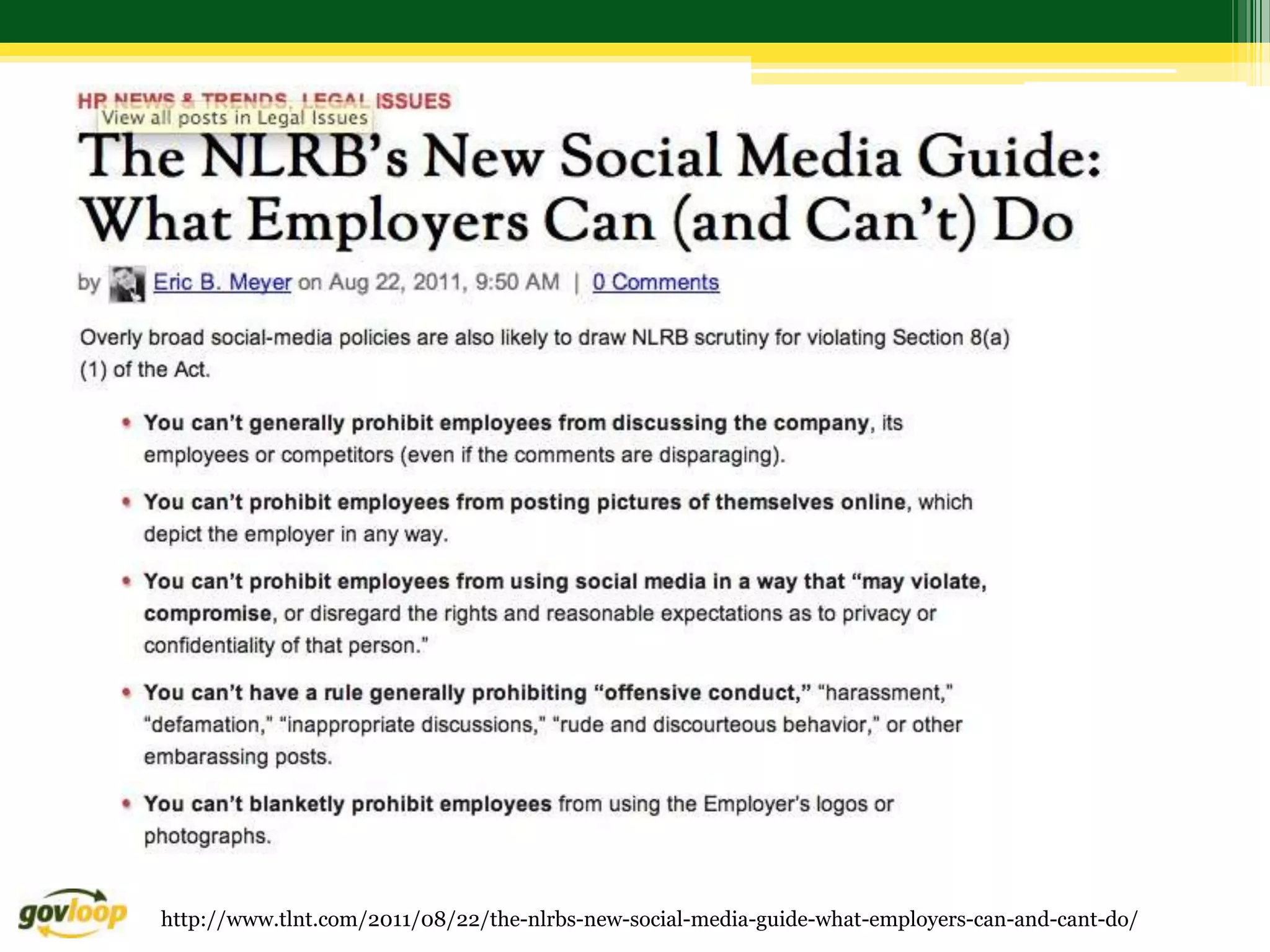
Here are 3 recommendations for addressing this scenario from different perspectives:
1. For the supervisor - address the behavior issues, including the Facebook photo, as performance elements in Dan's evaluation. Set a deadline for removing the photo and have a joint meeting with both employees to address the issues.
2. For HR - establish a clear policy for this type of scenario that ties into existing policies on appropriate use of the internet and posting inappropriate images. Work with the supervisor and legal counsel to determine the appropriate course of action.
3. For colleagues - remain neutral, avoid taking sides, and encourage both employees to resolve issues respectfully and professionally according to the organization's policies.

























![Scenario 3: Venting in the Wrong Venue
Karla is a Human Resources Specialist at an agency. After a
particularly difficult day, Karla is frustrated with a difficult
employee and makes the following comment on Twitter: “Ridiculous
how [name of agency] keeps incompetent people around. Time to
clean house!” There are rumors of a reduction in force coming on the
horizon, but nothing official has been announced. She makes the
comment after work hours from a home computer on her personal
Twitter account.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phillyfebeeoanddiversityslides-120320080017-phpapp01/75/How-Not-to-Get-Fired-Using-Social-Media-at-Work-EEO-Diversity-and-Social-Media-37-2048.jpg)