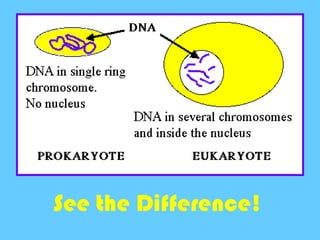
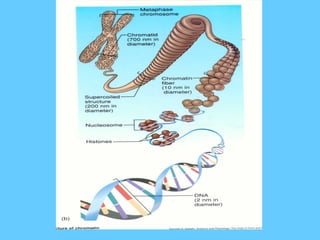
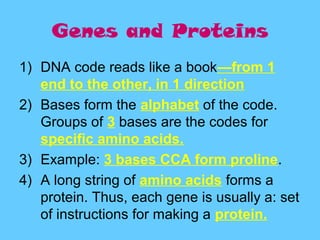
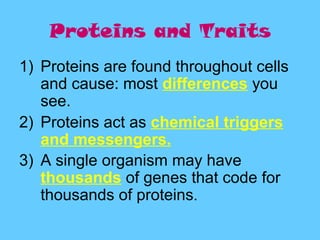
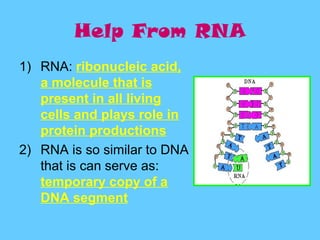
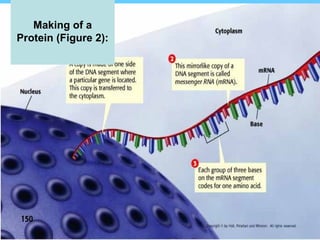
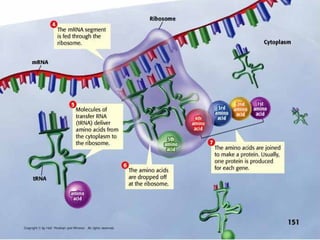
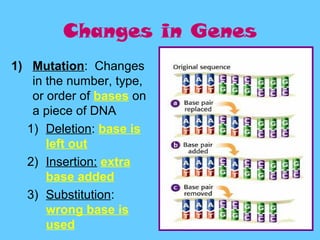
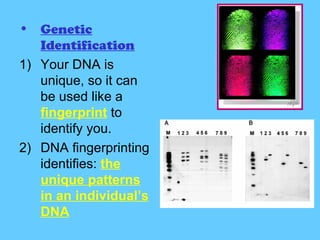
DNA contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms. It is found in the nuclei of cells and organelles called mitochondria. DNA is made up of nucleotides containing combinations of four bases that code for the production of proteins. Genes are sections of DNA that carry these instructions. Through DNA replication, cell division, and sexual reproduction, organisms pass their genetic material to offspring. Mutations in genes can result in genetic variations that impact traits.