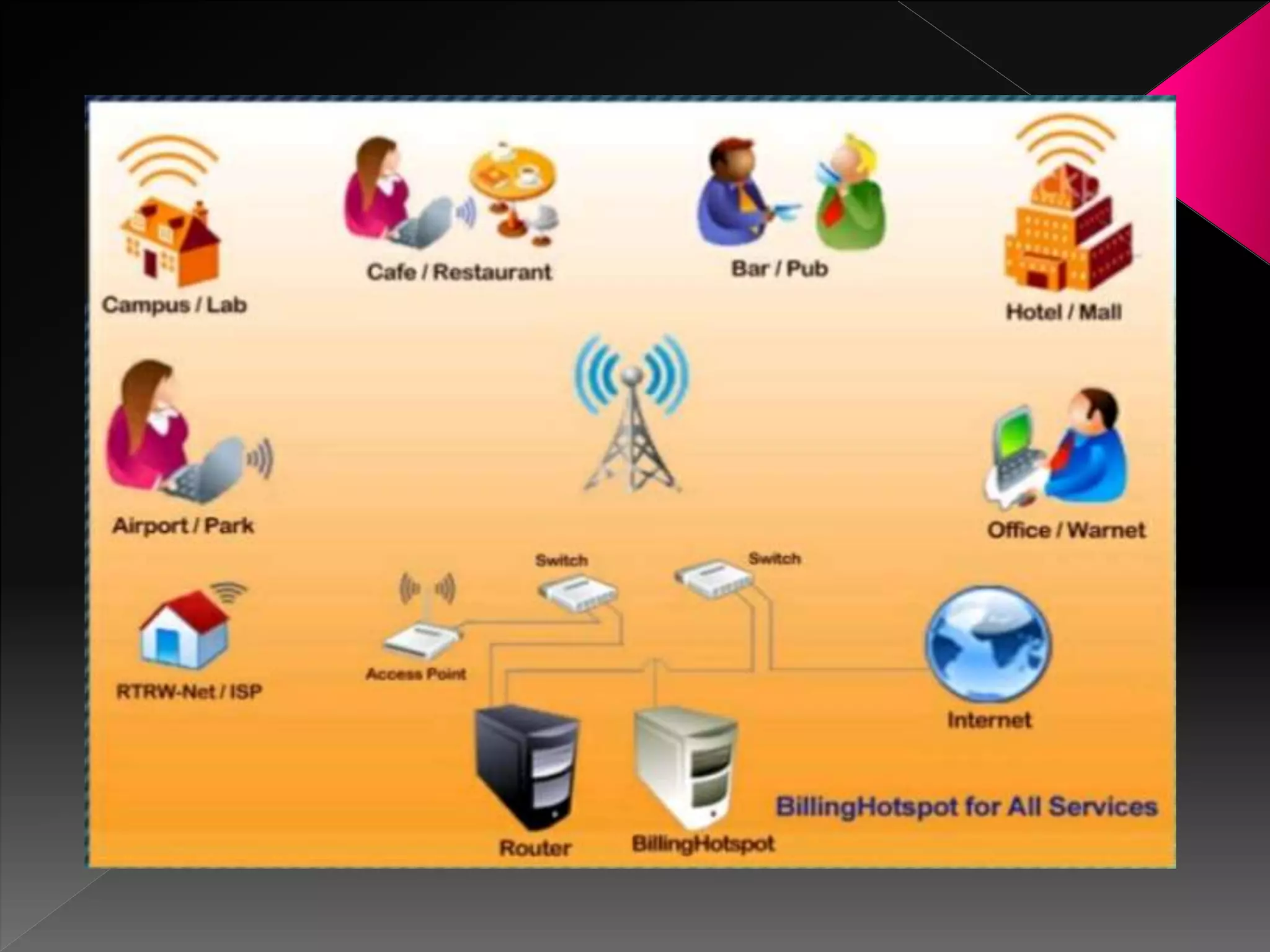
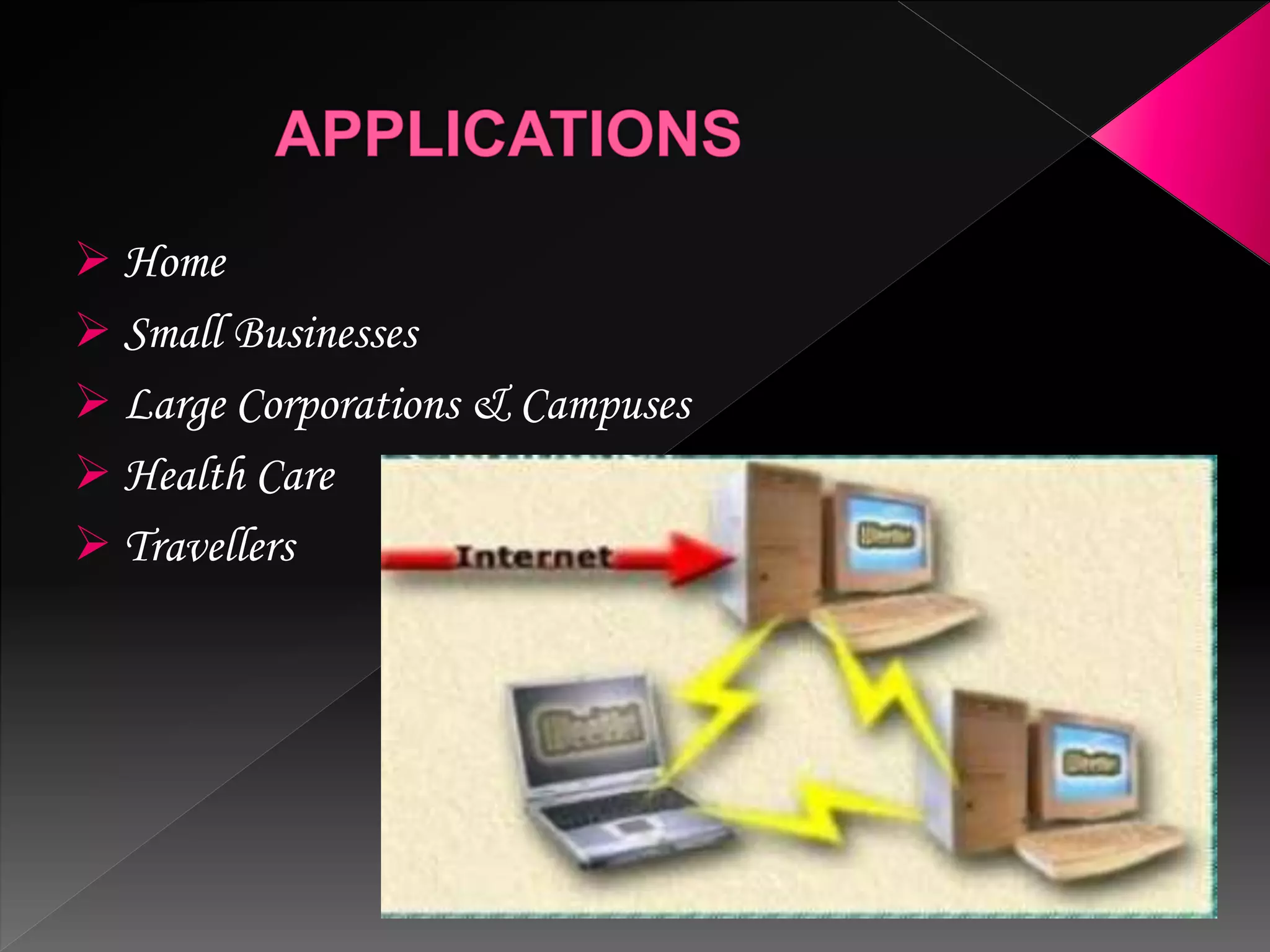
A Wi-Fi hotspot provides wireless internet access to devices like laptops and smartphones in public places. It works by installing an access point that is connected to the internet, acting as a base station for Wi-Fi enabled devices to connect to wirelessly within a range of 100-150 feet indoors. Hotspots can be found in cafes, libraries, airports and hotels for public use. Businesses also use internal hotspots for their wireless networks. New devices have built-in Wi-Fi adapters, but older devices need separate USB or card adapters to connect to hotspots. There are different types of hotspots including commercial ones that may require payment, software hotspots that allow sharing an internet connection,