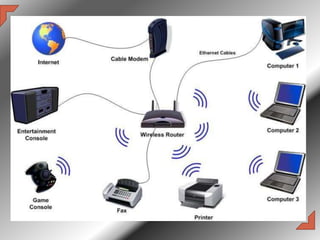
The document presents an overview of wireless communication, which enables information transfer without physical connections, utilizing technologies like radio waves. It highlights the rapid growth and trends in wireless technology, including advancements in smartphones, Bluetooth, and internet access methods. The presentation emphasizes the convenience and innovations brought by wireless technologies across various applications, from gaming to wireless power transfer and printing.