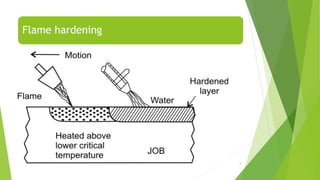
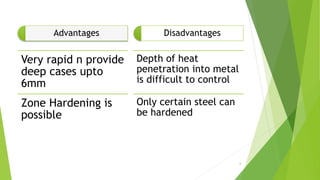
Selective hardening processes allow for hardening of only specific areas of large or complex parts. This improves dimensional accuracy and reduces costs compared to fully hardening the entire part. Common selective hardening methods include flame, induction, laser, and electron beam hardening. Flame hardening uses an oxy-acetylene torch to heat treat small areas, while induction hardening uses induction coils to rapidly harden surfaces like gears or camshafts. Laser and electron beam hardening offer precise control over case depth and produce clean, self-quenched parts without quenching media. Selective hardening improves properties in localized areas while minimizing distortion of the overall part.