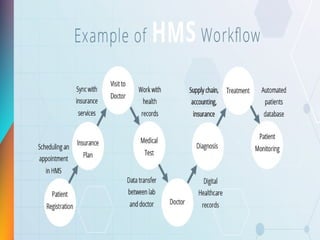
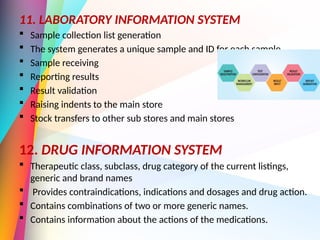
The document discusses the significance and evolution of Hospital Management Information Systems (HMIS), highlighting various components and functions that enhance healthcare delivery and administrative processes in hospitals. Key aspects include patient registration, admissions, billing, and data management, while also addressing the importance of effective information systems in improving governance and operational efficiency. Furthermore, it mentions the advantages, pitfalls, and challenges faced by HMIS in modern healthcare settings.